Modern Art emphasizes human creativity and emotional expression through traditional mediums, capturing unique perspectives and cultural moments. Generative Art leverages algorithms and artificial intelligence to autonomously create dynamic, evolving visuals that challenge conventional definitions of authorship. The convergence of these art forms highlights the evolving relationship between technology and artistic innovation.
Table of Comparison
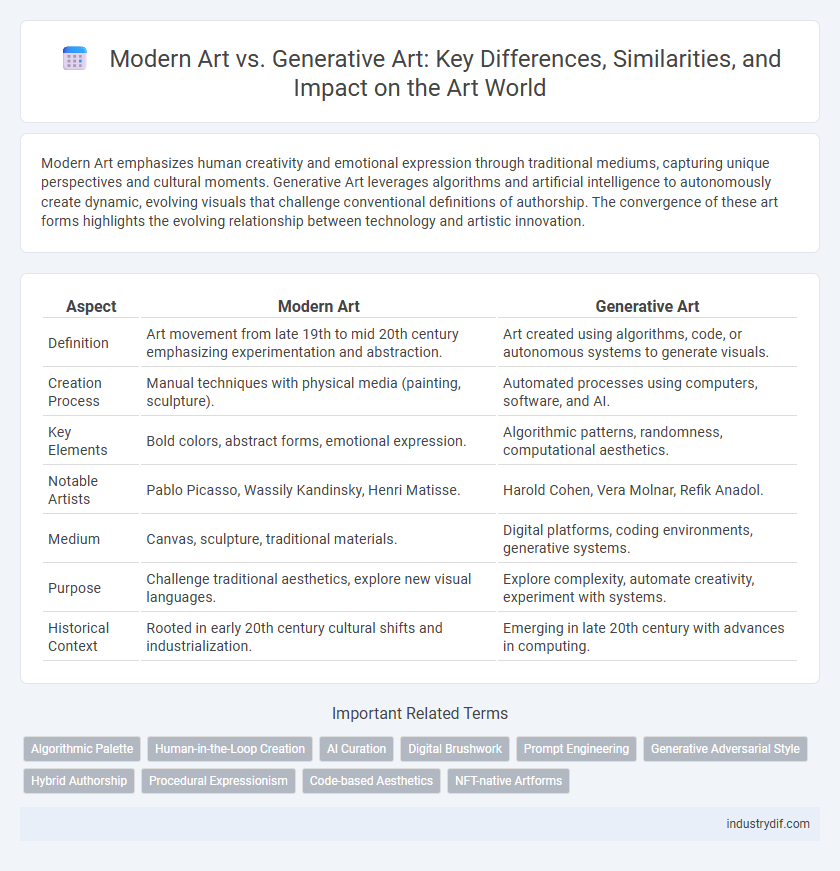
| Aspect | Modern Art | Generative Art |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art movement from late 19th to mid 20th century emphasizing experimentation and abstraction. | Art created using algorithms, code, or autonomous systems to generate visuals. |
| Creation Process | Manual techniques with physical media (painting, sculpture). | Automated processes using computers, software, and AI. |
| Key Elements | Bold colors, abstract forms, emotional expression. | Algorithmic patterns, randomness, computational aesthetics. |
| Notable Artists | Pablo Picasso, Wassily Kandinsky, Henri Matisse. | Harold Cohen, Vera Molnar, Refik Anadol. |
| Medium | Canvas, sculpture, traditional materials. | Digital platforms, coding environments, generative systems. |
| Purpose | Challenge traditional aesthetics, explore new visual languages. | Explore complexity, automate creativity, experiment with systems. |
| Historical Context | Rooted in early 20th century cultural shifts and industrialization. | Emerging in late 20th century with advances in computing. |
Defining Modern Art: Origins and Evolution
Modern Art originated in the late 19th century as a response to traditional artistic conventions, emphasizing innovation, experimentation, and individual expression. It evolved through diverse movements such as Impressionism, Cubism, and Surrealism, each challenging established aesthetics and exploring new perspectives. This period marked a radical shift towards abstraction and conceptual depth, laying the groundwork for contemporary artistic practices.
Understanding Generative Art: Algorithms and Creativity
Generative art harnesses algorithms and computational processes to produce creative works, blending technology with artistic expression. Unlike traditional modern art, which relies heavily on human intuition and manual techniques, generative art uses artificial intelligence, fractals, and code to generate complex, evolving visuals. This approach expands creative possibilities by introducing unpredictability and collaboration between human input and machine autonomy.
Key Influences: From Impressionism to Artificial Intelligence
Modern Art, rooted in Impressionism and early 20th-century movements, emphasized human perception, emotion, and experimentation with color and form. Generative Art leverages artificial intelligence and algorithmic processes to create dynamic, evolving works that challenge traditional notions of creativity and authorship. This transition highlights the shift from human-centered expression to collaboration between artists and machines in contemporary art practices.
Artistic Techniques: Traditional vs Code-Based Approaches
Modern Art utilizes traditional techniques such as painting, sculpture, and collage, emphasizing manual skill and material experimentation to convey conceptual depth and aesthetic innovation. Generative Art relies on algorithmic processes, coding languages, and computational systems to produce dynamic, often unpredictable visual compositions, blending creativity with artificial intelligence and machine learning. These code-based approaches challenge conventional notions of authorship and artistic control by enabling autonomous or semi-autonomous art generation through software.
Aesthetic Values: Human Expression vs Machine Generation
Modern art emphasizes human expression through unique emotional depth and intentional imperfections, reflecting the artist's personal experiences and cultural context. Generative art, created by algorithms and artificial intelligence, challenges traditional aesthetics by introducing patterns and variations beyond human capability, offering new forms of beauty rooted in complexity and randomness. Both styles reevaluate aesthetic values, contrasting handcrafted creativity with machine-generated innovation.
