Data entry involves manually inputting information into databases, which is time-consuming and prone to human error. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) streamlines administrative tasks by automating repetitive data entry processes, enhancing accuracy and efficiency. Implementing RPA reduces operational costs and frees employees to focus on higher-value work.
Table of Comparison
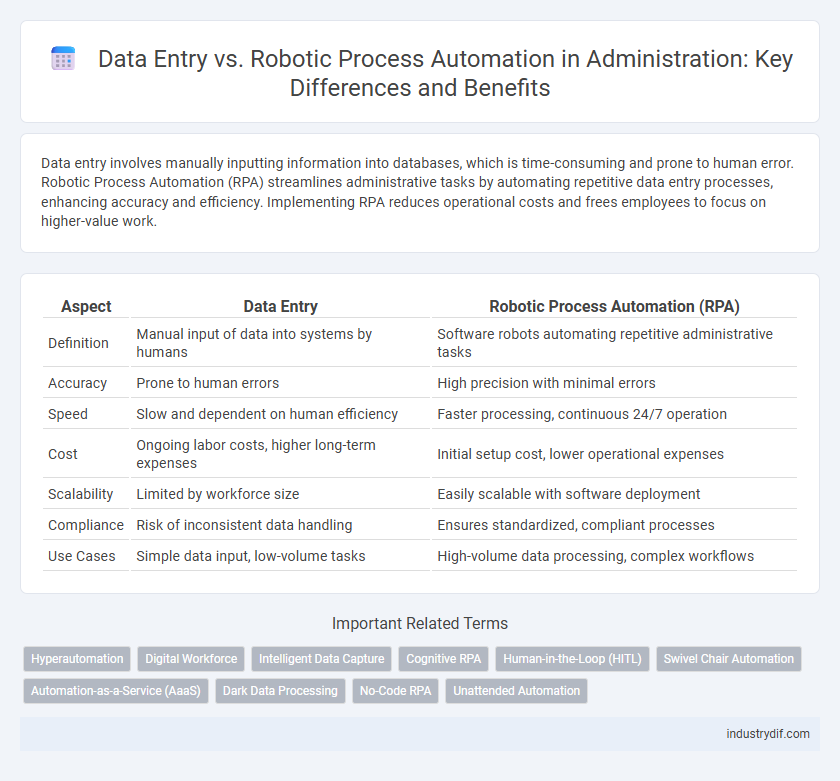
| Aspect | Data Entry | Robotic Process Automation (RPA) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manual input of data into systems by humans | Software robots automating repetitive administrative tasks |
| Accuracy | Prone to human errors | High precision with minimal errors |
| Speed | Slow and dependent on human efficiency | Faster processing, continuous 24/7 operation |
| Cost | Ongoing labor costs, higher long-term expenses | Initial setup cost, lower operational expenses |
| Scalability | Limited by workforce size | Easily scalable with software deployment |
| Compliance | Risk of inconsistent data handling | Ensures standardized, compliant processes |
| Use Cases | Simple data input, low-volume tasks | High-volume data processing, complex workflows |
Introduction to Data Entry and Robotic Process Automation
Data entry involves manually inputting information into digital systems, requiring accuracy and speed to maintain data integrity. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) uses software robots to automate repetitive administrative tasks, significantly increasing efficiency and reducing human error. Implementing RPA can streamline data entry processes by handling large volumes of information with precision and consistency.
Defining Data Entry in Administrative Tasks
Data entry in administrative tasks involves manually inputting, updating, and managing information within databases, spreadsheets, or other digital systems to maintain accurate records. This process requires human intervention to ensure data accuracy and handle diverse formats, often leading to time-consuming and repetitive workloads. Compared to Robotic Process Automation (RPA), traditional data entry relies on human effort rather than automated software bots designed to streamline and accelerate data processing.
What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a technology that uses software robots or artificial intelligence to automate repetitive, rule-based administrative tasks typically performed by human workers, such as data entry, invoice processing, and customer onboarding. By mimicking human actions within digital systems, RPA increases efficiency, reduces errors, and lowers operational costs across various industries. It enables organizations to streamline workflows, improve accuracy, and free up employees to focus on higher-value activities.
Key Differences between Data Entry and RPA
Data entry involves manual input of information into digital systems, typically requiring human intervention and prone to errors, whereas Robotic Process Automation (RPA) uses software robots to automate repetitive tasks with higher accuracy and speed. RPA integrates with multiple applications to perform data entry, validation, and transfer without human intervention, significantly reducing operational costs and time. Unlike traditional data entry, RPA offers scalability, audit trails, and the ability to handle complex workflows beyond simple data input tasks.
Efficiency and Productivity Comparison
Data entry involves manual input, which often results in slower processing times and higher error rates, reducing overall efficiency in administrative tasks. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) streamlines workflows by automating repetitive data input and validation, significantly increasing productivity and accuracy. Organizations implementing RPA report up to 70% faster task completion and a substantial decrease in human errors compared to traditional data entry methods.
Impact on Accuracy and Error Reduction
Data Entry relies heavily on manual input, which increases the risk of human error and inconsistent accuracy in administrative tasks. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) utilizes software bots to execute repetitive data entry processes with high precision, significantly reducing errors and enhancing data reliability. Implementing RPA in administrative workflows leads to improved accuracy metrics, decreased error rates, and streamlined compliance through automated validation checks.
