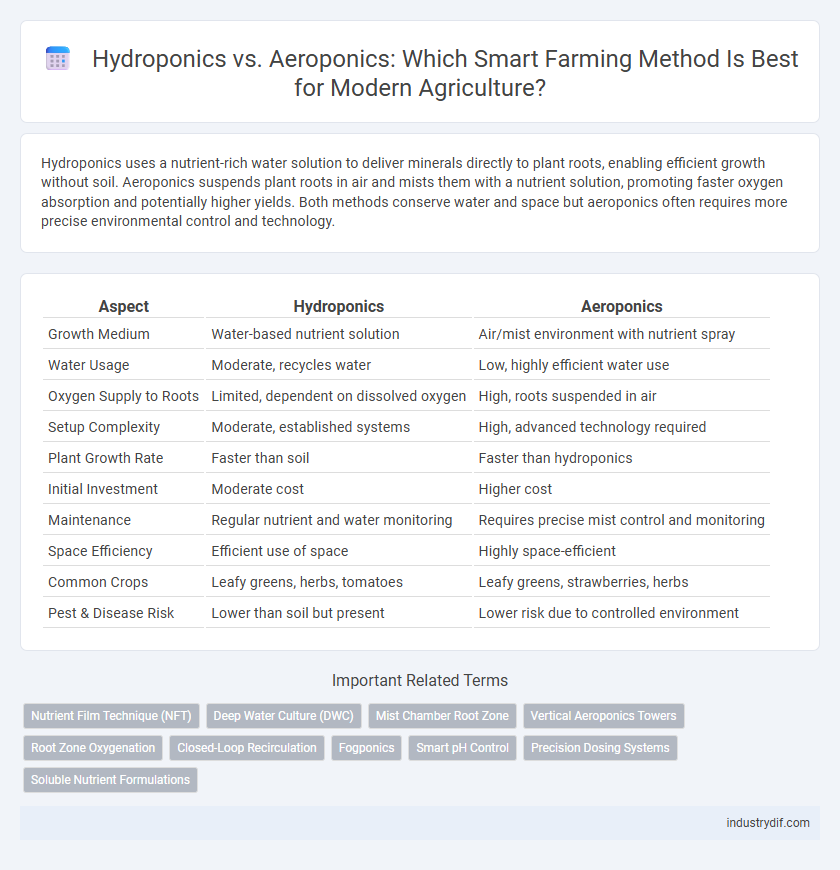
Hydroponics uses a nutrient-rich water solution to deliver minerals directly to plant roots, enabling efficient growth without soil. Aeroponics suspends plant roots in air and mists them with a nutrient solution, promoting faster oxygen absorption and potentially higher yields. Both methods conserve water and space but aeroponics often requires more precise environmental control and technology.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Hydroponics | Aeroponics |
|---|---|---|
| Growth Medium | Water-based nutrient solution | Air/mist environment with nutrient spray |
| Water Usage | Moderate, recycles water | Low, highly efficient water use |
| Oxygen Supply to Roots | Limited, dependent on dissolved oxygen | High, roots suspended in air |
| Setup Complexity | Moderate, established systems | High, advanced technology required |
| Plant Growth Rate | Faster than soil | Faster than hydroponics |
| Initial Investment | Moderate cost | Higher cost |
| Maintenance | Regular nutrient and water monitoring | Requires precise mist control and monitoring |
| Space Efficiency | Efficient use of space | Highly space-efficient |
| Common Crops | Leafy greens, herbs, tomatoes | Leafy greens, strawberries, herbs |
| Pest & Disease Risk | Lower than soil but present | Lower risk due to controlled environment |
Introduction to Soilless Farming
Hydroponics and aeroponics are innovative soilless farming techniques that optimize plant growth by delivering nutrients directly to the roots through water-based solutions or mist environments, respectively. Hydroponics uses nutrient-rich water circulated in a medium such as coconut coir or perlite, maximizing nutrient uptake and water efficiency. Aeroponics suspends plant roots in air and periodically mists them with nutrient solutions, significantly enhancing oxygen availability and accelerating growth rates compared to traditional soil farming.
Defining Hydroponics and Aeroponics
Hydroponics is a soil-less cultivation technique where plant roots are submerged in a nutrient-rich water solution, optimizing nutrient uptake and growth rates. Aeroponics involves suspending plant roots in air while periodically misting them with a nutrient solution, enhancing oxygen access and nutrient absorption. Both systems enable efficient water use and controlled growing conditions, but aeroponics offers higher oxygen exposure to roots, potentially increasing growth speed and crop yield.
How Hydroponics Works
Hydroponics works by growing plants in a nutrient-rich water solution, eliminating the need for soil and allowing precise control over nutrient delivery to the root system. This method uses inert growing media like perlite or coconut coir to support plant roots while ensuring optimal oxygen and moisture levels. Automated nutrient dosing and pH monitoring systems enhance growth efficiency and promote higher yields compared to traditional soil farming.
How Aeroponics Works
Aeroponics cultivates plants by suspending roots in the air and continuously misting them with a nutrient-rich solution, optimizing oxygen exposure and nutrient absorption. This method enhances root aeration compared to hydroponics, where roots are submerged in a nutrient water solution. The precise delivery of nutrients in aeroponics promotes faster growth rates and higher yields, making it a highly efficient soilless cultivation technique.
Key Differences Between Hydroponics and Aeroponics
Hydroponics grows plants in nutrient-rich water solutions, while aeroponics suspends roots in air and mists them with nutrients. Hydroponic systems typically require less energy but more water compared to aeroponics, which maximizes oxygen exposure for faster growth. Aeroponics offers higher yields and better disease control due to enhanced root aeration but involves more complex setup and maintenance.
