Face-to-face meetings foster direct human connection, allowing for nuanced body language and immediate feedback that enhance understanding and trust. Virtual reality meetings simulate in-person interactions through immersive environments, offering flexibility and accessibility for remote participants. Both methods have unique benefits; traditional meetings excel in emotional engagement, while VR meetings provide innovative solutions for global collaboration.
Table of Comparison
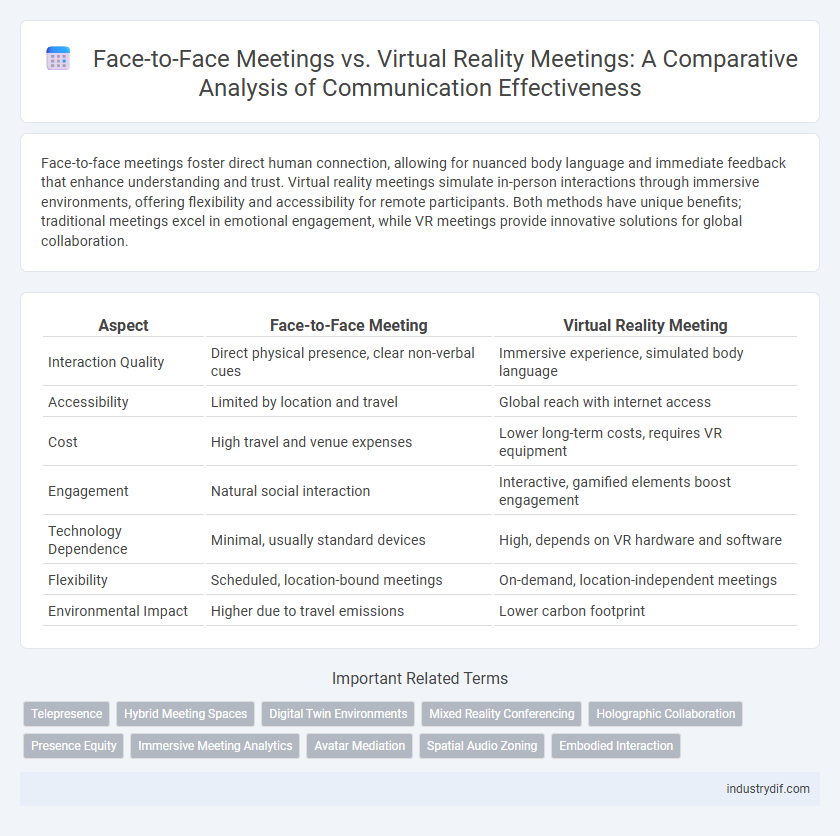
| Aspect | Face-to-Face Meeting | Virtual Reality Meeting |
|---|---|---|
| Interaction Quality | Direct physical presence, clear non-verbal cues | Immersive experience, simulated body language |
| Accessibility | Limited by location and travel | Global reach with internet access |
| Cost | High travel and venue expenses | Lower long-term costs, requires VR equipment |
| Engagement | Natural social interaction | Interactive, gamified elements boost engagement |
| Technology Dependence | Minimal, usually standard devices | High, depends on VR hardware and software |
| Flexibility | Scheduled, location-bound meetings | On-demand, location-independent meetings |
| Environmental Impact | Higher due to travel emissions | Lower carbon footprint |
Introduction to Face-to-Face and Virtual Reality Meetings
Face-to-face meetings facilitate direct interpersonal communication, enabling participants to interpret nonverbal cues such as body language and facial expressions, which enhances mutual understanding and trust-building. Virtual reality meetings simulate immersive environments using 3D avatars and spatial audio, allowing remote participants to interact in real-time with a sense of presence and spatial awareness. Both meeting types serve distinct roles in communication strategies, balancing tangible human connection and technological innovation for collaborative engagement.
Key Differences in Communication Dynamics
Face-to-face meetings enable rich nonverbal communication such as body language and facial expressions, enhancing emotional connection and immediate feedback. Virtual reality meetings simulate presence through avatars but often lack subtle cues, potentially limiting nuanced interpersonal understanding. Latency and technological barriers in VR can disrupt conversational flow, whereas in-person interactions maintain seamless, spontaneous communication dynamics.
Engagement Levels: Physical vs Digital Presence
Face-to-face meetings drive higher engagement levels due to physical presence, non-verbal cues, and immediate feedback, which enhance interpersonal connection and focus. Virtual reality meetings simulate physical environments, offering immersive digital presence that can reduce distractions and foster interaction, but they may lack the spontaneity and emotional richness of real-world encounters. Choosing between these formats depends on the communication goals, with in-person settings excelling in deep relational engagement and VR enabling scalable, interactive experiences.
Cost and Resource Efficiency Comparison
Face-to-face meetings require travel expenses, venue rental, and time investment, significantly increasing overall costs and resource use. Virtual reality meetings reduce overhead by eliminating travel and physical space needs, allowing participants to engage from any location with minimal setup costs. The scalable nature of virtual reality platforms enhances resource efficiency, optimizing time management and reducing carbon footprints associated with traditional meetings.
Impact on Collaboration and Team Building
Face-to-face meetings enhance collaboration and team building through direct nonverbal cues and spontaneous interactions, fostering stronger trust and rapport among team members. Virtual reality meetings simulate immersive environments that promote engagement across remote teams, but may face technological barriers that limit natural communication flow. Effective use of VR can complement physical meetings by enabling diverse collaboration, though in-person interactions remain superior for deep relationship development.