Notable Artists and Pioneers in Both Fields
Modern Art features influential pioneers such as Pablo Picasso and Jackson Pollock, whose innovative techniques transformed 20th-century visual expression. Generative Art is propelled by contemporary artists like Casey Reas and Joshua Davis, who integrate algorithms and computational processes to create dynamic, evolving works. Both fields emphasize groundbreaking creativity, with Modern Art focusing on human intuition and Generative Art leveraging artificial intelligence and code.
The Role of Technology in Shaping Art Movements
Modern Art revolutionized artistic expression through industrial innovations and new materials, emphasizing human creativity and abstraction. Generative Art harnesses advanced algorithms, artificial intelligence, and computational processes to autonomously create or assist in producing dynamic, evolving artworks. This technological integration redefines authorship and creativity, expanding art movements beyond traditional boundaries into interactive and data-driven realms.
Collecting and Valuing Modern vs Generative Art
Collecting Modern Art often emphasizes the artist's historical significance, unique handcrafted techniques, and limited edition works, which traditionally drive market value and prestige. Generative Art, leveraging algorithms and code, challenges conventional notions by valuing creativity through digital rarity, provenance verified by blockchain, and evolving aesthetics that appeal to tech-savvy collectors. The convergence of art and technology in Generative Art creates a dynamic valuation landscape distinct from Modern Art's tangible and established paradigms.
Impact on Art Markets and Galleries
Modern Art transformed traditional art markets by introducing avant-garde movements that challenged conventional aesthetics and expanded collector bases globally. Generative Art leverages algorithms and AI, creating dynamic, novel pieces that disrupt traditional galleries' roles by enabling decentralized digital sales and NFT marketplaces. Both forms diversify art investment portfolios, yet Generative Art accelerates market fluidity through blockchain authentication and instantaneous global accessibility.
Future Trends: The Convergence of Art and Technology
Modern Art continues to inspire innovation by blending traditional techniques with digital tools, while Generative Art leverages algorithms and artificial intelligence to create autonomous, evolving pieces. Future trends highlight an increasing convergence of art and technology, where immersive experiences using virtual reality and machine learning will redefine artistic expression. This fusion is expected to expand creative possibilities, enabling artists to generate complex, interactive installations that challenge conventional boundaries.
Related Important Terms
Algorithmic Palette
Modern art emphasizes human creativity and emotional expression through diverse media, while generative art leverages algorithmic palettes composed of code-driven rules and parameters to autonomously produce visual compositions. The algorithmic palette in generative art enables endless variations, blending randomness and computational logic to create complex, evolving aesthetics unattainable by traditional manual methods.
Human-in-the-Loop Creation
Human-in-the-loop creation remains integral to modern art, where artists directly manipulate materials and concepts to produce unique expressions. In generative art, this human input shifts towards designing algorithms and setting parameters, enabling machines to autonomously generate evolving visual or auditory compositions.
AI Curation
Modern art challenges traditional aesthetics with human-driven creativity and expressive techniques, while generative art harnesses AI algorithms to produce evolving and dynamic visual forms. AI curation in generative art enables personalized exhibitions by analyzing audience preferences and optimizing artwork selection, enhancing viewer engagement beyond conventional modern art displays.
Digital Brushwork
Digital brushwork in modern art emphasizes the deliberate manipulation of pixels through software tools, reflecting artists' direct control over texture and form. In contrast, generative art leverages algorithms to autonomously create complex brushstroke patterns, producing dynamic and often unpredictable digital compositions.
Prompt Engineering
Modern Art embraces traditional techniques and human creativity, whereas Generative Art relies on algorithm-driven processes and artificial intelligence to produce visuals. Prompt engineering in Generative Art is crucial for guiding AI models to create specific styles, themes, and compositions, optimizing the interaction between artist input and machine output.
Generative Adversarial Style
Generative adversarial style, a subset of generative art, leverages neural networks to create original artworks by pitting two models against each other: a generator and a discriminator. This technique transforms traditional modern art paradigms by introducing algorithmic creativity, enabling the production of complex, abstract visuals that challenge conventional artistic expression.
Hybrid Authorship
Modern Art traditionally emphasizes the singular vision and intentionality of the artist, whereas Generative Art introduces algorithms and machines as co-creators, resulting in hybrid authorship that blurs the boundaries between human creativity and computational processes. This fusion challenges conventional notions of authorship by distributing creative agency across both artist and technology, redefining artistic identity in contemporary art practice.
Procedural Expressionism
Procedural Expressionism in modern art emphasizes algorithm-driven creativity where artists embed emotions and narratives within code, contrasting traditional Modern Art's manual techniques. Generative Art leverages computational processes to autonomously produce evolving visual experiences, redefining artistic expression through dynamic systems and procedural aesthetics.
Code-based Aesthetics
Modern Art challenges traditional aesthetics with innovative forms and materials, while Generative Art leverages algorithms and code to create dynamic, evolving visuals. Code-based aesthetics in Generative Art emphasize procedural creativity, enabling artists to harness computational systems that produce unique, data-driven artworks beyond manual craftsmanship.
NFT-native Artforms
Modern Art emphasizes traditional techniques and individual creativity, while Generative Art leverages algorithmic processes and digital innovation, especially within NFT-native artforms that utilize blockchain technology to authenticate and distribute unique digital assets. The emergence of NFT-native Generative Art transforms art ownership and provenance, enabling artists to monetize dynamic, code-generated works directly within decentralized marketplaces.
Modern Art vs Generative Art Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com