Advantages of Hydroponics
Hydroponics offers significant advantages such as efficient water usage, with up to 90% less water consumption compared to traditional soil farming. It enables controlled nutrient delivery directly to plant roots, promoting faster growth rates and higher crop yields. This soil-free method reduces the risk of soil-borne diseases, enhancing plant health and reducing the need for pesticides.
Advantages of Aeroponics
Aeroponics offers significant advantages such as enhanced nutrient uptake efficiency by delivering oxygen-rich nutrient mist directly to plant roots, which accelerates growth rates and increases crop yields. This soil-free system reduces water usage by up to 90% compared to traditional farming and minimizes disease risk by limiting root contact with water. Aeroponics also allows precise control over environmental factors, promoting healthier plants and optimizing resource utilization.
Challenges and Limitations of Each System
Hydroponics faces challenges such as the risk of root diseases due to stagnant water and the high initial setup costs for nutrient delivery systems, while managing pH and nutrient balance precisely remains critical to prevent crop failure. Aeroponics encounters limitations including the dependence on continuous misting, making it vulnerable to pump failures that can quickly stress or kill plants, and often requires more technical expertise to maintain ideal humidity and oxygen levels. Both systems demand constant monitoring and energy inputs, which can increase operational complexity and costs for large-scale agricultural production.
Cost and Resource Efficiency Comparison
Hydroponics systems generally require lower initial investment costs and consume less energy compared to aeroponics, making them more accessible for small to medium-scale farmers. Aeroponics offers superior water and nutrient efficiency by delivering mist directly to plant roots, reducing water usage by up to 90% compared to traditional soil farming and about 50% more efficient than hydroponics systems. Despite higher setup and maintenance expenses, aeroponics can yield faster growth rates and higher crop yields, optimizing resource utilization in high-tech agricultural operations.
Future Trends in Soilless Agriculture
Hydroponics and aeroponics represent cutting-edge methods in soilless agriculture, with future trends emphasizing automation, AI integration, and resource efficiency to maximize crop yields. Innovations in sensor technology and data analytics enable precise nutrient delivery and environmental control, promoting sustainable urban farming and reducing water usage by up to 90% compared to traditional methods. The growing demand for year-round, high-quality produce positions hydroponics and aeroponics as pivotal solutions in addressing global food security challenges.
Related Important Terms
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)
The Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) in hydroponics circulates a thin layer of nutrient-rich water over plant roots, maximizing oxygen exposure and nutrient uptake for rapid growth. In contrast, aeroponics suspends plant roots in air and misting them with nutrient solution, offering higher oxygen levels but requiring more precise environmental control.
Deep Water Culture (DWC)
Deep Water Culture (DWC) hydroponics involves suspending plant roots in oxygenated nutrient-rich water, promoting rapid growth through constant access to nutrients and oxygen. Aeroponics, by misting roots in air, uses less water and nutrients but requires precise system control to prevent root desiccation and maximize yield.
Mist Chamber Root Zone
Aeroponics utilizes a mist chamber to deliver nutrient-rich water directly to plant roots suspended in air, enhancing oxygen availability and promoting rapid growth compared to hydroponic systems where roots are submerged in nutrient solutions. The mist chamber root zone in aeroponics improves nutrient absorption efficiency and reduces water usage by up to 90%, offering significant advantages for sustainable agriculture.
Vertical Aeroponics Towers
Vertical aeroponics towers enhance crop yields by delivering nutrient-rich mist directly to plant roots suspended in air, optimizing oxygen exposure and water efficiency compared to traditional hydroponics. This soil-less technique reduces water usage by up to 90%, accelerates growth cycles, and allows for high-density, space-saving agriculture in urban and indoor environments.
Root Zone Oxygenation
Hydroponics provides nutrient-rich water directly to plant roots, ensuring moderate oxygen availability through water aeration techniques. Aeroponics maximizes root zone oxygenation by suspending roots in air and misting them with nutrient solutions, promoting faster growth and higher oxygen diffusion.
Closed-Loop Recirculation
Closed-loop recirculation systems in hydroponics recycle nutrient-rich water through plants' roots, optimizing nutrient use efficiency and reducing water waste. Aeroponics employs a similar closed-loop method but delivers nutrients via mist, enhancing oxygen availability and promoting faster plant growth with minimal resource consumption.
Fogponics
Fogponics, a subset of aeroponics, enhances plant growth by delivering nutrient-rich mist composed of ultra-fine droplets directly to the root zone, maximizing oxygen exposure and nutrient absorption. This method demonstrates higher water efficiency and nutrient uptake compared to traditional hydroponics and even standard aeroponics, promoting faster plant development and increased yields in controlled agricultural environments.
Smart pH Control
Smart pH control in hydroponics uses sensors and automated systems to maintain optimal nutrient solution acidity, enhancing plant nutrient absorption and growth efficiency. Aeroponics benefits from precise pH regulation through misting systems that deliver nutrient-rich solutions directly to roots, improving oxygen availability and reducing disease risk.
Precision Dosing Systems
Precision dosing systems in hydroponics deliver exact nutrient concentrations directly to plant roots through water-based solutions, optimizing growth efficiency and reducing waste. In aeroponics, these systems mist nutrient-rich solutions in controlled droplets, enhancing oxygen availability and nutrient absorption for faster plant development and higher yields.
Soluble Nutrient Formulations
Hydroponics relies on water-based soluble nutrient formulations carefully balanced to optimize nutrient uptake efficiency, ensuring plants receive essential macro and micronutrients directly through the solution. Aeroponics, however, demands more refined soluble nutrient formulations with higher oxygenation and nutrient solubility to support nutrient absorption via misted roots, enhancing growth rates and reducing nutrient wastage.
Hydroponics vs Aeroponics Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com