Voice call technology offers direct, real-time interaction but lacks the immersive experience provided by spatial audio communication. Spatial audio enhances user engagement by replicating three-dimensional sound environments, making conversations feel more natural and lifelike. This advancement improves clarity and spatial awareness, transforming remote communication into a more dynamic and intuitive experience.
Table of Comparison
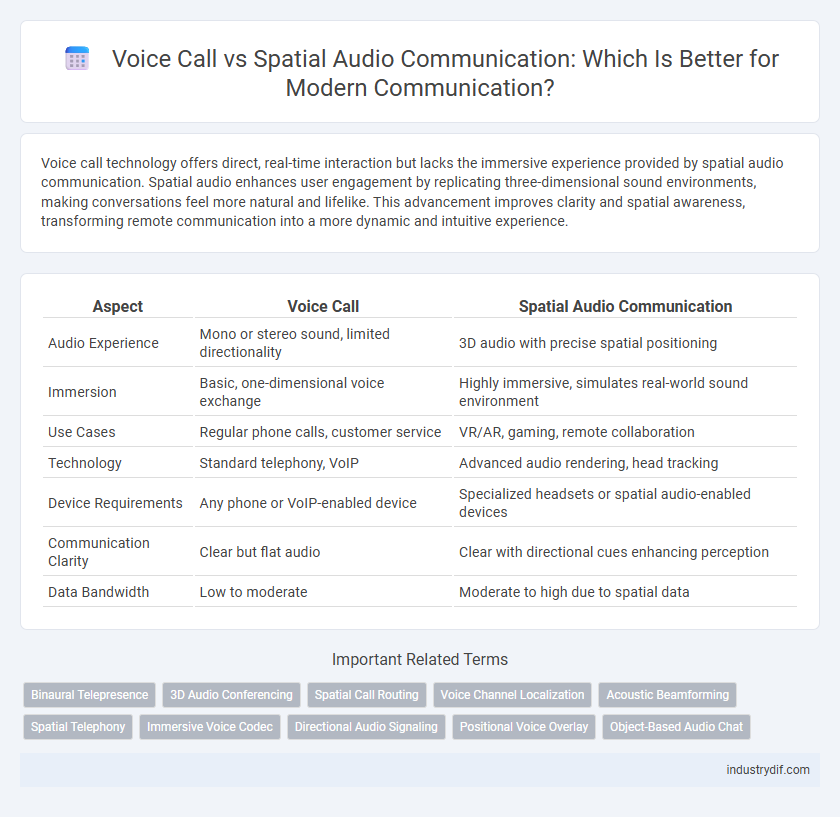
| Aspect | Voice Call | Spatial Audio Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Audio Experience | Mono or stereo sound, limited directionality | 3D audio with precise spatial positioning |
| Immersion | Basic, one-dimensional voice exchange | Highly immersive, simulates real-world sound environment |
| Use Cases | Regular phone calls, customer service | VR/AR, gaming, remote collaboration |
| Technology | Standard telephony, VoIP | Advanced audio rendering, head tracking |
| Device Requirements | Any phone or VoIP-enabled device | Specialized headsets or spatial audio-enabled devices |
| Communication Clarity | Clear but flat audio | Clear with directional cues enhancing perception |
| Data Bandwidth | Low to moderate | Moderate to high due to spatial data |
Understanding Voice Call Communication
Voice call communication relies on real-time audio transmission between two or more users, enabling direct and immediate vocal interaction regardless of distance. It primarily uses narrowband or wideband audio codecs to optimize voice clarity and minimize latency over networks. Understanding voice calls involves recognizing key factors such as echo cancellation, jitter buffering, and network stability to ensure seamless and intelligible communication.
Introduction to Spatial Audio Technology
Spatial audio technology recreates a three-dimensional sound environment, allowing users to perceive audio sources as if they are positioned around them in physical space. Unlike traditional voice calls, which transmit mono or stereo audio through a single channel, spatial audio enhances communication by providing directional sound cues that improve clarity and immersion. This technology relies on advanced algorithms and head-tracking capabilities to deliver a realistic audio experience, making remote conversations feel more natural and engaging.
Core Differences Between Voice Call and Spatial Audio
Voice calls transmit audio through a single channel, creating a flat sound experience where voices come from the same direction. Spatial audio communication simulates a three-dimensional sound environment, allowing users to perceive voices and sounds originating from distinct locations around them. This difference enhances immersion and situational awareness in spatial audio compared to traditional voice calls.
Audio Quality Comparison: Mono vs 3D Sound
Voice calls typically use mono audio, delivering sound from a single source which can limit spatial awareness and depth perception in communication. Spatial audio communication employs 3D sound technology, creating an immersive experience by simulating natural sound placement around the listener, enhancing clarity, localization, and overall comprehension. This advanced audio quality improves engagement and reduces listener fatigue compared to traditional mono voice calls.
User Experience: Immersion and Presence
Voice call technology offers clear, real-time audio essential for basic communication, but spatial audio communication enhances user experience by creating a multidimensional sound environment that simulates natural listening. Spatial audio enables users to perceive sound directionality and distance, increasing immersion and a sense of presence during conversations. This technology significantly improves virtual meetings, gaming, and remote collaboration by making interactions feel more lifelike and engaging.
