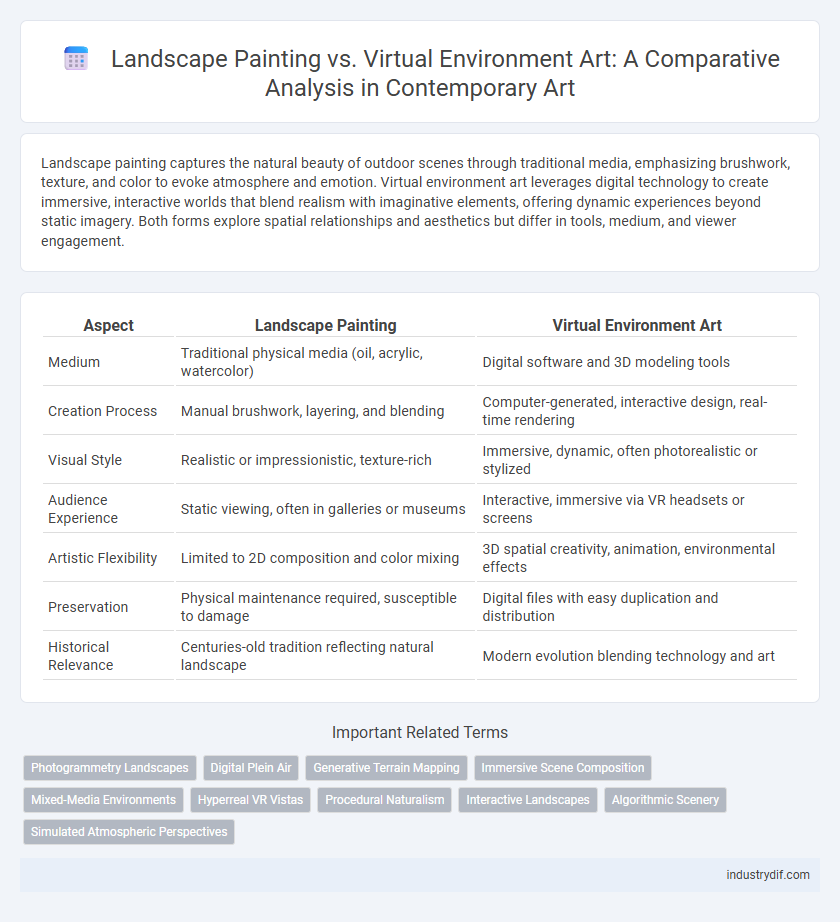
Landscape painting captures the natural beauty of outdoor scenes through traditional media, emphasizing brushwork, texture, and color to evoke atmosphere and emotion. Virtual environment art leverages digital technology to create immersive, interactive worlds that blend realism with imaginative elements, offering dynamic experiences beyond static imagery. Both forms explore spatial relationships and aesthetics but differ in tools, medium, and viewer engagement.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Landscape Painting | Virtual Environment Art |
|---|---|---|
| Medium | Traditional physical media (oil, acrylic, watercolor) | Digital software and 3D modeling tools |
| Creation Process | Manual brushwork, layering, and blending | Computer-generated, interactive design, real-time rendering |
| Visual Style | Realistic or impressionistic, texture-rich | Immersive, dynamic, often photorealistic or stylized |
| Audience Experience | Static viewing, often in galleries or museums | Interactive, immersive via VR headsets or screens |
| Artistic Flexibility | Limited to 2D composition and color mixing | 3D spatial creativity, animation, environmental effects |
| Preservation | Physical maintenance required, susceptible to damage | Digital files with easy duplication and distribution |
| Historical Relevance | Centuries-old tradition reflecting natural landscape | Modern evolution blending technology and art |
Defining Landscape Painting: Tradition and Technique
Landscape painting, rooted in centuries-old traditions, captures natural scenes using techniques such as perspective, light manipulation, and brushwork to evoke atmosphere and emotion. Artists employ mediums like oil, watercolor, and acrylics to depict mountains, forests, rivers, and rural vistas with attention to detail and composition. This classical art form emphasizes realism and the artist's interpretation of the natural world, distinct from the digital techniques and interactive aspects found in virtual environment art.
