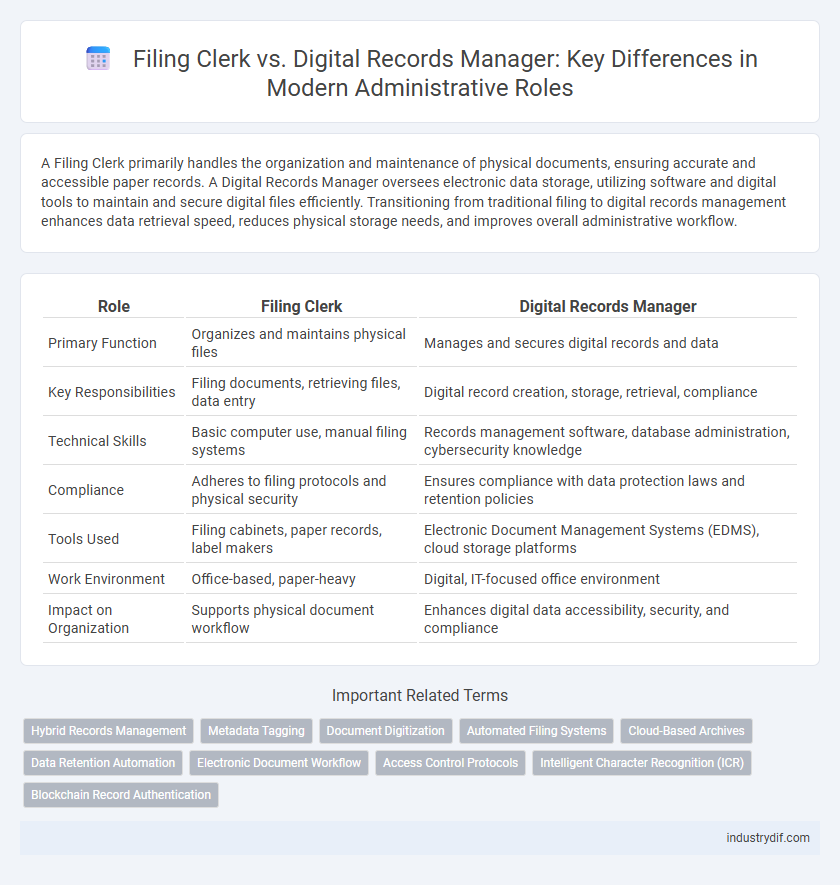
A Filing Clerk primarily handles the organization and maintenance of physical documents, ensuring accurate and accessible paper records. A Digital Records Manager oversees electronic data storage, utilizing software and digital tools to maintain and secure digital files efficiently. Transitioning from traditional filing to digital records management enhances data retrieval speed, reduces physical storage needs, and improves overall administrative workflow.
Table of Comparison
| Role | Filing Clerk | Digital Records Manager |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Organizes and maintains physical files | Manages and secures digital records and data |
| Key Responsibilities | Filing documents, retrieving files, data entry | Digital record creation, storage, retrieval, compliance |
| Technical Skills | Basic computer use, manual filing systems | Records management software, database administration, cybersecurity knowledge |
| Compliance | Adheres to filing protocols and physical security | Ensures compliance with data protection laws and retention policies |
| Tools Used | Filing cabinets, paper records, label makers | Electronic Document Management Systems (EDMS), cloud storage platforms |
| Work Environment | Office-based, paper-heavy | Digital, IT-focused office environment |
| Impact on Organization | Supports physical document workflow | Enhances digital data accessibility, security, and compliance |
Overview of Filing Clerk and Digital Records Manager Roles
Filing Clerks specialize in organizing, categorizing, and maintaining physical documents to ensure easy retrieval and efficient office operations. Digital Records Managers oversee the lifecycle of electronic records, implementing digital storage solutions and ensuring compliance with data retention policies and security standards. Both roles are critical in managing information assets, with Filing Clerks focusing on tangible records and Digital Records Managers emphasizing digital data governance.
Key Responsibilities and Duties
A Filing Clerk primarily handles the organization, storage, and retrieval of physical documents, ensuring accurate and efficient record-keeping through manual filing systems. In contrast, a Digital Records Manager oversees the maintenance, security, and accessibility of electronic records, implementing digital archiving systems and ensuring compliance with data protection regulations. Key responsibilities of a Digital Records Manager include managing digital workflows, conducting audits of electronic files, and facilitating data migration, while a Filing Clerk focuses on maintaining paper-based filing systems and processing document requests.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Filing Clerks require strong organizational skills, attention to detail, and proficiency in physical document handling and basic office software such as Microsoft Office. Digital Records Managers need advanced knowledge of electronic document management systems (EDMS), data security protocols, records retention policies, and often require certification like Certified Records Manager (CRM). Both roles demand excellent communication skills and a thorough understanding of compliance regulations related to information governance.
Tools and Technologies Used
Filing clerks primarily use physical filing systems, such as cabinets and paper-based indexing tools, alongside basic office software like spreadsheets and word processors to organize and retrieve documents. Digital records managers rely on advanced electronic document management systems (EDMS), cloud storage solutions, and data encryption technologies to securely store, categorize, and access records in digital formats. The integration of automation tools, metadata tagging, and compliance software is pivotal for digital records managers to enhance accuracy and regulatory adherence.
Workflow Processes and Efficiency
Filing Clerks primarily manage physical document organization and retrieval, relying on manual processes that can slow workflow efficiency. Digital Records Managers utilize electronic systems to streamline data storage, retrieval, and sharing, significantly enhancing access speed and reducing errors. Implementing digital management tools transforms administrative workflows by automating record handling and improving overall operational productivity.
