Clerical staff primarily handle routine administrative tasks such as data entry, scheduling, and document management, ensuring smooth office operations. Automation Workflow Specialists design and implement automated processes that optimize efficiency, reduce manual errors, and streamline repetitive tasks. Transitioning from clerical roles to automation specialists can enhance productivity and leverage technological advancements within administrative functions.
Table of Comparison
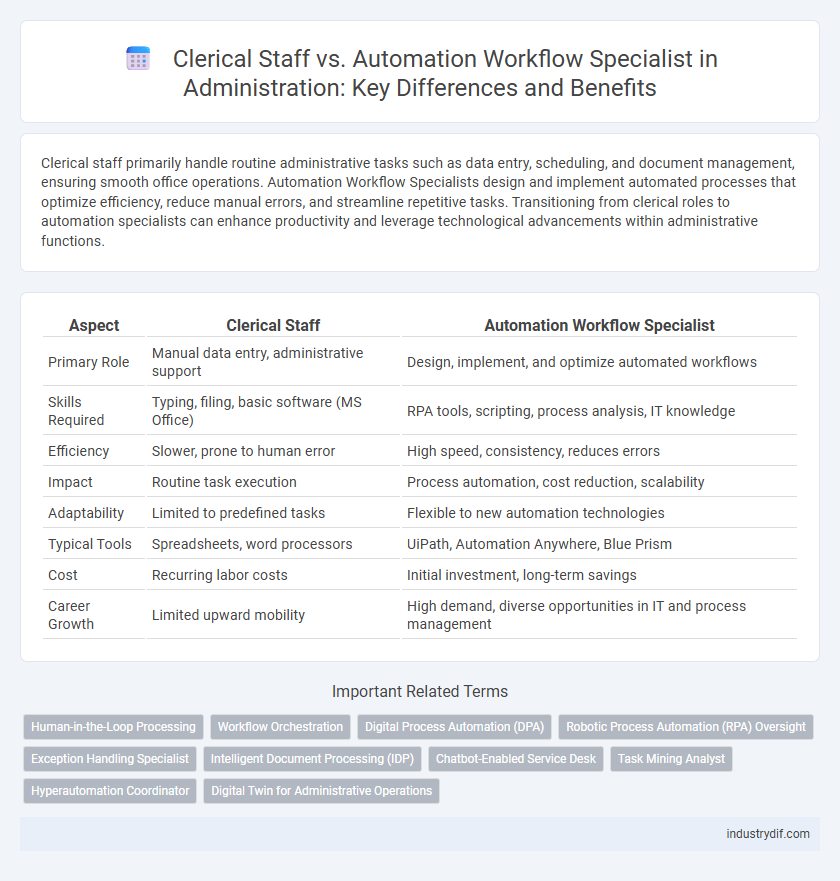
| Aspect | Clerical Staff | Automation Workflow Specialist |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Manual data entry, administrative support | Design, implement, and optimize automated workflows |
| Skills Required | Typing, filing, basic software (MS Office) | RPA tools, scripting, process analysis, IT knowledge |
| Efficiency | Slower, prone to human error | High speed, consistency, reduces errors |
| Impact | Routine task execution | Process automation, cost reduction, scalability |
| Adaptability | Limited to predefined tasks | Flexible to new automation technologies |
| Typical Tools | Spreadsheets, word processors | UiPath, Automation Anywhere, Blue Prism |
| Cost | Recurring labor costs | Initial investment, long-term savings |
| Career Growth | Limited upward mobility | High demand, diverse opportunities in IT and process management |
Defining Clerical Staff Roles in Administration
Clerical staff in administration handle essential tasks such as data entry, file management, and scheduling that ensure smooth organizational operations. Their roles often involve managing physical and digital records, coordinating communication, and supporting day-to-day office functions. In contrast, Automation Workflow Specialists focus on designing and implementing automated processes to improve efficiency and reduce manual workload.
Automation Workflow Specialists: Key Responsibilities
Automation Workflow Specialists design, implement, and manage automated processes to streamline administrative tasks, reducing manual errors and increasing efficiency across operations. They analyze existing clerical workflows to identify opportunities for automation using tools like robotic process automation (RPA) and workflow management software. These specialists collaborate closely with IT and business units to optimize data integration, monitor system performance, and ensure compliance with organizational standards.
Skillsets: Traditional Clerical vs. Automation Experts
Traditional clerical staff excel in data entry, document management, and interpersonal communication, with proficiency in standard office software like Microsoft Office and basic database systems. Automation workflow specialists possess advanced skills in process modeling, software automation tools such as UiPath or Blue Prism, and scripting languages like Python or JavaScript to optimize business operations. These specialists focus on integrating AI-driven technologies and robotic process automation (RPA) to streamline workflows, significantly reducing manual errors and increasing efficiency.
Efficiency Metrics: Human vs. Automated Processes
Clerical staff typically manage routine administrative tasks with an average processing speed of 15-20 transactions per hour, whereas automation workflow specialists implement systems that can increase throughput to over 200 tasks per hour. Efficiency metrics reveal automation reduces error rates by up to 90%, significantly improving data accuracy compared to human processing. Operational costs decrease by 30-50% when transitioning from manual clerical work to automated workflows, highlighting the financial benefits of automation in administrative environments.
Error Rates and Quality Control
Clerical staff typically exhibit higher error rates due to manual data entry and repetitive tasks, impacting overall quality control. Automation workflow specialists design and implement automated systems that significantly reduce human errors and enhance data accuracy. Incorporating automation leads to improved quality control metrics and streamlined administrative processes.