Evolution of Virtual Environment Art
Landscape painting, rooted in centuries of tradition, captures natural scenery through physical mediums, emphasizing composition and light. Virtual Environment Art has evolved rapidly with digital technology, enabling immersive, interactive spaces that transcend physical limitations. Advancements in VR, 3D modeling, and real-time rendering have transformed artistic expression, creating dynamic environments that engage viewers in multisensory experiences.
Key Differences in Creative Process
Landscape painting involves traditional techniques such as brushwork and color mixing on physical canvases, emphasizing natural light and texture to capture real-world scenes. Virtual environment art uses digital tools and 3D modeling software to construct immersive, interactive spaces, allowing for dynamic manipulation of perspective and atmosphere. The creative process in landscape painting is tactile and observational, while virtual environment art demands technical skills in programming, rendering, and spatial design.
Materials and Tools: Canvas vs Code
Landscape painting relies on traditional materials such as canvas, oil paints, brushes, and palette knives to create textured, tactile visuals that capture natural scenes. Virtual environment art employs digital tools, including software platforms, coding languages, and 3D modeling programs, enabling dynamic, interactive, and immersive experiences. The contrast between physical mediums and digital code shapes the artistic process, influencing both the final aesthetic and viewer engagement.
Approaches to Composition and Perspective
Landscape painting employs traditional techniques like linear perspective, atmospheric depth, and compositional rules such as the rule of thirds to create balanced, realistic scenes that evoke natural spaces. Virtual environment art leverages digital tools and 3D modeling software to manipulate perspective dynamically, allowing immersive, interactive compositions that can shift in real-time based on viewer interaction. Both art forms explore spatial relationships but differ fundamentally; landscape painting emphasizes fixed viewpoints and tactile brushwork, whereas virtual environments prioritize fluidity and user-driven exploration of space.
Realism and Abstraction Across Mediums
Landscape painting traditionally emphasizes realism through detailed depictions of natural scenes, capturing light, texture, and atmospheric effects on canvas with techniques like oil or watercolor. Virtual environment art, by contrast, leverages digital tools to blend realism and abstraction, enabling immersive, interactive spaces that transcend physical limitations and explore conceptual landscapes. Both mediums challenge perceptions of reality, with landscape paintings grounding viewers in tangible nature, while virtual environments offer fluid, malleable interpretations of spatial experience.
Impact of Technology on Artistic Expression
Landscape painting has traditionally captured the natural world through meticulous brushwork and composition, emphasizing light, color, and atmosphere. Virtual environment art leverages advanced technologies like 3D modeling, augmented reality, and interactive platforms to create immersive, dynamic spaces that transcend physical limitations. Technological innovation expands artistic expression by enabling artists to manipulate time, scale, and perspective in ways impossible in traditional landscapes.
Audience Experience: Gallery vs Interactive Worlds
Landscape painting offers viewers a contemplative experience through tactile textures and nuanced brushwork, typically encountered in gallery settings where time and space encourage reflection. Virtual environment art immerses audiences in interactive worlds, enabling dynamic exploration and personalized engagement that transcends traditional visual boundaries. The contrast highlights how physical presence in galleries fosters shared cultural appreciation, while digital realms prioritize individual agency and sensory immersion.
Conservation and Longevity of Artworks
Landscape painting, created with traditional mediums such as oil and acrylic, offers enduring physical presence that benefits from established conservation techniques like varnishing and controlled environmental conditions. Virtual environment art relies on digital technologies, requiring ongoing software updates and data migration to preserve its integrity and accessibility over time. The longevity of traditional landscape paintings is significantly influenced by material aging and environmental exposure, whereas virtual art faces challenges related to technological obsolescence and digital storage stability.
