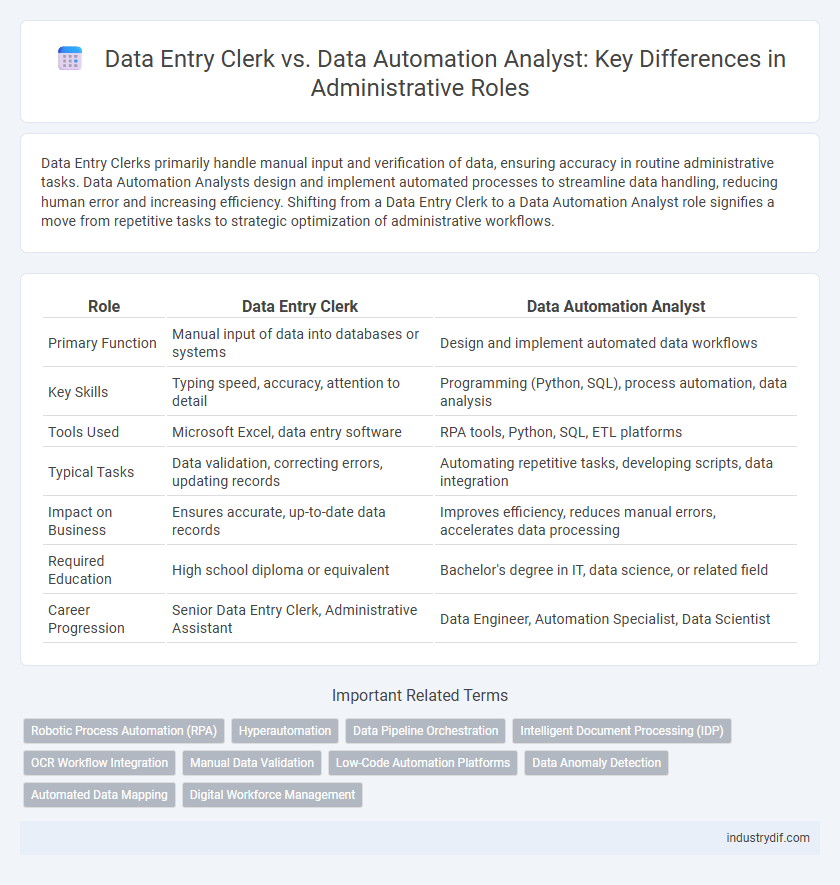
Data Entry Clerks primarily handle manual input and verification of data, ensuring accuracy in routine administrative tasks. Data Automation Analysts design and implement automated processes to streamline data handling, reducing human error and increasing efficiency. Shifting from a Data Entry Clerk to a Data Automation Analyst role signifies a move from repetitive tasks to strategic optimization of administrative workflows.
Table of Comparison
| Role | Data Entry Clerk | Data Automation Analyst |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Manual input of data into databases or systems | Design and implement automated data workflows |
| Key Skills | Typing speed, accuracy, attention to detail | Programming (Python, SQL), process automation, data analysis |
| Tools Used | Microsoft Excel, data entry software | RPA tools, Python, SQL, ETL platforms |
| Typical Tasks | Data validation, correcting errors, updating records | Automating repetitive tasks, developing scripts, data integration |
| Impact on Business | Ensures accurate, up-to-date data records | Improves efficiency, reduces manual errors, accelerates data processing |
| Required Education | High school diploma or equivalent | Bachelor's degree in IT, data science, or related field |
| Career Progression | Senior Data Entry Clerk, Administrative Assistant | Data Engineer, Automation Specialist, Data Scientist |
Role Overview: Data Entry Clerk vs Data Automation Analyst
Data Entry Clerks primarily focus on accurately inputting and updating information into databases or systems, emphasizing speed and error-free manual entry. In contrast, Data Automation Analysts design, implement, and optimize automated processes to streamline data handling, significantly reducing manual intervention and enhancing data accuracy. Organizations rely on Data Entry Clerks for routine data tasks, while Data Automation Analysts contribute to strategic improvements through automation technologies such as RPA and scripting.
