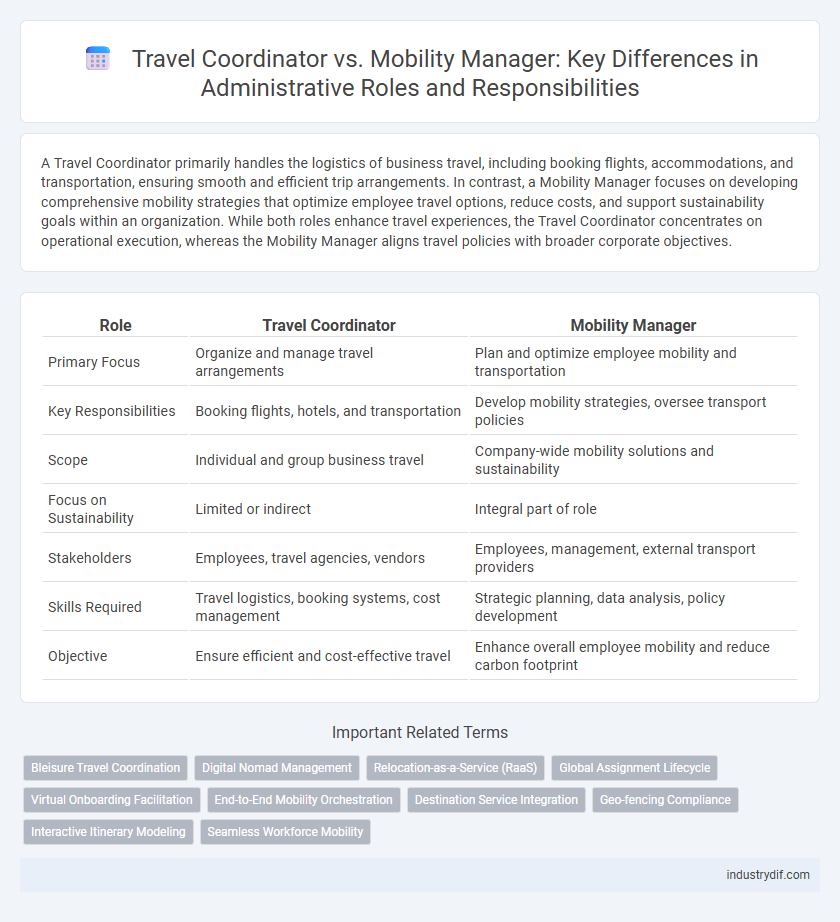
A Travel Coordinator primarily handles the logistics of business travel, including booking flights, accommodations, and transportation, ensuring smooth and efficient trip arrangements. In contrast, a Mobility Manager focuses on developing comprehensive mobility strategies that optimize employee travel options, reduce costs, and support sustainability goals within an organization. While both roles enhance travel experiences, the Travel Coordinator concentrates on operational execution, whereas the Mobility Manager aligns travel policies with broader corporate objectives.
Table of Comparison
| Role | Travel Coordinator | Mobility Manager |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Organize and manage travel arrangements | Plan and optimize employee mobility and transportation |
| Key Responsibilities | Booking flights, hotels, and transportation | Develop mobility strategies, oversee transport policies |
| Scope | Individual and group business travel | Company-wide mobility solutions and sustainability |
| Focus on Sustainability | Limited or indirect | Integral part of role |
| Stakeholders | Employees, travel agencies, vendors | Employees, management, external transport providers |
| Skills Required | Travel logistics, booking systems, cost management | Strategic planning, data analysis, policy development |
| Objective | Ensure efficient and cost-effective travel | Enhance overall employee mobility and reduce carbon footprint |
Understanding the Roles: Travel Coordinator vs Mobility Manager
A Travel Coordinator manages the logistics of business travel, including booking flights, accommodations, and transportation, ensuring cost efficiency and compliance with company policies. In contrast, a Mobility Manager oversees broader employee mobility strategies, integrating travel, relocation, and commuting solutions to optimize workforce movement and sustainability. Both roles require coordination and planning but differ significantly in scope and strategic impact within organizational administration.
