A Payroll Clerk handles data entry, employee payment processing, and ensures compliance with payroll policies using manual systems, focusing on accuracy and troubleshooting routine issues. A Payroll Automation Specialist designs, implements, and manages automated payroll systems to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and reduce errors in payment processing. Both roles require strong knowledge of payroll regulations, but the specialist emphasizes technology integration and process optimization over manual data handling.
Table of Comparison
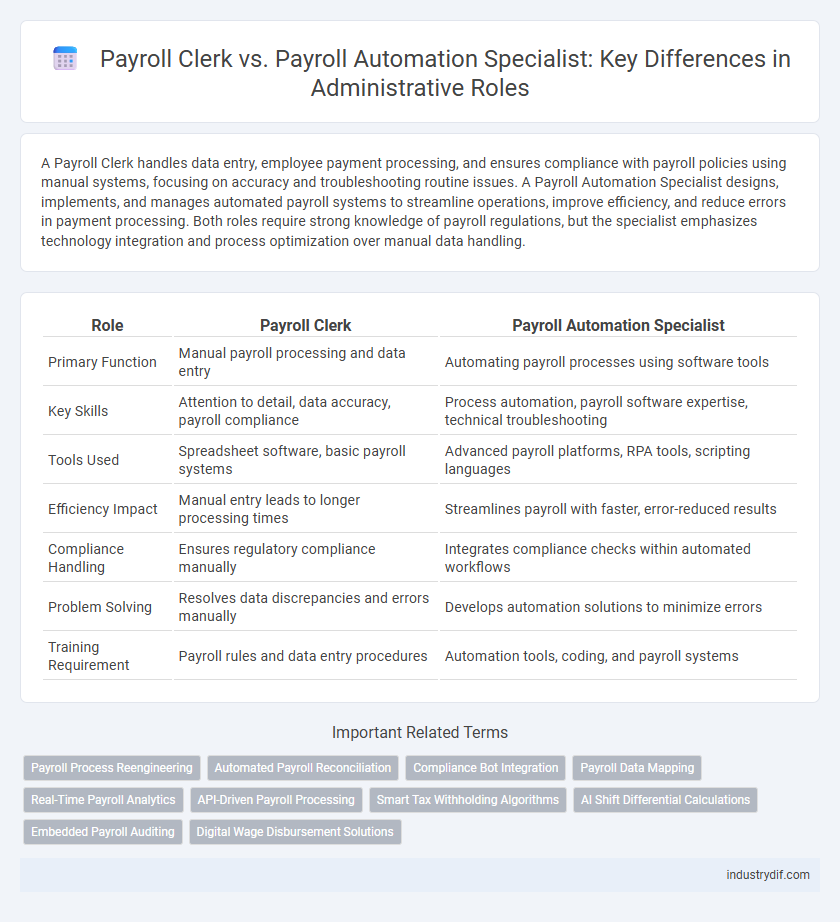
| Role | Payroll Clerk | Payroll Automation Specialist |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Manual payroll processing and data entry | Automating payroll processes using software tools |
| Key Skills | Attention to detail, data accuracy, payroll compliance | Process automation, payroll software expertise, technical troubleshooting |
| Tools Used | Spreadsheet software, basic payroll systems | Advanced payroll platforms, RPA tools, scripting languages |
| Efficiency Impact | Manual entry leads to longer processing times | Streamlines payroll with faster, error-reduced results |
| Compliance Handling | Ensures regulatory compliance manually | Integrates compliance checks within automated workflows |
| Problem Solving | Resolves data discrepancies and errors manually | Develops automation solutions to minimize errors |
| Training Requirement | Payroll rules and data entry procedures | Automation tools, coding, and payroll systems |
Introduction to Payroll Roles
Payroll Clerks manage employee compensation records, process payroll transactions, and ensure accurate tax withholdings in compliance with labor regulations. Payroll Automation Specialists design and implement automated systems to streamline payroll processing, enhance data accuracy, and reduce manual errors using software tools like ADP or SAP SuccessFactors. Both roles are critical for maintaining payroll efficiency, but the specialist focuses on leveraging technology while the clerk handles day-to-day payroll operations.