Future Trends in Landscape and Digital Art
Future trends in landscape painting emphasize the integration of augmented reality and AI-driven techniques to create immersive, interactive experiences that blend traditional brushwork with digital enhancements. Virtual environment art is rapidly evolving, leveraging real-time rendering and photogrammetry to construct hyper-realistic, explorable worlds that redefine audience engagement in digital spaces. The convergence of these mediums points toward a hybrid artistic form where physical landscapes inspire virtual representations, promoting cross-disciplinary innovation in art and technology.
Related Important Terms
Photogrammetry Landscapes
Photogrammetry landscapes in virtual environment art capture hyper-realistic details by digitally reconstructing physical terrains through photographic data, surpassing traditional landscape painting's reliance on artistic interpretation and manual brushwork. This technology enhances immersive experiences in digital art by replicating real-world textures and spatial depth, offering unprecedented accuracy and engagement compared to static painted landscapes.
Digital Plein Air
Digital plein air merges traditional landscape painting techniques with virtual environment art, enabling artists to capture natural scenes through immersive digital tools. This innovative approach expands creative possibilities by blending real-time digital brushwork with the dynamic interactivity of virtual landscapes.
Generative Terrain Mapping
Landscape painting captures natural scenery through traditional brushstrokes, emphasizing texture and color variations, while virtual environment art utilizes generative terrain mapping algorithms to create dynamic, realistic 3D landscapes with procedural detail. Generative terrain mapping leverages noise functions and heightmaps to simulate natural topography, enabling artists to manipulate virtual environments with precision and scalability beyond the constraints of physical canvases.
Immersive Scene Composition
Landscape painting masterfully captures natural environments through traditional brushwork, emphasizing texture, light, and atmospheric perspective to evoke emotional resonance. Virtual environment art creates immersive scene composition by integrating 3D modeling, dynamic lighting, and interactive elements, allowing viewers to explore and engage with digitally constructed worlds in real time.
Mixed-Media Environments
Landscape painting captures natural scenes using traditional media like oil or watercolor, emphasizing texture and light to evoke emotion. Mixed-media environments in virtual environment art blend digital techniques with physical elements, creating immersive experiences that transcend static imagery and engage multiple senses.
Hyperreal VR Vistas
Hyperreal VR vistas redefine landscape painting by immersing viewers in meticulously crafted virtual environments that simulate natural and fantastical landscapes with unprecedented detail and interactivity. These digital masterpieces harness advanced 3D modeling and real-time rendering techniques to evoke emotional responses and spatial awareness beyond traditional two-dimensional canvases.
Procedural Naturalism
Landscape painting emphasizes the portrayal of natural scenery through traditional techniques that capture atmospheric conditions and organic textures, while virtual environment art leverages procedural naturalism to generate dynamic, algorithmically-driven ecosystems and terrains in real-time. Procedural naturalism in virtual art allows for infinite variation and interaction, enabling immersive experiences that adapt and evolve, contrasting with the static but meticulously crafted compositions of landscape paintings.
Interactive Landscapes
Interactive landscapes in virtual environment art merge traditional landscape painting's aesthetic principles with immersive digital technology, allowing users to engage dynamically with evolving scenes. This fusion enhances spatial perception and emotional connection by enabling real-time manipulation of natural elements and atmospheric effects within a digitally constructed terrain.
Algorithmic Scenery
Algorithmic scenery in landscape painting uses procedural techniques to simulate natural elements, creating dynamic compositions rooted in traditional aesthetics. Virtual environment art leverages advanced algorithms and real-time rendering to build immersive, interactive landscapes that evolve based on user input and environmental factors.
Simulated Atmospheric Perspectives
Landscape painting utilizes traditional techniques like aerial perspective to create depth by simulating atmospheric haze, softening colors, and blurring details with distance. Virtual environment art advances this by dynamically adjusting atmospheric effects such as volumetric fog, light scattering, and real-time weather conditions to enhance immersive spatial perception.
Landscape Painting vs Virtual Environment Art Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com