Organic farming emphasizes the use of natural inputs and sustainable practices to enhance soil health and reduce environmental impact, avoiding synthetic chemicals and genetically modified organisms. Biodynamic farming incorporates organic methods but adds spiritual and astrological principles, treating the farm as a self-sustaining ecosystem with preparations like compost sprays and lunar planting cycles. Both approaches prioritize ecological balance, but biodynamic farming uniquely integrates holistic and cosmic influences to enhance farm vitality.
Table of Comparison
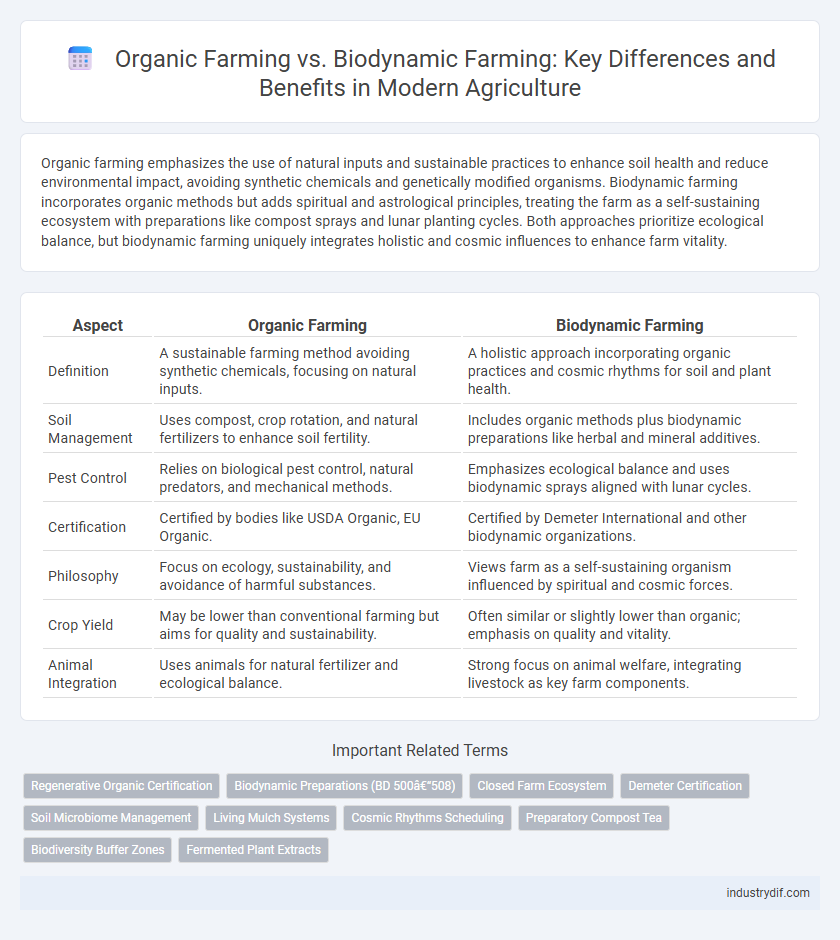
| Aspect | Organic Farming | Biodynamic Farming |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A sustainable farming method avoiding synthetic chemicals, focusing on natural inputs. | A holistic approach incorporating organic practices and cosmic rhythms for soil and plant health. |
| Soil Management | Uses compost, crop rotation, and natural fertilizers to enhance soil fertility. | Includes organic methods plus biodynamic preparations like herbal and mineral additives. |
| Pest Control | Relies on biological pest control, natural predators, and mechanical methods. | Emphasizes ecological balance and uses biodynamic sprays aligned with lunar cycles. |
| Certification | Certified by bodies like USDA Organic, EU Organic. | Certified by Demeter International and other biodynamic organizations. |
| Philosophy | Focus on ecology, sustainability, and avoidance of harmful substances. | Views farm as a self-sustaining organism influenced by spiritual and cosmic forces. |
| Crop Yield | May be lower than conventional farming but aims for quality and sustainability. | Often similar or slightly lower than organic; emphasis on quality and vitality. |
| Animal Integration | Uses animals for natural fertilizer and ecological balance. | Strong focus on animal welfare, integrating livestock as key farm components. |
Introduction to Organic and Biodynamic Farming
Organic farming emphasizes natural inputs, avoiding synthetic chemicals to promote soil health and biodiversity. Biodynamic farming integrates organic practices with spiritual and cosmic principles, treating the farm as a self-sustaining ecosystem. Both methods enhance ecological balance but differ in their philosophical foundations and specific agricultural techniques.