Core Responsibilities and Functions
Travel Coordinators manage the logistics of business travel, including booking transportation, accommodations, and ensuring compliance with company travel policies. Mobility Managers oversee broader employee mobility strategies, optimizing transportation options, promoting sustainable travel programs, and coordinating relocation processes. Key functions for Travel Coordinators emphasize operational execution, while Mobility Managers focus on strategic planning and policy development for workforce mobility.
Key Skills and Qualifications Required
Travel Coordinators require expertise in itinerary planning, vendor negotiation, and expense management, emphasizing strong organizational and communication skills to manage corporate travel efficiently. Mobility Managers focus on strategic transportation planning, sustainable mobility solutions, and employee travel behavior analysis, demanding qualifications in urban planning, project management, and data analysis. Both roles benefit from proficiency in travel software, budget control, and stakeholder coordination within corporate or governmental environments.
Overlapping Duties and Distinct Differences
Travel Coordinators and Mobility Managers both handle employee travel arrangements, expense tracking, and compliance with corporate policies, ensuring smooth and cost-efficient business trips. Travel Coordinators focus on booking flights, accommodations, and transportation, while Mobility Managers oversee broader strategic initiatives such as international relocations, visa processes, and employee mobility programs. The distinct difference lies in the scope: Travel Coordinators manage daily travel logistics, whereas Mobility Managers plan and execute long-term workforce mobility and global mobility strategies.
Impact on Organizational Efficiency
A Travel Coordinator primarily streamlines travel arrangements, reducing costs and minimizing scheduling conflicts, which directly enhances organizational efficiency by ensuring seamless employee mobility. A Mobility Manager extends this role by developing strategic policies and integrating sustainable transportation solutions, significantly improving long-term operational effectiveness and employee satisfaction. Optimizing both roles collaboratively leads to comprehensive travel management that boosts productivity and supports corporate sustainability goals.
Technology and Tools in Travel and Mobility Management
Travel Coordinators primarily utilize booking platforms, expense management software, and itinerary tracking tools to streamline corporate travel arrangements. Mobility Managers leverage advanced data analytics, integrated mobility platforms, and sustainable transportation technologies to optimize employee mobility and reduce environmental impact. Both roles increasingly adopt AI-driven solutions and mobile apps to enhance efficiency and real-time management in travel and mobility operations.
Compliance, Policy, and Risk Management
Travel Coordinators ensure adherence to corporate travel policies by managing bookings and monitoring compliance with internal guidelines, minimizing risk through direct oversight of travel arrangements. Mobility Managers adopt a broader approach by integrating travel strategies with overall corporate mobility policies, focusing extensively on risk management related to employee relocation, transportation security, and regulatory compliance across diverse jurisdictions. Both roles emphasize policy enforcement and risk mitigation, but Mobility Managers typically oversee comprehensive compliance frameworks that align mobility programs with organizational objectives and legal requirements.
Career Pathways and Advancement Opportunities
Travel coordinators typically begin their careers managing logistics and bookings for business trips, gaining expertise in vendor relations and travel policy compliance. Mobility managers advance by overseeing broader employee relocation strategies, integrating transportation options, and optimizing workforce mobility on a global scale. Career pathways in mobility management often lead to senior roles in global mobility or corporate HR, offering greater strategic influence and leadership responsibilities compared to the more operational focus of travel coordination.
Industry Trends Shaping Administrator Roles
Travel Coordinators primarily manage logistical details such as booking, itineraries, and expense tracking, while Mobility Managers oversee broader strategic initiatives including employee relocation policies and transportation sustainability. Emerging industry trends like digital transformation, remote work, and green mobility are increasingly shifting administrative roles towards integrated mobility solutions and data-driven decision-making. The rise of smart travel technologies and global workforce mobility demands administrators to adopt agile, comprehensive strategies that streamline operations and enhance workforce flexibility.