Cost Implications: Manual vs Automated Processes
Manual data entry requires significant labor costs due to the repetitive, time-consuming nature of the task and higher potential for human error, which can increase expenses relating to corrections and rework. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) reduces operational costs by streamlining workflows and improving accuracy, leading to faster processing times and lower overhead associated with human intervention. Initial investment in RPA technology may be substantial, but the long-term savings from increased productivity and error reduction typically outweigh manual data entry expenses.
Workforce Transformation: Roles and Skills Evolved
Data Entry roles have traditionally required manual input skills and attention to detail, but with the rise of Robotic Process Automation (RPA), workforce transformation emphasizes advanced technical skills such as RPA bot management and process optimization. Employees now transition from repetitive data entry tasks to overseeing automated workflows, focusing on exception handling and system integration. This shift demands upskilling in programming languages, RPA tools like UiPath or Automation Anywhere, and analytical capabilities to enhance operational efficiency.
Challenges in Transitioning to RPA from Data Entry
Transitioning from traditional data entry to Robotic Process Automation (RPA) presents challenges such as ensuring data accuracy during automation setup and managing resistance from employees accustomed to manual processes. Integration with existing legacy systems often requires complex customization, increasing implementation time and costs. Continuous monitoring and updating of RPA scripts are critical to handle exceptions and maintain process reliability in dynamic administrative environments.
Future Trends in Administrative Automation
Future trends in administrative automation highlight Robotic Process Automation (RPA) as a transformative tool surpassing traditional data entry by enabling end-to-end workflow automation and reducing human error. Increasing integration of AI-powered RPA with machine learning enhances real-time data processing, predictive analytics, and decision-making efficiency in administrative tasks. Organizations adopting these advanced automation technologies experience significant improvements in operational speed, accuracy, and scalability.
Related Important Terms
Hyperautomation
Data Entry involves manual input of information, which is time-consuming and prone to human error, whereas Robotic Process Automation (RPA) leverages software bots to automate repetitive tasks with high accuracy. Hyperautomation extends RPA by integrating advanced technologies like AI, machine learning, and process mining, enabling end-to-end automation and intelligent decision-making in administrative functions.
Digital Workforce
Data entry traditionally involves manual input of information into systems, whereas Robotic Process Automation (RPA) leverages software bots to execute repetitive administrative tasks with higher accuracy and speed. Implementing RPA enhances the digital workforce by automating routine data handling processes, reducing errors, and enabling employees to focus on strategic, value-added activities.
Intelligent Data Capture
Intelligent Data Capture (IDC) enhances traditional data entry by automating extraction and classification of unstructured data using AI and machine learning algorithms, significantly reducing manual errors and processing time. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) leverages IDC to streamline repetitive administrative tasks, enabling scalable and accurate data management with minimal human intervention.
Cognitive RPA
Data Entry involves manual input of information into systems, whereas Robotic Process Automation (RPA), especially Cognitive RPA, leverages artificial intelligence to interpret, analyze, and automate complex tasks beyond simple rule-based processes. Cognitive RPA enhances administrative efficiency by integrating natural language processing and machine learning to handle unstructured data and decision-making workflows.
Human-in-the-Loop (HITL)
Data entry traditionally relies on manual input, increasing error risks and limiting scalability, whereas Robotic Process Automation (RPA) with Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) integrates automated workflows that allow human intervention for complex decision-making, enhancing accuracy and flexibility. Incorporating HITL in RPA ensures continuous process optimization, reduces operational costs, and maintains regulatory compliance by combining machine efficiency with human judgment.
Swivel Chair Automation
Swivel Chair Automation reduces manual data entry errors by seamlessly integrating multiple systems without human intervention, significantly improving administrative efficiency. Leveraging Robotic Process Automation enables organizations to minimize repetitive tasks and streamline workflows, unlike traditional data entry that requires constant human oversight.
Automation-as-a-Service (AaaS)
Data Entry traditionally involves manual input of information, whereas Robotic Process Automation (RPA) leverages Automation-as-a-Service (AaaS) to enable scalable, cloud-based automation of repetitive administrative tasks, enhancing accuracy and efficiency. AaaS platforms integrate RPA tools that streamline data processing workflows by automating rule-based tasks without extensive IT infrastructure investments.
Dark Data Processing
Dark data processing in administrative tasks highlights the limitations of traditional data entry, which often overlooks unstructured or hidden data sets. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) enhances efficiency by automating the extraction and analysis of dark data, transforming previously inaccessible information into actionable insights.
No-Code RPA
No-Code Robotic Process Automation (RPA) significantly enhances administrative efficiency by automating repetitive data entry tasks without requiring programming expertise, reducing human error and operational costs. Organizations adopting No-Code RPA solutions benefit from faster deployment and scalable workflow automation compared to traditional manual data entry methods.
Unattended Automation
Unattended automation in Robotic Process Automation (RPA) enables fully autonomous data entry processes, reducing manual errors and increasing operational efficiency compared to traditional data entry methods. Leveraging AI-driven bots for unattended automation minimizes human intervention, accelerates task completion, and ensures consistent data accuracy in administrative workflows.
Data Entry vs Robotic Process Automation Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com