Data Security and Compliance
Filing Clerks primarily manage physical documents, relying on manual organization methods that increase the risk of data breaches due to limited security controls. Digital Records Managers utilize advanced software to securely store and manage electronic records, ensuring compliance with data protection regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA. Implementing digital document management significantly enhances data security through access controls, encryption, and audit trails, reducing non-compliance risks and improving administrative efficiency.
Career Path and Advancement Opportunities
Filing Clerks typically begin with entry-level tasks such as organizing physical documents, offering limited advancement mainly into supervisory or specialized administrative roles. Digital Records Managers oversee electronic document systems, requiring advanced skills in information technology and data management, which opens pathways to senior management positions like Records Director or Compliance Officer. Career progression for Digital Records Managers is accelerated by expertise in digital archiving, regulatory compliance, and data security, making it a more dynamic and growth-oriented role compared to traditional filing positions.
Salary and Compensation Comparison
Filing Clerks typically earn an average annual salary ranging from $28,000 to $40,000, reflecting entry-level administrative responsibilities focused on physical document management. Digital Records Managers command higher compensation, often between $55,000 and $85,000 per year, due to specialized skills in electronic records management, data security, and compliance with information governance policies. The salary disparity is influenced by the increasing demand for expertise in digital archiving, regulatory knowledge, and proficiency with electronic document management systems (EDMS).
Impact of Digital Transformation
The shift from traditional Filing Clerks to Digital Records Managers highlights the profound impact of digital transformation in administrative processes. Digital Records Managers utilize advanced software to ensure efficient data retrieval, enhanced security, and compliance with regulatory standards, vastly improving organizational workflow. This evolution reduces reliance on physical documents, streamlining operations and enabling real-time access to records across multiple platforms.
Choosing the Right Career Path in Records Management
Filing Clerks typically handle physical document organization, retrieval, and basic record-keeping tasks, making them essential for maintaining traditional filing systems. Digital Records Managers oversee electronic records management, data security, and compliance with information governance policies, reflecting the growing reliance on digital archives. Choosing the right career path depends on one's proficiency with technology, interest in information systems, and long-term career goals within the records management field.
Related Important Terms
Hybrid Records Management
A Filing Clerk primarily handles the physical organization and retrieval of paper documents, while a Digital Records Manager oversees the creation, maintenance, and security of electronic records within a hybrid records management system. Emphasizing hybrid records management ensures seamless integration and compliance by combining traditional filing methods with advanced digital asset management and records retention policies.
Metadata Tagging
Filing clerks primarily organize physical documents using manual labeling systems, whereas digital records managers leverage advanced metadata tagging to categorize, retrieve, and maintain electronic records efficiently. Metadata tagging by digital records managers enhances searchability, compliance, and lifecycle management within digital information systems.
Document Digitization
Document digitization streamlines administrative workflows by converting physical files into searchable digital formats, a task where Digital Records Managers oversee metadata accuracy, digital storage systems, and compliance with electronic record-keeping standards. Filing Clerks typically handle manual organization and physical document retrieval, whereas Digital Records Managers implement advanced digitization technologies and ensure secure, efficient access to electronic records.
Automated Filing Systems
Filing Clerks traditionally manage physical documents, but Digital Records Managers leverage automated filing systems to streamline document storage, retrieval, and compliance with regulatory standards. Automated filing systems reduce human error, enhance data accessibility, and optimize workflow efficiency in administrative record management.
Cloud-Based Archives
Filing Clerks primarily manage physical documents and traditional filing systems, whereas Digital Records Managers specialize in organizing and maintaining cloud-based archives to ensure secure, scalable, and easily retrievable digital records. Cloud-based archives enhance data accessibility and disaster recovery capabilities, making Digital Records Managers crucial for modern administrative practices.
Data Retention Automation
Filing clerks primarily handle manual organization and physical storage of documents, resulting in time-consuming data retention processes prone to human error. Digital Records Managers leverage automated data retention systems with metadata tagging and lifecycle management, ensuring efficient compliance and secure, timely disposal of digital assets.
Electronic Document Workflow
A Filing Clerk primarily handles the physical organization and retrieval of paper documents, while a Digital Records Manager oversees the systematic electronic document workflow, ensuring efficient digital storage, access control, and compliance with data retention policies. Implementing advanced electronic document management systems optimizes collaboration, reduces retrieval time, and enhances the security of sensitive administrative records.
Access Control Protocols
Filing Clerks manage physical document storage with manual access controls, relying on locked cabinets and sign-out sheets to ensure secure access. Digital Records Managers implement advanced access control protocols including role-based permissions, multi-factor authentication, and audit trails to safeguard electronic records from unauthorized access.
Intelligent Character Recognition (ICR)
Filing Clerks primarily manage physical documents, whereas Digital Records Managers leverage Intelligent Character Recognition (ICR) technology to automate the extraction and classification of data from scanned documents, enhancing accuracy and retrieval speed. ICR enables Digital Records Managers to transform handwritten or printed content into editable, searchable digital formats, streamlining administrative workflows and reducing manual entry errors.
Blockchain Record Authentication
Filing Clerks primarily handle physical document organization and retrieval, lacking the tools for blockchain-based verification, while Digital Records Managers utilize blockchain technology to authenticate digital records, ensuring tamper-proof and transparent record-keeping. Implementing blockchain for record authentication enhances security, traceability, and compliance in administrative processes, positioning Digital Records Managers as critical in modern data management systems.
Filing Clerk vs Digital Records Manager Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com