Choosing the Right Role for Your Business Needs
Selecting between a Travel Coordinator and a Mobility Manager depends on your business's scale and specific needs; a Travel Coordinator focuses on booking and managing travel logistics, ideal for organizations with routine travel demands. In contrast, a Mobility Manager oversees comprehensive transportation solutions, including employee commuting strategies and cost optimization, suited for larger enterprises aiming to enhance sustainability and operational efficiency. Understanding these roles ensures alignment with corporate travel policies and budgetary goals, optimizing resource allocation and employee satisfaction.
Related Important Terms
Bleisure Travel Coordination
A Travel Coordinator manages logistical arrangements for business trips, ensuring seamless booking and compliance, while a Mobility Manager oversees broader employee movement strategies, including policies for bleisure travel to optimize cost efficiency and employee satisfaction. Effective bleisure travel coordination requires integrating travel policies with mobility management to balance corporate goals and personal travel benefits within administrative frameworks.
Digital Nomad Management
Travel Coordinators handle logistical arrangements such as booking flights and accommodations, ensuring smooth travel for digital nomads, while Mobility Managers develop strategic policies that optimize remote work mobility, compliance, and employee well-being in global contexts. Emphasizing digital nomad management, Mobility Managers integrate technology platforms to monitor location data, visa requirements, and tax regulations, fostering seamless international work experiences.
Relocation-as-a-Service (RaaS)
Travel Coordinators primarily handle logistics and booking for employee travel, while Mobility Managers oversee broader strategic planning including Relocation-as-a-Service (RaaS), integrating employee relocation with travel, housing, and compliance solutions. RaaS platforms enable Mobility Managers to streamline employee transitions by offering end-to-end services that combine travel coordination, temporary accommodations, and local onboarding support.
Global Assignment Lifecycle
Travel Coordinators primarily handle logistical arrangements such as booking flights, accommodations, and local transportation, ensuring smooth travel execution within the Global Assignment Lifecycle. Mobility Managers oversee broader strategic elements including policy development, compliance, and employee relocation, optimizing global talent movement and assignment success.
Virtual Onboarding Facilitation
Travel Coordinators streamline logistical arrangements and manage itineraries for international assignments, while Mobility Managers oversee comprehensive employee relocation strategies, integrating virtual onboarding facilitation to ensure seamless acclimation in remote environments. Emphasizing virtual onboarding enables Mobility Managers to coordinate digital orientation sessions, compliance training, and resource access, optimizing global workforce integration without physical presence.
End-to-End Mobility Orchestration
A Travel Coordinator manages logistical aspects of employee travel, such as booking flights, accommodations, and car rentals, ensuring seamless itinerary execution. Mobility Managers oversee End-to-End Mobility Orchestration by integrating travel, transportation, and relocation services to optimize workforce movement and enhance operational efficiency.
Destination Service Integration
Travel Coordinators primarily manage logistics and bookings, ensuring seamless itinerary planning, while Mobility Managers integrate destination services by aligning transportation options, accommodation, and local support to optimize employee mobility. Effective destination service integration requires Mobility Managers to collaborate with local providers and tailor solutions that enhance efficiency and employee satisfaction.
Geo-fencing Compliance
Travel Coordinators manage employee travel arrangements while ensuring geo-fencing compliance by monitoring location-based restrictions through booking systems and travel itineraries. Mobility Managers oversee broader employee movement strategies, implementing geo-fencing technologies to enforce location-specific policies and optimize organizational mobility compliance.
Interactive Itinerary Modeling
Travel Coordinators streamline booking processes and manage travel logistics, leveraging basic itinerary tools to ensure smooth trip execution. Mobility Managers employ interactive itinerary modeling to optimize travel plans dynamically, integrating real-time data for enhanced route efficiency and compliance with organizational policies.
Seamless Workforce Mobility
Travel Coordinators specialize in managing employees' travel arrangements for short-term assignments, ensuring cost-effective bookings and compliance with company policies. Mobility Managers oversee broader workforce mobility strategies, including relocations, immigration, and long-term assignments, to facilitate seamless transitions and maximize employee productivity across global locations.
Travel Coordinator vs Mobility Manager Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com