Video conferencing enables remote teams to connect visually and share content in real-time, enhancing collaboration through face-to-face interaction. Spatial audio meetings create an immersive experience by simulating natural sound environments, allowing participants to distinguish voices based on virtual positioning. This technology reduces auditory fatigue and improves focus, making discussions more engaging and efficient.
Table of Comparison
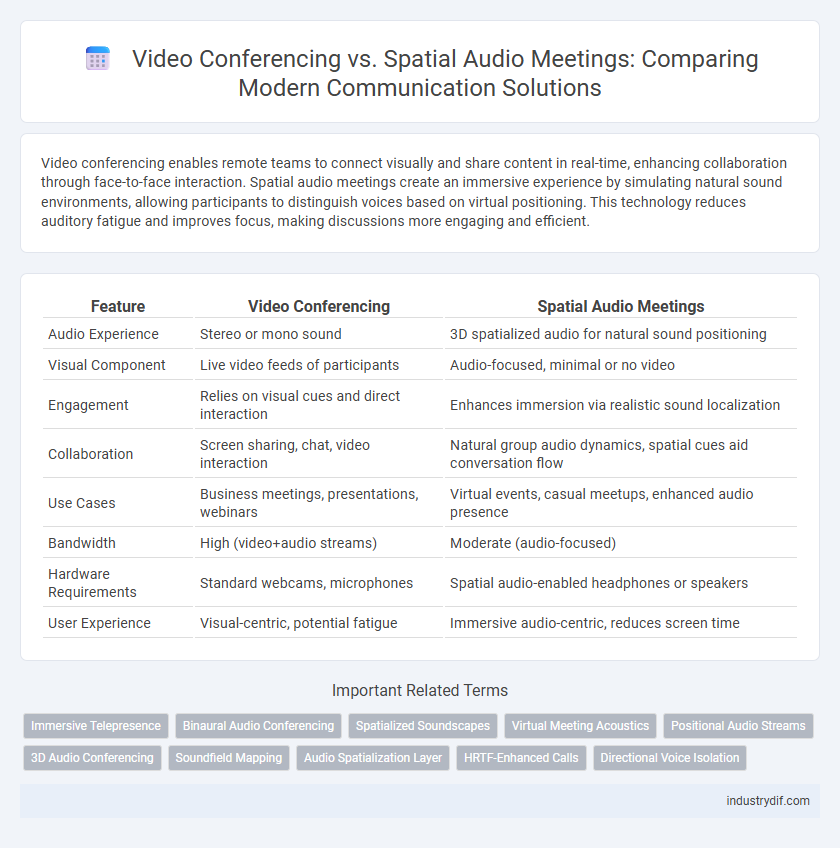
| Feature | Video Conferencing | Spatial Audio Meetings |
|---|---|---|
| Audio Experience | Stereo or mono sound | 3D spatialized audio for natural sound positioning |
| Visual Component | Live video feeds of participants | Audio-focused, minimal or no video |
| Engagement | Relies on visual cues and direct interaction | Enhances immersion via realistic sound localization |
| Collaboration | Screen sharing, chat, video interaction | Natural group audio dynamics, spatial cues aid conversation flow |
| Use Cases | Business meetings, presentations, webinars | Virtual events, casual meetups, enhanced audio presence |
| Bandwidth | High (video+audio streams) | Moderate (audio-focused) |
| Hardware Requirements | Standard webcams, microphones | Spatial audio-enabled headphones or speakers |
| User Experience | Visual-centric, potential fatigue | Immersive audio-centric, reduces screen time |
Introduction to Video Conferencing and Spatial Audio Meetings
Video conferencing enables real-time visual and audio interaction across remote locations, utilizing cameras and microphones to replicate face-to-face meetings. Spatial audio meetings enhance this experience by simulating 3D sound environments, allowing participants to perceive voices as if they are coming from specific directions. This technology improves clarity, engagement, and immersion during virtual communications.
Key Features of Video Conferencing
Video conferencing platforms offer key features such as real-time video streaming, screen sharing, and multi-participant chat to facilitate clear visual communication and collaboration. High-definition video quality, background noise suppression, and recording capabilities enhance the user experience and meeting productivity. Integration with calendar apps and virtual whiteboards further supports seamless scheduling and interactive discussions.
Key Features of Spatial Audio Meetings
Spatial audio meetings create an immersive communication experience by simulating natural sound direction and distance, allowing participants to perceive voices as if they were in the same physical space. This technology enhances clarity and reduces listener fatigue by preventing audio overlap and improving focus on individual speakers. Key features include 3D sound positioning, customizable audio zones, and seamless integration with video conferencing platforms.
Audio Quality Comparison: Mono vs Spatial
Mono audio in video conferencing delivers a single audio channel, often resulting in limited sound clarity and reduced ability to distinguish between multiple speakers or background noise. Spatial audio meetings use multi-directional sound placement to create an immersive experience, enhancing speech intelligibility and allowing users to perceive distinct audio sources as if they were in a physical space. This improvement in audio quality significantly reduces listener fatigue and increases engagement during virtual meetings.
Enhancing Remote Collaboration with Spatial Audio
Spatial audio meetings create a more immersive remote collaboration experience by accurately simulating the direction and distance of participants' voices, which reduces cognitive load and improves focus. Unlike traditional video conferencing, spatial audio fosters natural conversation flow and spatial awareness, helping team members distinguish speakers easily and interpret vocal cues more effectively. This technology bridges communication gaps, promoting stronger engagement and better teamwork in virtual environments.