Definition of Payroll Clerk
A Payroll Clerk is responsible for processing employee payroll, maintaining accurate records, and ensuring compliance with relevant tax laws and labor regulations. This role typically involves data entry, verifying timesheets, and managing deductions and benefits for timely salary distribution. Payroll Clerks play a crucial role in supporting the payroll department by ensuring precision and consistency in employee compensation.
Definition of Payroll Automation Specialist
A Payroll Automation Specialist is a professional responsible for designing, implementing, and managing automated payroll systems to improve efficiency and accuracy in payroll processing. This role involves leveraging software tools and technologies to streamline data entry, tax calculations, and compliance reporting, reducing manual errors common in traditional payroll clerk tasks. By integrating automation, the specialist enhances payroll operations, ensuring timely payments and adherence to legal standards.
Key Responsibilities Comparison
Payroll Clerks primarily manage accurate employee wage calculations, process timesheets, and ensure timely payment distribution, focusing on data entry and record maintenance within payroll systems. Payroll Automation Specialists design, implement, and optimize payroll software workflows, leveraging automation tools to streamline processes, reduce manual errors, and improve compliance with tax regulations. The key responsibility difference lies in the Payroll Clerk's operational execution of payroll tasks versus the Automation Specialist's strategic role in enhancing payroll system efficiency through technology.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Payroll Clerks require proficiency in data entry, basic accounting principles, and familiarity with payroll software such as ADP or QuickBooks, alongside strong attention to detail and organizational skills. Payroll Automation Specialists demand advanced technical skills, including expertise in programming languages like SQL and Python, experience with robotic process automation (RPA) tools, and deep knowledge of payroll systems integration and data analytics. Both roles benefit from a solid understanding of tax regulations, compliance standards, and confidentiality protocols.
Tools and Technologies Used
Payroll Clerks primarily use payroll software such as ADP and QuickBooks to process employee salaries and maintain records, ensuring compliance with tax regulations. Payroll Automation Specialists leverage advanced technologies including robotic process automation (RPA), AI-driven payroll platforms, and cloud-based HR systems like Workday and SAP SuccessFactors to streamline and optimize payroll workflows. Emphasizing integration capabilities and real-time data analytics, specialists enhance accuracy and efficiency beyond traditional payroll processing tools.
Efficiency and Productivity Differences
A Payroll Clerk manually processes employee payments, often leading to longer processing times and higher error rates, which can reduce overall efficiency. In contrast, a Payroll Automation Specialist leverages advanced payroll software and automation tools to streamline workflows, significantly increasing productivity and accuracy. Implementing automated systems reduces repetitive tasks and allows specialists to focus on troubleshooting and compliance, optimizing payroll operations across the organization.
Impact on Compliance and Accuracy
Payroll Clerks manually process employee pay, increasing the risk of errors and compliance issues due to human oversight. Payroll Automation Specialists implement advanced software solutions that enhance accuracy by reducing manual input, ensuring strict adherence to tax regulations and labor laws. Automated systems enable real-time updates and audits, minimizing penalties and improving overall compliance in payroll management.
Career Pathways and Advancement
Payroll Clerks typically begin with entry-level tasks such as data entry and payroll processing, developing foundational skills in compliance and accuracy. Payroll Automation Specialists advance by integrating technology to streamline payroll systems, requiring expertise in software tools like ADP, Workday, or SAP SuccessFactors. Career pathways for Payroll Automation Specialists offer higher earning potential and leadership roles in payroll management or human resources information systems (HRIS).