Training and Upskilling Requirements
Clerical staff typically require foundational training in office software, data entry, and document management, with ongoing upskilling focused on efficiency and accuracy. Automation workflow specialists demand advanced training in process automation tools, scripting languages like Python or JavaScript, and workflow optimization techniques. Continuous professional development for both roles enhances operational productivity, but automation specialists need deeper technical proficiency to manage and improve automated systems effectively.
Cost Comparison: Salaries and Tech Investments
Clerical staff salaries typically range from $30,000 to $45,000 annually, while automation workflow specialists command higher wages between $60,000 and $90,000 due to specialized skills. Investment in technology for automation workflows involves upfront costs averaging $20,000 to $50,000 for software and integration, which can reduce long-term operational expenses. Over time, automation can lower overall costs by decreasing manual labor hours and minimizing errors, offsetting the higher initial salaries and tech investments.
Impact on Employee Satisfaction and Morale
Clerical staff often experience repetitive tasks that can lead to decreased job satisfaction and lower morale, whereas automation workflow specialists actively design and manage systems that reduce manual workload and enhance efficiency. Implementing automation workflows can improve employee engagement by minimizing errors and freeing clerical employees from routine duties, allowing them to focus on higher-value tasks. Organizations that invest in automation specialists tend to see higher overall employee satisfaction and morale due to streamlined processes and increased opportunities for professional development.
Future Trends in Administrative Workflows
Clerical staff roles are increasingly being augmented or replaced by automation workflow specialists who design and maintain intelligent systems for document processing and task management. Future trends in administrative workflows emphasize AI-driven automation, robotic process automation (RPA), and integration of cloud-based platforms to enhance efficiency and reduce human error. Organizations investing in automation technology see significant improvements in productivity, data accuracy, and real-time analytics, redefining administrative job functions.
Strategic Decision-Making: Balancing Clerical Staff and Automation
Clerical staff provide essential human judgment and adaptability in administrative tasks, ensuring nuanced decision-making in complex scenarios. Automation workflow specialists design and implement automated processes that enhance efficiency and reduce errors, enabling data-driven insights for strategic decisions. Balancing clerical expertise with automation optimizes operational performance by leveraging human creativity alongside technological precision.
Related Important Terms
Human-in-the-Loop Processing
Clerical staff play a critical role in human-in-the-loop processing by ensuring data accuracy and providing context-sensitive judgment that automation workflows alone cannot achieve. Automation workflow specialists design systems that integrate human oversight with machine efficiency to optimize administrative operations and reduce errors.
Workflow Orchestration
Clerical staff primarily handle routine administrative tasks and data entry, whereas Automation Workflow Specialists design and manage workflow orchestration systems to streamline processes and improve operational efficiency. Leveraging advanced automation tools, specialists reduce manual intervention, enabling scalable and error-free task execution within business workflows.
Digital Process Automation (DPA)
Clerical staff manage routine data entry and document handling, while Automation Workflow Specialists design and implement Digital Process Automation (DPA) solutions to streamline tasks, increase accuracy, and reduce manual workload. Emphasizing DPA technologies like robotic process automation (RPA) and AI-driven workflows enhances operational efficiency and supports scalable administrative processes.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) Oversight
Clerical staff often handle routine administrative tasks manually, whereas Automation Workflow Specialists focus on designing, implementing, and overseeing Robotic Process Automation (RPA) to optimize these processes. Effective RPA oversight ensures seamless integration of automated workflows, reducing errors and increasing operational efficiency within administrative environments.
Exception Handling Specialist
Exception Handling Specialists in automation workflows focus on identifying, managing, and resolving anomalies within automated processes, ensuring seamless operational continuity. Clerical staff typically handle routine administrative tasks, whereas Exception Handling Specialists apply advanced problem-solving skills and technical knowledge to maintain workflow efficiency and minimize downtime.
Intelligent Document Processing (IDP)
Clerical staff traditionally manage data entry and document handling manually, while Automation Workflow Specialists leverage Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) technologies to automate extraction, classification, and validation of information from various documents, significantly increasing accuracy and efficiency. Implementation of IDP reduces human error and accelerates administrative workflows, enabling organizations to optimize operational costs and enhance data governance.
Chatbot-Enabled Service Desk
Clerical staff traditionally manage routine administrative tasks, while Automation Workflow Specialists design and implement chatbot-enabled service desk solutions to enhance efficiency and reduce manual workload. Integrating AI-powered chatbots streamlines ticket management and user support, increasing response accuracy and accelerating issue resolution.
Task Mining Analyst
Clerical staff primarily handle routine administrative tasks such as data entry and document management, while Automation Workflow Specialists leverage Task Mining Analysts to identify inefficiencies and optimize business processes through data-driven automation solutions. Task Mining Analysts utilize advanced software to analyze user interactions and workflows, enabling organizations to implement targeted automation strategies that enhance productivity and reduce manual workload.
Hyperautomation Coordinator
Clerical staff handle routine administrative tasks such as data entry, scheduling, and document management, while Automation Workflow Specialists, particularly Hyperautomation Coordinators, design and implement integrated automated processes using AI, RPA, and advanced analytics to optimize operational efficiency. Hyperautomation Coordinators focus on orchestrating intelligent automation solutions that reduce manual intervention, improve accuracy, and accelerate business workflows across multiple departments.
Digital Twin for Administrative Operations
Clerical staff manage traditional administrative tasks, while Automation Workflow Specialists leverage digital twin technology to simulate, analyze, and optimize administrative operations, enhancing efficiency through real-time process modeling. Implementing digital twins enables precise monitoring and continuous improvement of workflow automation, reducing manual errors and accelerating decision-making in administrative functions.
Clerical Staff vs Automation Workflow Specialist Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com