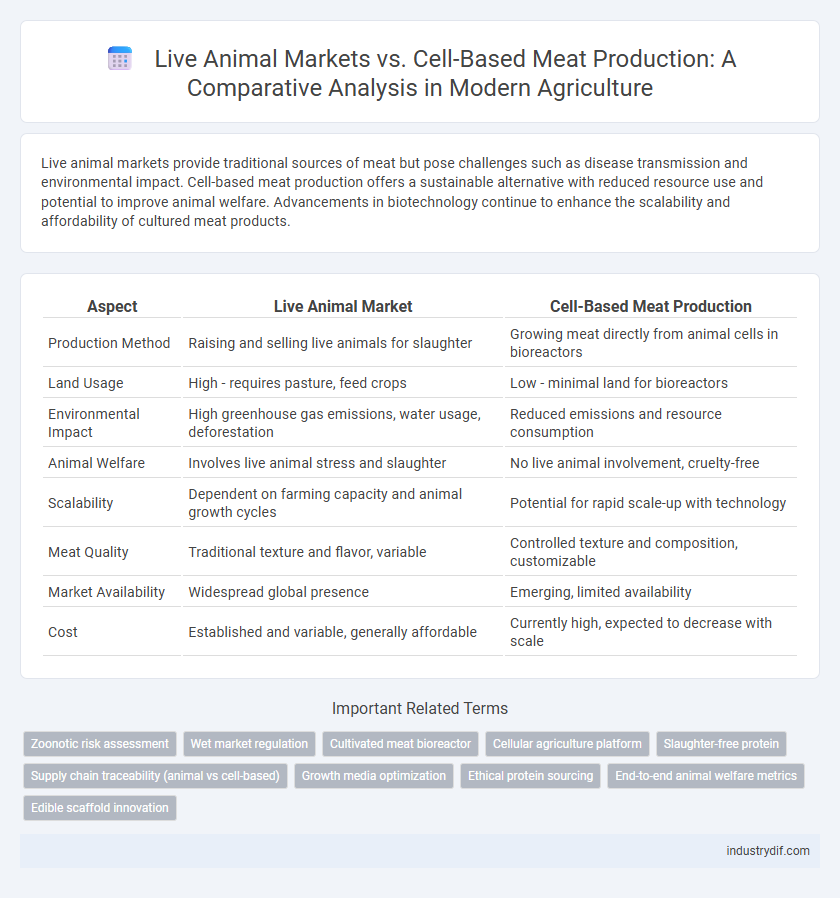
Live animal markets provide traditional sources of meat but pose challenges such as disease transmission and environmental impact. Cell-based meat production offers a sustainable alternative with reduced resource use and potential to improve animal welfare. Advancements in biotechnology continue to enhance the scalability and affordability of cultured meat products.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Live Animal Market | Cell-Based Meat Production |
|---|---|---|
| Production Method | Raising and selling live animals for slaughter | Growing meat directly from animal cells in bioreactors |
| Land Usage | High - requires pasture, feed crops | Low - minimal land for bioreactors |
| Environmental Impact | High greenhouse gas emissions, water usage, deforestation | Reduced emissions and resource consumption |
| Animal Welfare | Involves live animal stress and slaughter | No live animal involvement, cruelty-free |
| Scalability | Dependent on farming capacity and animal growth cycles | Potential for rapid scale-up with technology |
| Meat Quality | Traditional texture and flavor, variable | Controlled texture and composition, customizable |
| Market Availability | Widespread global presence | Emerging, limited availability |
| Cost | Established and variable, generally affordable | Currently high, expected to decrease with scale |
Overview of Live Animal Markets and Cell-Based Meat
Live animal markets serve as traditional hubs for trading livestock, providing fresh meat directly sourced from farmers but face challenges related to animal welfare, disease transmission, and environmental impact. Cell-based meat production, an innovative biotechnology, cultivates meat from animal cells in controlled environments, offering a sustainable and ethical alternative with reduced greenhouse gas emissions and land use. This emerging industry aims to transform food systems by combining scientific advancement with consumer demand for sustainable protein sources.
Historical Development in Meat Production
Traditional live animal markets have shaped meat production for millennia, relying heavily on livestock farming techniques developed during the Neolithic Revolution around 10,000 years ago. In contrast, cell-based meat production emerged in the early 21st century, leveraging advancements in tissue engineering and biotechnology to cultivate animal cells without raising or slaughtering animals. This innovative approach promises to transform the meat industry by reducing environmental impact and addressing ethical concerns associated with conventional livestock farming.
Supply Chain Dynamics: Traditional vs. Cell-Based
The live animal market relies on extensive supply chains involving multiple intermediaries such as breeders, transporters, and slaughterhouses, leading to longer lead times and higher vulnerability to disruptions. Cell-based meat production streamlines supply chains by centralizing production in controlled bioreactors, reducing the need for animal transport and minimizing logistical complexity. This shift enables faster scaling, improved traceability, and lower environmental impact within agricultural supply networks.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Live animal markets generate significant greenhouse gas emissions, including methane and nitrous oxide, contributing to climate change and environmental degradation. Cell-based meat production offers a lower carbon footprint by reducing land use, water consumption, and methane emissions through lab-grown processes. Transitioning to cell-based meat could alleviate biodiversity loss and deforestation linked to conventional livestock farming practices.
Animal Welfare Considerations
Live animal markets pose significant animal welfare challenges, including stress during transportation and overcrowded conditions that increase the risk of injury and disease. Cell-based meat production eliminates the need for raising and slaughtering animals, thereby reducing suffering and improving overall ethical standards. This technology offers a promising alternative by addressing animal welfare concerns while meeting growing demand for sustainable protein sources.