Historical Development of Each Farming Method
Organic farming emerged in the early 20th century as a response to the environmental damage caused by synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, emphasizing natural inputs and soil health. Biodynamic farming, developed by Rudolf Steiner in 1924, integrates spiritual and cosmic principles with organic practices, creating a holistic agricultural system. Both methods evolved through scientific research and farmer-led innovation, shaping sustainable agriculture worldwide.
Core Principles and Philosophies
Organic farming prioritizes natural inputs, soil health, and ecological balance by avoiding synthetic chemicals and GMOs, ensuring sustainable crop production. Biodynamic farming incorporates these organic principles while emphasizing spiritual and cosmic forces, using preparations like manure composts and planting according to lunar cycles to enhance soil vitality. Both systems aim for environmental sustainability, but biodynamic farming uniquely integrates holistic and metaphysical elements to foster farm ecosystem harmony.
Certification Standards Compared
Organic farming certification standards are regulated by organizations like USDA Organic and EU Organic, emphasizing the exclusion of synthetic pesticides, fertilizers, and GMOs, with specific requirements for soil health and crop rotation. Biodynamic farming certification follows more comprehensive standards set by Demeter International, which incorporate organic requirements plus additional practices such as the use of biodynamic preparations, lunar planting calendars, and holistic ecosystem management. Both certifications require rigorous auditing and traceability, but biodynamic standards demand a deeper integration of spiritual and ecological principles beyond conventional organic guidelines.
Soil Health and Fertility Management
Organic farming emphasizes enhancing soil health through natural inputs like compost and green manure, promoting microbial diversity and preventing chemical contamination. Biodynamic farming integrates organic practices with spiritual principles, using specific preparations such as horn manure to stimulate soil vitality and balance. Both approaches prioritize fertility management by fostering nutrient cycling and improving soil structure, but biodynamics incorporates cosmic rhythms to influence planting and soil treatment schedules.
Pest and Disease Control Approaches
Organic farming utilizes natural predators, crop rotation, and biopesticides to manage pests and diseases while avoiding synthetic chemicals. Biodynamic farming incorporates similar pest control methods along with unique preparations like herbal composts and field sprays designed to enhance soil and plant vitality. Both approaches emphasize ecological balance and soil health to sustainably reduce pest and disease incidence.
Biodiversity and Ecosystem Impact
Biodynamic farming enhances biodiversity by integrating holistic ecosystem management practices, such as using compost preparations and planting according to lunar cycles, which stimulate soil microbial activity and support diverse plant and animal species. Organic farming prioritizes the elimination of synthetic chemicals, fostering healthier soils and reducing pollution, but may not systematically incorporate cosmic rhythms or specific herbal preparations characteristic of biodynamics. Both methods improve ecosystem health compared to conventional agriculture, yet biodynamic practices aim for greater ecological synergy and resilience through their unique biodiverse approaches.
Inputs and Allowed Substances
Organic farming strictly prohibits synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, and genetically modified organisms, relying instead on natural inputs like compost, manure, and biological pest control. Biodynamic farming incorporates all organic standards but additionally uses specific preparations such as fermented herbal and mineral concoctions, like horn manure and silica, to enhance soil vitality and plant health. Both methods prioritize ecological balance, yet biodynamic farming integrates spiritual and cosmic principles influencing input selection and timing.
Market Trends and Consumer Perceptions
Organic farming continues to dominate market growth due to increasing consumer demand for pesticide-free and non-GMO products, with global sales surpassing $120 billion in 2023. Biodynamic farming, though niche, attracts premium prices by emphasizing soil health and holistic ecosystem practices, appealing to environmentally conscious and wellness-focused consumers. Market trends indicate a rising preference for transparency and certification, driving producers to adopt both organic and biodynamic methods to meet consumer expectations.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Organic farming faces challenges such as maintaining soil fertility without synthetic inputs and controlling pests through natural methods, which can limit crop yields and scalability. Biodynamic farming adds complexity by integrating spiritual and cosmic principles, requiring specialized knowledge and increased labor, leading to slower adoption rates. Future outlooks for both emphasize sustainable practices with advancements in technology and education potentially overcoming current limitations to enhance productivity and environmental benefits.