User Experience: Engagement and Immersion
Video conferencing offers visual cues and face-to-face interaction that enhance engagement but often lacks the depth of spatial audio's immersive sound environment. Spatial audio meetings create a three-dimensional soundscape, allowing users to perceive voice directionality and distance, significantly boosting immersion and natural conversational flow. This auditory realism reduces cognitive load and increases user presence, leading to higher satisfaction and more productive communication sessions.
Technical Requirements and Platform Compatibility
Video conferencing relies on high-definition cameras, microphones, and stable broadband internet to transmit clear visuals and audio, requiring platforms like Zoom, Microsoft Teams, or Google Meet, which support both desktop and mobile devices. Spatial audio meetings demand advanced audio processing hardware and software support for 3D sound reproduction, compatible primarily with platforms such as Dolby.io, Gather Town, and Engage, often requiring specialized earbuds or headphones for optimal experience. Cross-platform compatibility varies, with video conferencing tools offering seamless integration across operating systems, whereas spatial audio solutions may be limited by device capabilities and software environment constraints.
Scalability for Large Teams and Organizations
Video conferencing platforms must support high-definition streams and extensive participant management features to ensure scalability for large teams and organizations. Spatial audio meetings enhance scalability by providing a more natural, immersive sound environment that reduces audio fatigue and improves communication clarity among numerous attendees. Combining robust video streaming infrastructure with spatial audio technology optimizes collaboration efficiency in expansive corporate settings.
Security and Privacy in Communication Platforms
Video conferencing platforms often implement end-to-end encryption and multi-factor authentication to safeguard user data during virtual meetings. Spatial audio meetings enhance privacy by simulating real-world sound environments, reducing the risk of eavesdropping through more natural sound localization. Both technologies require robust security protocols, but spatial audio's immersive nature demands advanced signal processing to prevent unauthorized interception and ensure confidentiality.
Future Trends in Virtual Communication Technologies
Video conferencing remains a dominant tool for virtual meetings, leveraging high-definition video and real-time interaction to connect global teams. Spatial audio meetings are emerging as a transformative trend, enhancing user experience by creating immersive, 3D sound environments that mimic in-person conversations. Future virtual communication technologies will increasingly integrate augmented reality and AI-driven spatial audio to provide more natural, engaging, and context-aware remote collaborations.
Related Important Terms
Immersive Telepresence
Video conferencing delivers visual and auditory connectivity but often lacks depth in spatial cues, while spatial audio meetings enhance immersive telepresence by simulating three-dimensional sound environments that improve participant presence and engagement. Spatial audio technology replicates real-world audio dynamics, enabling clearer communication and reducing cognitive fatigue during remote collaboration.
Binaural Audio Conferencing
Binaural audio conferencing leverages spatial audio technology to create immersive, 3D sound environments that enhance clarity and participant presence compared to traditional video conferencing. This spatial audio approach improves communication efficiency by accurately simulating real-life auditory cues, reducing listener fatigue and increasing engagement during virtual meetings.
Spatialized Soundscapes
Spatialized soundscapes in video conferencing enhance communication by creating a three-dimensional audio environment that mimics real-life interactions, improving spatial awareness and reducing listener fatigue. This immersive audio technology allows participants to distinguish individual voices based on their virtual locations, fostering clearer conversations and more natural collaboration.
Virtual Meeting Acoustics
Video conferencing often suffers from limited spatial audio cues, causing overlapping voices to blur and reduce speech intelligibility, whereas spatial audio meetings enhance virtual meeting acoustics by simulating real-world directional sound, improving voice separation and participant engagement. Employing advanced spatial audio technology in remote communication platforms optimizes auditory clarity, reduces cognitive load, and creates a more natural conversational environment.
Positional Audio Streams
Video conferencing platforms typically rely on standard stereo or mono audio streams that lack spatial cues, limiting the ability to perceive sound directionality and speaker location. In contrast, spatial audio meetings employ positional audio streams to create immersive communication environments where voices are accurately localized, enhancing understanding and reducing cognitive load during multi-participant interactions.
3D Audio Conferencing
3D audio conferencing enhances communication by creating a spatial audio environment where participants' voices appear to come from distinct directions, improving clarity and reducing listener fatigue. This immersive technology surpasses traditional video conferencing by simulating face-to-face interaction through accurate spatial sound positioning, fostering more natural and effective meetings.
Soundfield Mapping
Soundfield mapping in spatial audio meetings creates an immersive communication environment by accurately positioning participants' voices in a 3D sound space, enhancing clarity and reducing listener fatigue compared to traditional video conferencing audio. This technology improves conversational flow and spatial awareness, making remote collaboration feel more natural and engaging.
Audio Spatialization Layer
Video conferencing platforms typically rely on standard stereo or mono audio, which can limit the clarity and spatial distinction of individual speakers, while spatial audio meetings use advanced audio spatialization layers to create a three-dimensional sound environment that improves participant localization and enhances communication dynamics. The audio spatialization layer processes sound inputs to simulate real-world audio positioning, reducing cognitive load and increasing engagement during remote meetings.
HRTF-Enhanced Calls
HRTF-enhanced video conferencing leverages Head-Related Transfer Function technology to create immersive spatial audio experiences that simulate natural sound localization, improving participant engagement and reducing cognitive load during virtual meetings. Unlike traditional stereo audio, spatial audio meetings utilizing HRTF enable clearer voice distinction and directional cues, fostering more effective communication and collaboration in remote work environments.
Directional Voice Isolation
Directional Voice Isolation in video conferencing enhances audio clarity by filtering background noise and emphasizing the speaker's voice, while spatial audio meetings provide immersive sound that replicates real-life spatial positioning of participants. This technology improves communication efficiency by allowing attendees to distinguish overlapping conversations and reducing cognitive load during virtual interactions.
Video Conferencing vs Spatial Audio Meetings Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com