Food Safety and Public Health Risks
Live animal markets pose significant food safety challenges due to the risk of zoonotic disease transmission and contamination from handling and slaughter practices, increasing public health risks. Cell-based meat production offers a controlled, sterile environment that minimizes contamination and pathogen exposure, thereby reducing the likelihood of foodborne illnesses. Regulatory frameworks for cultured meat emphasize stringent safety standards, further enhancing its potential to mitigate public health threats compared to traditional live animal markets.
Regulatory and Compliance Challenges
Live animal markets face complex regulatory challenges involving animal welfare, disease control, and trade standards set by agencies like the USDA and OIE. Cell-based meat production encounters emerging compliance issues relating to food safety, labeling, and novel ingredient approvals under frameworks such as the FDA's regulatory oversight of biotechnology products. Navigating these distinct regulatory landscapes requires aligning with evolving policies to ensure public health, environmental standards, and market acceptance.
Consumer Acceptance and Market Trends
Live animal markets continue to dominate consumer preferences in many regions due to cultural traditions and perceived naturalness, but cell-based meat production is rapidly gaining traction as innovative sensory qualities and sustainability benefits attract early adopters. Market trends indicate increasing investment in cell-based technologies, driven by growing consumer demand for ethical, environmentally friendly, and health-conscious protein alternatives. Consumer acceptance of cell-based meat is positively correlated with transparency, price parity, and regulatory approvals, signaling a transformative shift in global meat consumption patterns.
Economic Viability and Scalability
Live animal markets have historically dominated agricultural economies due to established supply chains and consumer familiarity, but they face challenges with scalability and environmental costs. Cell-based meat production offers promising economic viability through potential reductions in land use, water consumption, and greenhouse gas emissions, while scaling up remains dependent on technological advancements and cost reductions in bioreactor infrastructure. Market adoption and regulatory frameworks will significantly influence the comparative economic scalability of cell-based meat versus traditional live animal sources.
Future Outlook of Meat Production Technologies
Live animal markets remain integral to traditional meat supply but face challenges from emerging cell-based meat production technologies, which promise sustainable and ethical alternatives. Advances in cellular agriculture aim to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, land use, and water consumption associated with conventional livestock farming. Market projections indicate rapid growth of cultured meat sectors, driven by technological innovation and shifting consumer preferences toward plant-based and lab-grown proteins.
Related Important Terms
Zoonotic risk assessment
Live animal markets present a significantly higher zoonotic risk due to close human-animal interactions, enabling the transmission of pathogens like avian influenza and coronaviruses. In contrast, cell-based meat production reduces zoonotic risks by eliminating direct contact with live animals, thus limiting opportunities for cross-species disease spillover.
Wet market regulation
Wet market regulation in live animal markets remains critical to control zoonotic disease transmission and ensure food safety standards, particularly in regions heavily reliant on traditional markets for fresh produce. In contrast, cell-based meat production offers a controlled, biosecure environment that minimizes health risks and environmental impact, presenting a scalable alternative that challenges the regulatory frameworks governing wet markets.
Cultivated meat bioreactor
Cultivated meat bioreactors enable scalable, controlled production of cell-based meat, reducing reliance on traditional live animal markets that involve ethical and environmental concerns. These bioreactors optimize growth conditions for animal cells, increasing yield efficiency while minimizing land use and greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional livestock farming.
Cellular agriculture platform
The cellular agriculture platform enables sustainable cell-based meat production by cultivating animal cells in controlled environments, reducing reliance on traditional live animal markets and minimizing environmental impacts such as greenhouse gas emissions and land use. This innovative technology offers scalable meat alternatives with consistent quality, enhancing food security and animal welfare compared to conventional livestock farming.
Slaughter-free protein
Live animal markets remain a primary source for fresh meat but face challenges such as animal welfare concerns and zoonotic disease risks. Cell-based meat production offers a sustainable, slaughter-free protein alternative by cultivating muscle cells in bioreactors, significantly reducing environmental impact and ethical issues associated with traditional livestock farming.
Supply chain traceability (animal vs cell-based)
Live animal markets rely heavily on physical supply chain traceability through animal tagging, transport logs, and slaughterhouse records, which often face challenges in transparency and disease tracking. In contrast, cell-based meat production offers enhanced traceability via digital monitoring of cell cultures and bioreactor conditions, enabling precise tracking from growth to packaging and reducing risks associated with animal health and contamination.
Growth media optimization
Growth media optimization in cell-based meat production significantly reduces dependency on traditional livestock, offering scalable nutrient formulations that enhance cell proliferation and differentiation efficiency. This innovation addresses cost and sustainability challenges in live animal markets by providing a controlled environment to produce high-quality meat with minimal resource input.
Ethical protein sourcing
Live animal markets often raise concerns about animal welfare, disease transmission, and environmental impact, whereas cell-based meat production offers a sustainable and ethical alternative by eliminating the need for animal slaughter and reducing resource consumption. This shift supports ethical protein sourcing by promoting animal rights and minimizing the carbon footprint associated with traditional livestock farming.
End-to-end animal welfare metrics
Live animal markets present challenges in monitoring end-to-end animal welfare due to variable handling practices and transportation stress, increasing the risk of injury and disease transmission. Cell-based meat production offers a controlled environment that eliminates transport and slaughter-related stress, enabling precise measurement and optimization of animal welfare metrics throughout the production cycle.
Edible scaffold innovation
Edible scaffold innovation enhances cell-based meat production by providing a structured matrix that supports cell growth and tissue formation, offering a sustainable alternative to live animal markets. This technology reduces reliance on traditional livestock farming, decreases environmental impact, and promotes ethical food production in agriculture.
Live animal market vs Cell-based meat production Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com