Supply chain traceability in agriculture relies on traditional record-keeping and manual tracking methods, which can result in inefficiencies and limited transparency. Blockchain traceability enhances supply chain management by providing a decentralized, immutable ledger that ensures data accuracy, real-time tracking, and improved trust among stakeholders. This technology enables farmers, distributors, and retailers to verify product origins, reduce fraud, and optimize overall supply chain efficiency.
Table of Comparison
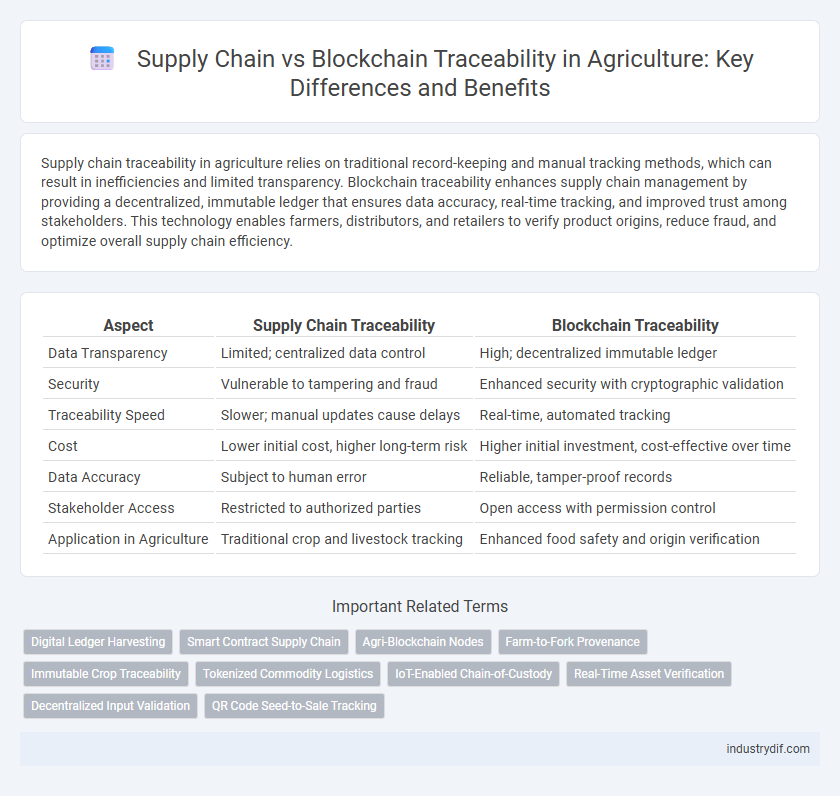
| Aspect | Supply Chain Traceability | Blockchain Traceability |
|---|---|---|
| Data Transparency | Limited; centralized data control | High; decentralized immutable ledger |
| Security | Vulnerable to tampering and fraud | Enhanced security with cryptographic validation |
| Traceability Speed | Slower; manual updates cause delays | Real-time, automated tracking |
| Cost | Lower initial cost, higher long-term risk | Higher initial investment, cost-effective over time |
| Data Accuracy | Subject to human error | Reliable, tamper-proof records |
| Stakeholder Access | Restricted to authorized parties | Open access with permission control |
| Application in Agriculture | Traditional crop and livestock tracking | Enhanced food safety and origin verification |
Understanding Traditional Agricultural Supply Chain
Traditional agricultural supply chains involve multiple intermediaries, including farmers, processors, distributors, and retailers, leading to complex logistics and potential delays. Lack of transparency in these chains often results in difficulty tracing product origin, quality, and safety, increasing risks of fraud and contamination. Efficient management relies on manual documentation and centralized databases, which are prone to errors and limited real-time visibility.
Challenges in Conventional Supply Chain Traceability
Conventional supply chain traceability in agriculture faces challenges such as data fragmentation, limited transparency, and susceptibility to fraud, which hinder accurate tracking of products from farm to consumer. Inconsistent record-keeping and manual processes create delays and errors in verifying product origins and quality, impacting food safety and trust. These issues often lead to inefficiencies, increased costs, and difficulties in meeting regulatory compliance and consumer demand for traceable agricultural products.
Introduction to Blockchain Technology in Agriculture
Blockchain technology introduces a decentralized and immutable ledger for agriculture supply chains, enhancing transparency and trust among producers, distributors, and consumers. By enabling real-time tracking of crops, livestock, and inputs, blockchain ensures accurate provenance and reduces fraud in agricultural products. This innovation improves efficiency in supply chain management, minimizes losses, and supports sustainable farming practices through verified data sharing.
Blockchain vs Traditional Supply Chain: Key Differences
Blockchain traceability in agriculture offers immutable and transparent record-keeping, enhancing trust compared to traditional supply chains that often rely on centralized databases prone to data tampering. Unlike conventional methods that may have delayed updates and lack end-to-end visibility, blockchain provides real-time, decentralized tracking of agricultural products from farm to fork. This technology significantly reduces fraud, improves food safety compliance, and enables efficient recall processes by ensuring every transaction is securely recorded and easily auditable.
Enhancing Transparency with Blockchain Traceability
Blockchain traceability revolutionizes agricultural supply chains by providing an immutable ledger that captures every transaction from farm to table, significantly enhancing transparency. Unlike traditional supply chains, blockchain enables farmers, distributors, and retailers to verify product origins, quality, and handling conditions in real time. This increased transparency strengthens consumer trust and reduces fraud while optimizing inventory management and compliance with food safety regulations.