Core Responsibilities and Daily Tasks
Data Entry Clerks primarily focus on accurately inputting, updating, and maintaining data within databases or systems, ensuring data integrity and consistency. Data Automation Analysts design, develop, and implement automated workflows and scripts to streamline data processing tasks, reducing manual intervention and increasing efficiency. While Data Entry Clerks handle repetitive, manual data tasks, Data Automation Analysts leverage technical skills to optimize data management through automation tools and software.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Data Entry Clerks require proficiency in typing speed and accuracy, familiarity with data management software, and basic knowledge of database systems, emphasizing attention to detail and organizational skills. Data Automation Analysts need advanced expertise in programming languages such as Python or SQL, strong analytical capabilities, and experience with automation tools to design and implement efficient data workflows. Both roles demand strong problem-solving skills and a solid understanding of data integrity principles, but Data Automation Analysts typically require higher technical qualifications and experience in process optimization.
Software and Tools Utilized
Data Entry Clerks primarily use spreadsheet software like Microsoft Excel and data management systems such as Oracle or SAP for manual input and basic data processing. Data Automation Analysts leverage advanced tools including Python, R, and automation platforms like UiPath or Alteryx to streamline data workflows and implement machine learning algorithms. Both roles utilize database management systems, but Automation Analysts focus more on integrating APIs and scripting to enhance efficiency and reduce manual effort.
Impact on Workflow Efficiency
A Data Entry Clerk primarily enhances workflow efficiency by ensuring accurate and timely input of information, reducing manual errors and maintaining data integrity. In contrast, a Data Automation Analyst significantly amplifies efficiency by designing and implementing automated processes that minimize repetitive tasks and accelerate data handling. Integrating automation not only streamlines operations but also allows for scalable improvements and real-time data processing, fundamentally transforming administrative workflows.
Error Management and Quality Control
Data Entry Clerks primarily focus on accurate manual input of information, relying heavily on attention to detail to minimize errors during data entry processes. Data Automation Analysts implement and maintain automated systems that detect and correct anomalies, enhancing overall data quality and reducing human-induced errors. Both roles emphasize error management and quality control, but Automation Analysts leverage technology to streamline validation and improve data integrity at scale.
Training and Career Development Paths
Data Entry Clerks typically undergo basic training focused on typing accuracy and database management, enabling them to handle routine data input tasks efficiently. In contrast, Data Automation Analysts require advanced training in programming languages, data analytics, and automation tools to design and implement automated workflows. Career development for Data Entry Clerks often leads to supervisory roles or specialization in data quality, while Data Automation Analysts advance toward positions in data science, process optimization, and strategic IT management.
Salary Expectations and Job Outlook
Data Entry Clerks typically earn an average salary ranging from $28,000 to $40,000 annually, reflecting entry-level administrative roles with limited growth potential. Data Automation Analysts command higher salaries, often between $65,000 and $90,000, due to specialized skills in automating data processes and advanced software proficiency. The job outlook for Data Automation Analysts is significantly stronger, driven by increasing demand for automation in business operations, whereas Data Entry Clerk positions face gradual decline due to automation technologies reducing manual data entry needs.
Industry Trends in Administrative Data Management
Data Entry Clerks traditionally handle manual input tasks, but Industry Trends indicate a swift shift toward automation and data analytics, elevating Data Automation Analysts as key players in administrative data management. Automation tools and AI-driven software streamline data processing, reducing errors and increasing efficiency, thereby redefining job roles within organizations. Businesses now prioritize professionals skilled in data integration, real-time reporting, and process optimization to stay competitive in rapidly evolving markets.