Technical Requirements for Each Communication Type
Voice calls require stable network bandwidth, low latency, and high audio codec efficiency such as Opus or AAC to maintain clear and uninterrupted two-way communication. Spatial audio communication demands advanced audio processing hardware, multi-channel microphone arrays, and real-time 3D audio rendering algorithms to accurately simulate sound localization and immersive spatial perception. Both communication types need robust error correction protocols and synchronization mechanisms, but spatial audio also relies heavily on precise head tracking sensors and spatial mapping data for enhanced user experience.
Applications in Modern Communication Platforms
Voice call technology remains a fundamental aspect of modern communication platforms, enabling real-time, direct interaction suited for personal and business contexts. Spatial audio communication enhances these platforms by creating immersive soundscapes that simulate realistic environments, improving user experience in virtual meetings, gaming, and remote collaboration. Integrating spatial audio with voice calls increases engagement and clarity, making it essential for advanced communication tools in both professional and social applications.
Accessibility and Inclusivity Considerations
Voice calls provide straightforward, widely accessible communication but may limit users with hearing impairments due to lack of spatial cues. Spatial audio communication enhances inclusivity by simulating real-world sound environments, aiding users in distinguishing multiple speakers and improving comprehension for those with auditory processing challenges. Designing systems with customizable spatial audio settings and voice call alternatives ensures accessibility across diverse user needs.
Security and Privacy in Audio Communications
Voice call encryption protocols like TLS and SRTP ensure end-to-end security by protecting voice data from interception and tampering. Spatial audio communication integrates advanced biometric authentication and dynamic audio channel isolation, enhancing privacy by preventing unauthorized access and eavesdropping within multi-user environments. Robust security frameworks in both methods are essential for safeguarding sensitive conversations against cyber threats and preserving user confidentiality.
Future Trends in Audio Communication Technologies
Voice calls remain a fundamental communication tool with widespread adoption, but spatial audio communication is rapidly emerging as a transformative technology that enhances user experience by creating immersive, 3D sound environments. Future trends in audio communication technologies emphasize integration of artificial intelligence for real-time audio processing, spatial sound localization, and personalized audio environments within virtual and augmented reality platforms. These advancements are expected to revolutionize remote collaboration, gaming, and social interaction by delivering a more natural and engaging auditory experience.
Related Important Terms
Binaural Telepresence
Binaural telepresence in spatial audio communication creates a three-dimensional sound environment that replicates natural human hearing, enhancing voice call experiences by providing precise auditory localization and immersive interaction. This technology significantly reduces listener fatigue and improves conversational clarity compared to traditional mono or stereo voice calls, enabling more effective remote communication.
3D Audio Conferencing
Voice calls provide clear, direct communication using traditional stereo audio, while spatial audio communication enhances immersion through 3D sound positioning, allowing participants in audio conferencing to perceive voices as if they are coming from specific locations in a virtual space. 3D audio conferencing improves collaboration by increasing spatial awareness and reducing cognitive load, making virtual meetings more natural and engaging.
Spatial Call Routing
Spatial call routing enhances voice communication by dynamically directing audio signals based on the physical location of participants, resulting in immersive and context-aware interactions. Unlike traditional voice calls, this technology leverages 3D audio positioning and spatial awareness to reduce background noise and improve clarity, significantly benefiting virtual meetings and remote collaborations.
Voice Channel Localization
Voice call technology delivers clear, direct audio through a single voice channel, enabling straightforward communication but lacking spatial cues for sound localization. Spatial audio communication enhances voice channel localization by simulating three-dimensional sound, allowing users to perceive the direction and distance of voices for a more immersive and natural interaction experience.
Acoustic Beamforming
Acoustic beamforming enhances spatial audio communication by directing sound waves precisely toward the listener, creating an immersive and clear audio experience that outperforms traditional voice calls with omnidirectional sound. This technology reduces background noise and improves speech intelligibility by isolating the speaker's voice within a three-dimensional sound field, essential for applications like virtual meetings and augmented reality interactions.
Spatial Telephony
Spatial telephony enhances traditional voice calls by delivering immersive 3D audio that mimics real-life sound localization, improving conversational clarity and presence. This technology leverages spatial audio algorithms to create a natural communication environment, making remote interactions more engaging and intuitive than conventional mono or stereo voice calls.
Immersive Voice Codec
Immersive Voice Codec enhances spatial audio communication by delivering high-fidelity, three-dimensional sound that replicates real-life voice positioning, significantly surpassing traditional voice call clarity and immersion. This advanced codec enables clearer, more natural interactions in virtual environments, improving user engagement and spatial awareness during communication.
Directional Audio Signaling
Voice call technology uses mono or stereo audio signals that lack spatial differentiation, limiting the ability to perceive the direction of sound sources. Spatial audio communication enhances directional audio signaling by simulating three-dimensional sound environments, improving user immersion and situational awareness during conversations.
Positional Voice Overlay
Positional voice overlay in spatial audio communication enhances immersion by accurately mapping sound sources to their respective locations in a 3D environment, enabling users to discern direction and distance of speakers naturally. Traditional voice calls lack this spatial dimension, resulting in a flat audio experience that reduces situational awareness and engagement in collaborative settings.
Object-Based Audio Chat
Object-based audio chat in spatial audio communication enhances voice calls by delivering immersive, three-dimensional sound that accurately positions speakers within a virtual space, improving clarity and natural interaction. Unlike traditional voice calls that mix audio channels, object-based audio enables individualized sound sources, allowing for dynamic spatial cues and a more engaging conversational experience.
Voice Call vs Spatial Audio Communication Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com