Clerical staff in administrative roles handle routine tasks such as data entry, scheduling, and record keeping, ensuring accuracy and personalized attention. Automation facilitators focus on integrating and managing software systems that streamline repetitive processes, increasing efficiency and reducing human error. Balancing skilled clerical work with automation technology optimizes administrative operations and enhances overall productivity.
Table of Comparison
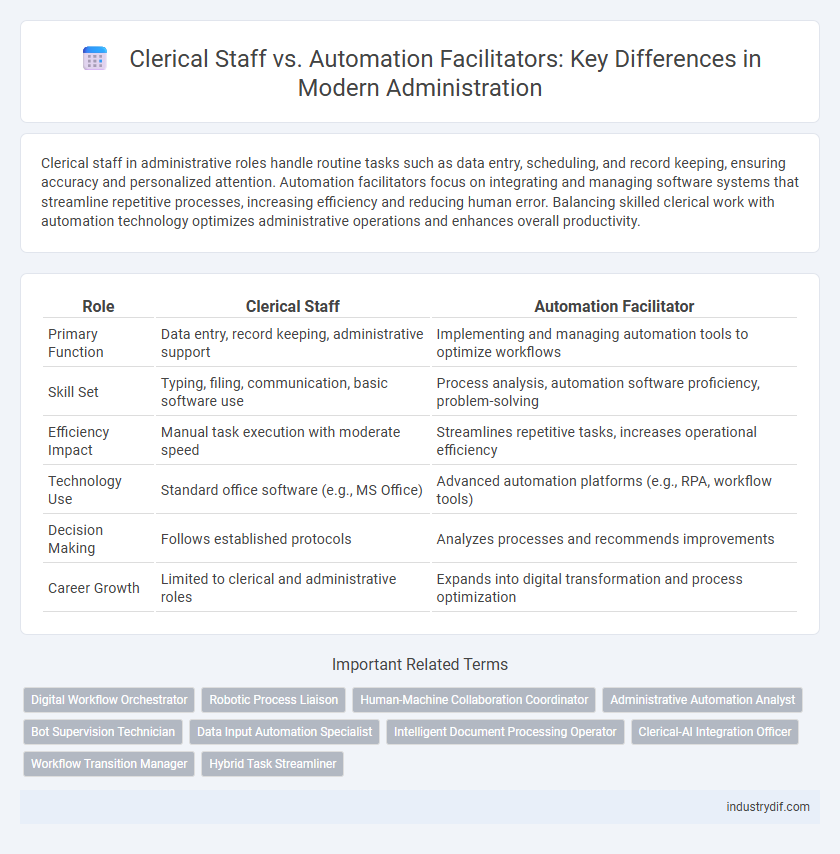
| Role | Clerical Staff | Automation Facilitator |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Data entry, record keeping, administrative support | Implementing and managing automation tools to optimize workflows |
| Skill Set | Typing, filing, communication, basic software use | Process analysis, automation software proficiency, problem-solving |
| Efficiency Impact | Manual task execution with moderate speed | Streamlines repetitive tasks, increases operational efficiency |
| Technology Use | Standard office software (e.g., MS Office) | Advanced automation platforms (e.g., RPA, workflow tools) |
| Decision Making | Follows established protocols | Analyzes processes and recommends improvements |
| Career Growth | Limited to clerical and administrative roles | Expands into digital transformation and process optimization |
Overview of Clerical Staff Roles
Clerical staff primarily perform administrative tasks such as data entry, filing, scheduling, and managing correspondence, ensuring smooth office operations. Their roles require attention to detail, organizational skills, and proficiency in office software to support various departments. Automation facilitators, in contrast, focus on implementing and managing technologies that streamline these clerical processes, enhancing efficiency and reducing manual workload.
Defining the Automation Facilitator
The Automation Facilitator in administrative settings is responsible for bridging the gap between traditional clerical staff and advanced automation technologies, ensuring seamless integration of automated processes. This role involves analyzing workflow inefficiencies, implementing digital tools, and training staff to adapt to evolving systems, thereby increasing productivity and reducing manual errors. Unlike clerical staff who handle routine administrative tasks, the Automation Facilitator drives innovation by optimizing operational workflows through automation strategies.
Key Responsibilities: Clerical Staff vs Automation Facilitator
Clerical staff primarily manage data entry, filing, and routine administrative tasks to maintain organized records and support office operations efficiently. Automation facilitators design, implement, and oversee automated systems, leveraging technology to streamline workflows and reduce manual intervention. These roles differ significantly, with clerical staff focusing on manual process execution, while automation facilitators drive digital transformation and process optimization.
Required Skills in Each Role
Clerical staff must excel in organizational skills, data entry accuracy, and proficiency with office software such as Microsoft Office and Google Workspace. Automation facilitators require expertise in workflow automation tools, programming languages like Python or RPA platforms, and strong analytical abilities to design and optimize automated processes. Both roles demand effective communication and problem-solving skills, but automation facilitators focus more on technical knowledge and systems integration.
Efficiency and Productivity Comparison
Clerical staff primarily handle routine data entry, filing, and scheduling tasks, which can lead to time-consuming manual processes and potential human error. Automation facilitators implement and manage software solutions that streamline these workflows, significantly increasing operational efficiency by reducing repetitive tasks and improving accuracy. The integration of automation tools often results in higher productivity gains, allowing organizations to reallocate clerical staff to more strategic roles.