Related Important Terms
Regenerative Organic Certification
Regenerative Organic Certification integrates principles from both organic farming and biodynamic farming, emphasizing soil health, biodiversity, and animal welfare to enhance global ecosystem regeneration. This certification requires adherence to strict standards including carbon sequestration, fair labor practices, and holistic farming methods that surpass conventional organic requirements for sustainable agriculture.
Biodynamic Preparations (BD 500–508)
Biodynamic preparations (BD 500-508) are specialized herbal, mineral, and animal-based substances used in biodynamic farming to enhance soil fertility, stimulate plant growth, and balance ecosystems by promoting microbial diversity and nutrient cycling. Unlike organic farming, which primarily avoids synthetic chemicals and emphasizes natural inputs, biodynamic preparations follow precise composting methods and application timing based on lunar and cosmic rhythms to optimize crop vitality and farm sustainability.
Closed Farm Ecosystem
Organic farming emphasizes the use of natural inputs and sustainable practices to enhance soil fertility and biodiversity without synthetic chemicals, fostering a semi-closed ecosystem that relies on crop rotation and composting. Biodynamic farming extends this approach by integrating holistic practices, including cosmic rhythms and specific preparations, aiming for a fully closed farm ecosystem that self-regulates and sustains its nutrient cycles independently.
Demeter Certification
Demeter certification represents the highest standard in biodynamic farming, emphasizing ecological harmony and sustainable soil health through holistic practices beyond organic farming's requirements. While organic farming restricts synthetic inputs, Demeter-certified farms integrate biodynamic preparations and cosmic rhythms to enhance biodiversity and ecosystem vitality.
Soil Microbiome Management
Organic farming enhances soil microbiome diversity by avoiding synthetic chemicals and promoting natural composting processes, which supports nutrient cycling and plant health. Biodynamic farming integrates organic principles with holistic preparations and lunar planting calendars, aiming to balance microbial communities for improved soil vitality and ecosystem resilience.
Living Mulch Systems
Living mulch systems in organic farming enhance soil fertility and moisture retention by incorporating cover crops that suppress weeds and improve biodiversity, while biodynamic farming integrates these systems with holistic practices such as compost preparations and lunar planting calendars to strengthen soil life and ecosystem balance. Both approaches promote sustainable agriculture, but biodynamic farming emphasizes spiritual and cosmic factors influencing plant growth beyond conventional organic methods.
Cosmic Rhythms Scheduling
Organic farming emphasizes natural inputs and soil health without synthetic chemicals, while biodynamic farming integrates cosmic rhythms such as lunar and planetary cycles to schedule planting and harvesting, enhancing soil vitality and crop resilience. Biodynamic calendars guide farmers to align agricultural activities with celestial influences, aiming to optimize nutrient uptake and improve overall farm ecosystem balance.
Preparatory Compost Tea
Preparatory Compost Tea in organic farming enhances soil microbial activity using aerated water infused with compost extracts, promoting nutrient availability and plant health. Biodynamic farming's approach incorporates specialized herbal preparations into compost tea, aligning with lunar cycles to stimulate soil vitality and holistic ecosystem balance.
Biodiversity Buffer Zones
Biodynamic farming integrates biodiversity buffer zones as essential elements to enhance ecosystem resilience and promote beneficial insect habitats, improving soil fertility and crop health without synthetic inputs. In contrast, organic farming employs buffer zones primarily to prevent contamination from pesticides and fertilizers, emphasizing chemical-free production but with less focus on ecological interconnections found in biodynamic practices.
Fermented Plant Extracts
Fermented plant extracts in organic farming enhance soil nutrient availability and microbial activity through natural decomposition processes, supporting sustainable crop growth without synthetic inputs. Biodynamic farming utilizes these extracts within a holistic system, incorporating specific herbal preparations and lunar cycle timing to optimize soil vitality and plant resilience.
Organic Farming vs Biodynamic Farming Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com