Choosing the Right Role: Key Considerations
Choosing between a Data Entry Clerk and a Data Automation Analyst hinges on the level of technical expertise and career goals within data management. Data Entry Clerks focus on accurately inputting and maintaining data, requiring strong attention to detail but minimal programming skills, while Data Automation Analysts develop and optimize automated workflows using tools like Python, SQL, and RPA, demanding advanced analytical and coding proficiency. Understanding job responsibilities, required skills, and long-term career advancement opportunities is crucial for aligning role selection with organizational needs and personal growth.
Related Important Terms
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Data Entry Clerks primarily perform manual input of information into systems, while Data Automation Analysts leverage Robotic Process Automation (RPA) to design, implement, and maintain automated workflows that enhance data accuracy and operational efficiency. Utilizing RPA platforms like UiPath and Automation Anywhere, Data Automation Analysts reduce repetitive tasks, minimize human error, and enable scalable processing within administrative functions.
Hyperautomation
Data Entry Clerks specialize in manual input and validation of data records, while Data Automation Analysts leverage hyperautomation technologies such as AI, RPA, and machine learning to streamline and optimize data workflows. Implementing hyperautomation significantly reduces errors, accelerates processing times, and enhances overall data management efficiency within administrative operations.
Data Pipeline Orchestration
Data Entry Clerks primarily handle manual input and validation of data with limited involvement in data pipeline orchestration, focusing on accuracy and speed in entering information. In contrast, Data Automation Analysts design, implement, and manage automated workflows that streamline data pipeline orchestration, enhancing efficiency and reducing the risk of human error across data integration processes.
Intelligent Document Processing (IDP)
Data Entry Clerks primarily handle manual input of information into databases, whereas Data Automation Analysts leverage Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) technologies to streamline data extraction, validation, and integration, significantly enhancing accuracy and efficiency. IDP utilizes AI-driven tools like optical character recognition (OCR) and natural language processing (NLP) to automate document workflows, reducing reliance on manual data entry and optimizing administrative productivity.
OCR Workflow Integration
Data Entry Clerks primarily handle manual input of information, often relying on Optical Character Recognition (OCR) software to convert scanned documents into editable text, ensuring accuracy and consistency in data capture. Data Automation Analysts focus on optimizing OCR workflow integration by developing automated processes and algorithms that enhance data extraction efficiency, reduce errors, and streamline administrative operations.
Manual Data Validation
Data Entry Clerks perform manual data validation by accurately inputting and verifying information to ensure data integrity, while Data Automation Analysts develop and implement automated validation processes to reduce human error and increase efficiency. Manual data validation in data entry focuses on detailed accuracy checks, whereas automation analysts optimize workflows through scripting and software tools for scalable data quality management.
Low-Code Automation Platforms
Data Entry Clerks primarily focus on manual input and management of information, whereas Data Automation Analysts leverage low-code automation platforms to design, implement, and optimize data workflows, significantly enhancing efficiency and accuracy. By utilizing these platforms, Data Automation Analysts reduce repetitive tasks and enable scalable, user-friendly solutions that transform traditional administrative processes.
Data Anomaly Detection
Data Entry Clerks primarily handle manual input and verification of large volumes of data, whereas Data Automation Analysts specialize in leveraging machine learning algorithms and automated tools to detect data anomalies with higher accuracy and efficiency. The integration of anomaly detection systems by Data Automation Analysts significantly reduces human error and enhances data integrity in administrative processes.
Automated Data Mapping
Data Entry Clerks primarily handle manual input of information, whereas Data Automation Analysts focus on developing automated data mapping processes that increase accuracy and efficiency by transforming complex data sets into structured formats. Automated data mapping utilizes AI and machine learning algorithms to streamline data integration, significantly reducing human error and accelerating administrative workflows.
Digital Workforce Management
Data Entry Clerks primarily perform manual input and validation of data, ensuring accuracy in administrative records, while Data Automation Analysts leverage digital workforce management tools to streamline and optimize workflows through automation and advanced data analytics. The shift from traditional data entry roles to automation-focused positions significantly enhances operational efficiency and reduces human error in modern administrative environments.
Data Entry Clerk vs Data Automation Analyst Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com