Data Integrity and Security in Blockchain Solutions
Blockchain traceability enhances supply chain management in agriculture by ensuring data integrity through immutable ledgers that prevent tampering or unauthorized modifications. The decentralized nature of blockchain solutions secures sensitive agricultural data against cyber threats, enabling transparent and reliable tracking of produce from farm to consumer. In contrast, traditional supply chain systems often face challenges with data breaches and inaccuracies due to centralized databases and limited verification mechanisms.
Impact on Food Safety and Quality Assurance
Supply chain management in agriculture relies on traditional tracking methods that often lack real-time visibility and traceability, leading to delays in identifying contamination sources and quality issues. Blockchain traceability enhances food safety by providing immutable, transparent records of every transaction and movement within the supply chain, enabling rapid identification and recall of affected products. This technology improves quality assurance through verified data on origin, handling, and processing, fostering consumer trust and regulatory compliance.
Real-Time Visibility and Efficiency Improvements
Supply chain management in agriculture benefits significantly from blockchain traceability, enabling real-time visibility of product movement from farm to consumer. Blockchain technology ensures data integrity and transparency, reducing delays and inefficiencies caused by traditional tracking methods. Enhanced traceability improves inventory management, minimizes food waste, and strengthens trust among stakeholders throughout the agricultural supply chain.
Case Studies: Blockchain Applications in Agriculture
Case studies highlight blockchain applications in agriculture by demonstrating enhanced supply chain traceability through immutable record-keeping and real-time data sharing. Companies like AgriDigital and IBM Food Trust have successfully implemented blockchain to reduce fraud, improve product provenance, and increase transparency from farm to consumer. These implementations optimize logistics, ensure compliance with food safety standards, and foster trust among stakeholders.
Future Trends in Traceability for Agricultural Supply Chains
Future trends in traceability for agricultural supply chains emphasize blockchain technology to enhance transparency, security, and data integrity across all stages from farm to consumer. Blockchain enables immutable record-keeping of crop origins, processing, and transportation, facilitating real-time tracking and reducing fraud or contamination risks. Integration with IoT sensors and AI analytics further optimizes supply chain efficiency and sustainability by providing granular insights into crop conditions, resource use, and compliance with safety standards.
Related Important Terms
Digital Ledger Harvesting
Digital ledger harvesting enhances supply chain transparency by securely recording each step from farm to distribution, enabling precise traceability in agriculture. Blockchain technology ensures immutable, real-time data capture, reducing fraud and improving efficiency in tracking crop origin and quality.
Smart Contract Supply Chain
Smart contract supply chains leverage blockchain technology to automate and secure transactions, reducing delays and fraud in agricultural product tracking from farm to market. This approach enhances transparency, ensures real-time data integrity, and streamlines compliance with regulatory standards across the agriculture supply chain.
Agri-Blockchain Nodes
Agri-blockchain nodes enhance supply chain traceability by providing decentralized verification and immutable record-keeping for agricultural products, improving transparency from farm to consumer. These nodes enable real-time tracking, reduce fraud, and optimize inventory management by securely linking every transaction within the agricultural supply chain.
Farm-to-Fork Provenance
Supply chain management in agriculture involves traditional tracking methods that often lack transparency and real-time data accessibility, whereas blockchain traceability ensures immutable, transparent records from farm-to-fork provenance, enhancing food safety and consumer trust. Implementing blockchain technology in agricultural supply chains enables verifiable tracking of products' origins, production conditions, and logistics, reducing fraud and improving accountability at every stage.
Immutable Crop Traceability
Blockchain technology ensures immutable crop traceability by securely recording every transaction and movement within the agricultural supply chain, eliminating data tampering risks common in traditional systems. This decentralized ledger enhances transparency and trust among farmers, distributors, and consumers by providing verifiable, tamper-proof records from farm to fork.
Tokenized Commodity Logistics
Tokenized commodity logistics in agriculture enhances supply chain traceability by embedding immutable digital tokens that represent physical goods, enabling real-time tracking of provenance, ownership, and transaction history. Blockchain-based systems reduce fraud and inefficiencies by ensuring transparent, verifiable records across multiple stakeholders from farm to market.
IoT-Enabled Chain-of-Custody
IoT-enabled chain-of-custody enhances agricultural supply chain traceability by providing real-time data capture and verification at each stage, ensuring product authenticity and reducing fraud. Blockchain technology complements this by offering a decentralized, tamper-proof ledger that securely records IoT-generated data, improving transparency and accountability in farm-to-fork processes.
Real-Time Asset Verification
Supply chain traceability in agriculture relies on manual record-keeping, often causing delays and errors in asset verification, whereas blockchain traceability provides real-time, immutable data for every transaction and movement of agricultural products. This ensures instant verification of assets, enhances transparency, reduces fraud, and accelerates response times across the entire agricultural supply chain.
Decentralized Input Validation
Decentralized input validation within blockchain traceability enhances agricultural supply chains by ensuring data authenticity at each transaction point, eliminating centralized errors and reducing fraud risks. This process improves transparency and trust among stakeholders by securely validating inputs like crop origins, pesticide usage, and shipment details in real-time.
QR Code Seed-to-Sale Tracking
QR code seed-to-sale tracking enhances agricultural supply chain transparency by enabling real-time data capture and verification at every stage, from planting to distribution. Integrating blockchain with QR technology ensures immutable records and reduces fraud, improving traceability and consumer trust in food safety.
Supply Chain vs Blockchain Traceability Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com