Future Trends in Payroll Administration
Payroll Automation Specialists are increasingly vital as AI and machine learning streamline data entry and error detection in payroll processes, reducing manual workload traditionally handled by Payroll Clerks. Future trends indicate a shift towards real-time payroll processing and advanced analytics for compliance and forecasting, requiring specialized technical skills beyond basic payroll management. Organizations investing in automated payroll solutions enhance accuracy, efficiency, and regulatory adherence, positioning Payroll Automation Specialists at the forefront of administrative innovation.
Related Important Terms
Payroll Process Reengineering
Payroll Clerks handle routine data entry and basic payroll processing tasks, ensuring accurate employee compensation through manual verification and record-keeping. Payroll Automation Specialists focus on payroll process reengineering by implementing advanced software solutions and optimizing workflows to enhance efficiency, reduce errors, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
Automated Payroll Reconciliation
Payroll Clerks typically manage manual payroll processing tasks, while Payroll Automation Specialists implement automated payroll reconciliation systems that improve accuracy and reduce errors. Automated payroll reconciliation streamlines financial audits by cross-referencing payroll data with accounting records in real time, enhancing compliance and operational efficiency.
Compliance Bot Integration
Payroll Clerks primarily handle manual data entry and basic compliance tracking, often relying on traditional payroll software, while Payroll Automation Specialists focus on integrating advanced Compliance Bot systems to enhance accuracy and ensure real-time adherence to labor laws and tax regulations. Implementing Compliance Bot integration reduces human error and streamlines audit processes, enabling specialists to maintain up-to-date regulatory compliance across payroll operations.
Payroll Data Mapping
Payroll Clerks manually input and verify payroll data, often relying on spreadsheets and traditional software, leading to higher risks of errors in data mapping between employee records and payment systems. Payroll Automation Specialists design, implement, and optimize automated workflows that streamline payroll data mapping, reducing discrepancies and enhancing data accuracy across integrated payroll platforms.
Real-Time Payroll Analytics
Payroll clerks handle routine tasks such as data entry and payroll processing, which often limits their ability to perform real-time payroll analytics. In contrast, payroll automation specialists leverage advanced software and analytics tools to provide continuous, accurate insights into payroll data, enabling faster decision-making and compliance monitoring.
API-Driven Payroll Processing
Payroll Clerks manage manual payroll inputs and verify employee compensation using traditional software, while Payroll Automation Specialists leverage API-driven payroll processing to integrate real-time data from multiple HR and accounting systems, enhancing accuracy and efficiency. API-driven automation streamlines data exchange, reduces errors, and accelerates payroll cycles, transforming payroll management into a seamless, tech-enabled workflow.
Smart Tax Withholding Algorithms
Payroll Automation Specialists leverage smart tax withholding algorithms to enhance accuracy and compliance in employee paycheck calculations, reducing errors inherent in manual processes managed by Payroll Clerks. By integrating advanced data analytics and real-time tax code updates, these specialists optimize withholdings efficiently, ensuring precise deductions aligned with current regulations.
AI Shift Differential Calculations
Payroll Clerks manually process AI shift differential calculations by inputting employee shift data and applying standard pay rates, which often results in slower accuracy. Payroll Automation Specialists leverage AI-driven software to automatically calculate shift differentials, enhancing precision and efficiency in payroll management.
Embedded Payroll Auditing
Payroll Clerks typically handle manual data entry and routine payroll processing tasks, which can limit efficiency and increase the risk of errors in payroll auditing. Payroll Automation Specialists leverage embedded payroll auditing technologies to streamline compliance checks, detect discrepancies in real-time, and enhance the accuracy and reliability of payroll records.
Digital Wage Disbursement Solutions
Payroll Clerks manage employee wage data and process payments manually, ensuring accuracy through traditional methods, while Payroll Automation Specialists leverage digital wage disbursement solutions to streamline payroll operations, reduce errors, and enhance real-time payment tracking. Implementing advanced payroll automation software enables faster salary processing, compliance monitoring, and integration with financial systems, significantly improving operational efficiency and data security.
Payroll Clerk vs Payroll Automation Specialist Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com