Accessibility and Inclusivity in Meetings
Face-to-face meetings offer personal interaction but often pose accessibility challenges for individuals with mobility issues or geographic constraints. Virtual reality meetings enhance inclusivity by enabling participants from diverse locations and abilities to engage equally through immersive environments and adaptive technologies. These VR platforms accommodate various accessibility needs, promoting broader participation and reducing barriers associated with traditional in-person gatherings.
Non-Verbal Cues: Body Language and Facial Expressions
Face-to-face meetings provide direct access to non-verbal cues such as body language and facial expressions, enhancing emotional connection and communication clarity. Virtual reality meetings simulate these cues with avatars, but subtle gestures and micro-expressions are often less accurately conveyed, potentially affecting understanding. Effective communication in VR depends on advances in motion capture technology and avatar realism to bridge the gap with in-person interactions.
Technology Requirements and Limitations
Face-to-face meetings require minimal technology, relying primarily on physical presence and basic audiovisual tools, ensuring natural communication and non-verbal cue recognition. Virtual reality meetings depend on advanced hardware, including VR headsets, high-speed internet, and specialized software, which can limit accessibility and create technical challenges such as latency and user discomfort. Both formats face limitations: face-to-face meetings are constrained by location and scheduling, while VR meetings must overcome technology adoption barriers and potential sensory overload.
Security and Privacy Concerns
Face-to-face meetings provide a controlled environment with fewer cybersecurity risks compared to virtual reality (VR) meetings, which are vulnerable to data breaches, hacking, and unauthorized access to sensitive information. VR platforms require robust encryption protocols and compliance with privacy regulations like GDPR to safeguard participant data effectively. Ensuring end-to-end security measures and transparent privacy policies is critical to mitigating risks inherent in virtual communication technologies.
Future Trends in Professional Communication
Future trends in professional communication indicate a significant shift toward integrating virtual reality (VR) meetings to enhance remote collaboration, offering immersive environments that mimic face-to-face interactions. Advanced VR platforms enable real-time nonverbal cues and spatial audio, improving engagement and reducing misunderstandings compared to traditional video calls. While face-to-face meetings remain valuable for building trust and rapport, the scalability and flexibility of VR meetings position them as a critical tool for global teams and hybrid work models.
Related Important Terms
Telepresence
Telepresence technology in virtual reality meetings enhances communication by creating immersive environments that simulate face-to-face interactions, enabling participants to perceive spatial and non-verbal cues more effectively. This advanced form of telepresence reduces the limitations of traditional video conferencing, fostering greater engagement and collaboration across remote locations.
Hybrid Meeting Spaces
Hybrid meeting spaces blend face-to-face interactions with virtual reality environments to enhance communication flexibility and engagement. These spaces leverage immersive VR technology alongside traditional in-person dynamics to create seamless collaboration, increase participation, and reduce geographical barriers.
Digital Twin Environments
Face-to-face meetings offer direct interpersonal engagement, enhancing trust and nonverbal communication, while virtual reality meetings in digital twin environments create immersive, interactive spaces that replicate real-world settings for remote collaboration. Digital twins enable real-time data integration and spatial awareness, improving decision-making and team coordination across geographically dispersed participants.
Mixed Reality Conferencing
Mixed Reality Conferencing merges physical presence with digital environments, offering immersive face-to-face interaction that enhances non-verbal cues and collaboration efficiency beyond traditional virtual reality meetings. This hybrid approach leverages real-time spatial data and holographic projections, improving engagement and decision-making in remote communication settings.
Holographic Collaboration
Holographic collaboration in face-to-face meetings enhances communication by enabling participants to interact with three-dimensional, lifelike projections, fostering more natural and intuitive exchanges compared to traditional video calls. Virtual reality meetings incorporating holograms reduce geographical barriers while improving engagement, spatial understanding, and nonverbal cue recognition, making remote teamwork more effective and immersive.
Presence Equity
Face-to-face meetings foster presence equity by enabling direct nonverbal cues and shared physical environment, enhancing mutual understanding and engagement. Virtual reality meetings simulate presence through immersive avatars and spatial audio, reducing barriers but still facing challenges in replicating the full spectrum of human interaction.
Immersive Meeting Analytics
Immersive meeting analytics in face-to-face meetings provide real-time emotional and behavioral cues through direct observation, enhancing engagement assessment and decision-making accuracy. Virtual reality meetings utilize advanced sensors and AI-driven data collection to track participant interactions and spatial dynamics, offering deeper insights into collaboration patterns and communication effectiveness.
Avatar Mediation
Avatar mediation in virtual reality meetings enhances communication by providing nonverbal cues and spatial presence that closely mimic face-to-face interactions, improving engagement and emotional connection. Unlike traditional video calls, avatars allow participants to express body language and gestures in immersive environments, reducing misunderstandings and fostering collaborative dynamics.
Spatial Audio Zoning
Spatial audio zoning in face-to-face meetings naturally enhances communication clarity by allowing participants to focus on specific speakers and minimize background noise. In virtual reality meetings, advanced spatial audio zoning replicates this effect by creating distinct audio zones for each participant, improving immersion and reducing cognitive load.
Embodied Interaction
Face-to-face meetings enable rich embodied interaction through physical presence, nonverbal cues, and immediate sensory feedback, fostering stronger emotional connections and clearer communication. Virtual reality meetings simulate embodied interaction by combining avatars with spatial audio and gesture recognition, enhancing engagement and collaboration despite physical distance.
Face-to-Face Meeting vs Virtual Reality Meeting Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com