Impact on Workflow Management
Clerical staff traditionally handle data entry, scheduling, and document organization, which ensures accuracy but can slow overall workflow due to manual processing. Automation facilitators design and implement software solutions that streamline repetitive tasks, significantly accelerating workflow and reducing human error. This shift toward automation optimizes resource allocation, allowing administrative teams to focus on strategic responsibilities and improving overall operational efficiency.
Training and Onboarding Differences
Clerical staff typically undergo extensive training focused on manual data entry, record keeping, and traditional office procedures, requiring detailed instruction on software tools and organizational policies. In contrast, automation facilitators receive specialized training centered on configuring, managing, and optimizing automated workflows, emphasizing technical skills such as scripting, software integration, and process analysis. Onboarding clerical staff often involves a longer adjustment period to learn repetitive tasks, whereas automation facilitators adapt more quickly through hands-on experience with automation platforms and continuous professional development in emerging technologies.
Career Pathways and Advancement
Clerical staff primarily handle routine administrative tasks such as data entry, scheduling, and document management, offering clear entry-level career pathways with advancement potential through specialized administrative roles. Automation facilitators focus on integrating and managing digital tools and workflow automation, presenting opportunities for career growth in technology-driven positions like process analyst or automation specialist. Both roles require continuous skills development, but automation facilitators typically advance faster due to growing demand for expertise in digital transformation and operational efficiency.
Challenges and Limitations in Each Position
Clerical staff face challenges such as repetitive manual data entry, limited scalability, and high error rates due to human fatigue. Automation facilitators encounter limitations including the complexity of integrating diverse systems, managing software updates, and addressing resistance from employees adapting to new technologies. Both roles must navigate evolving organizational demands while balancing efficiency and accuracy within their operational scopes.
Future Outlook: Evolving Administrative Functions
Clerical staff roles are expected to shift from routine data entry to more analytical and strategic tasks as automation facilitators integrate advanced technologies like AI and RPA into administrative workflows. Automation facilitators will play a crucial role in designing, implementing, and managing digital tools that enhance operational efficiency and accuracy across office functions. The future outlook indicates a growing demand for professionals who combine administrative expertise with technical skills to optimize business processes and support organizational innovation.
Related Important Terms
Digital Workflow Orchestrator
Clerical staff traditionally manage routine administrative tasks such as data entry and document processing, while an Automation Facilitator leverages digital workflow orchestrators to optimize, streamline, and automate these processes, enhancing operational efficiency and accuracy. Digital workflow orchestrators integrate multiple software systems to create seamless, automated task sequences that reduce manual intervention and improve real-time data management across departments.
Robotic Process Liaison
Clerical staff primarily handle routine administrative tasks such as data entry and document management, whereas automation facilitators, particularly robotic process liaisons, specialize in integrating and coordinating robotic process automation (RPA) within organizational workflows. This role involves collaborating with IT and business units to optimize RPA deployment, ensuring seamless process automation and improved operational efficiency.
Human-Machine Collaboration Coordinator
Human-Machine Collaboration Coordinators bridge the gap between clerical staff and automation facilitators by optimizing workflows that integrate manual tasks with automated processes, enhancing operational efficiency. Their role focuses on managing and coordinating seamless interactions between human employees and automated systems to improve accuracy, reduce errors, and increase productivity in administrative environments.
Administrative Automation Analyst
Administrative Automation Analysts streamline clerical staff workflows by integrating advanced automation tools, enhancing data accuracy and operational efficiency. They analyze administrative processes to implement automation solutions that reduce manual tasks and improve overall organizational productivity.
Bot Supervision Technician
A Bot Supervision Technician enhances administrative efficiency by overseeing automation processes and addressing system errors, reducing the reliance on traditional clerical staff for routine tasks. This role bridges the gap between human oversight and AI-driven workflows, ensuring seamless bot performance and optimizing operational productivity.
Data Input Automation Specialist
Data Input Automation Specialists enhance administrative efficiency by integrating advanced software solutions to automate repetitive clerical tasks, significantly reducing human error and processing time. Their expertise in robotic process automation and machine learning tools positions them as vital assets in transitioning traditional data entry roles into streamlined, technology-driven operations.
Intelligent Document Processing Operator
Intelligent Document Processing Operators enhance clerical staff efficiency by utilizing advanced AI-driven automation tools to accurately capture, classify, and extract data from diverse documents, significantly reducing manual entry errors and processing time. This role bridges traditional administrative tasks and automation implementation, ensuring seamless integration of Intelligent Document Processing within organizational workflows for optimized operational productivity.
Clerical-AI Integration Officer
Clerical-AI Integration Officers specialize in merging traditional clerical tasks with advanced automation technologies to enhance workflow efficiency and data accuracy. Their expertise bridges human administrative skills and AI-driven solutions, optimizing office operations and reducing manual workload.
Workflow Transition Manager
Workflow Transition Managers streamline processes by bridging the gap between Clerical Staff and Automation Facilitators, ensuring seamless integration of automated systems into daily operations. They optimize task allocation and improve efficiency by coordinating human workflows with advanced automation technologies.
Hybrid Task Streamliner
Clerical staff often perform repetitive administrative tasks such as data entry, scheduling, and record keeping, which automation facilitators streamline by integrating hybrid workflows that combine human oversight with automated processes. This hybrid task streamliner enhances operational efficiency, reduces errors, and allows clerical workers to focus on higher-level problem-solving and decision-making activities.
Clerical Staff vs Automation Facilitator Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com