Written communication relies on text to convey messages clearly and precisely, making it ideal for detailed documentation and formal interactions. Augmented reality messaging enhances communication by overlaying digital information onto the physical environment, offering immersive and interactive experiences that increase engagement and understanding. Combining traditional written methods with augmented reality technologies can create more dynamic and effective communication strategies tailored to diverse audiences.
Table of Comparison
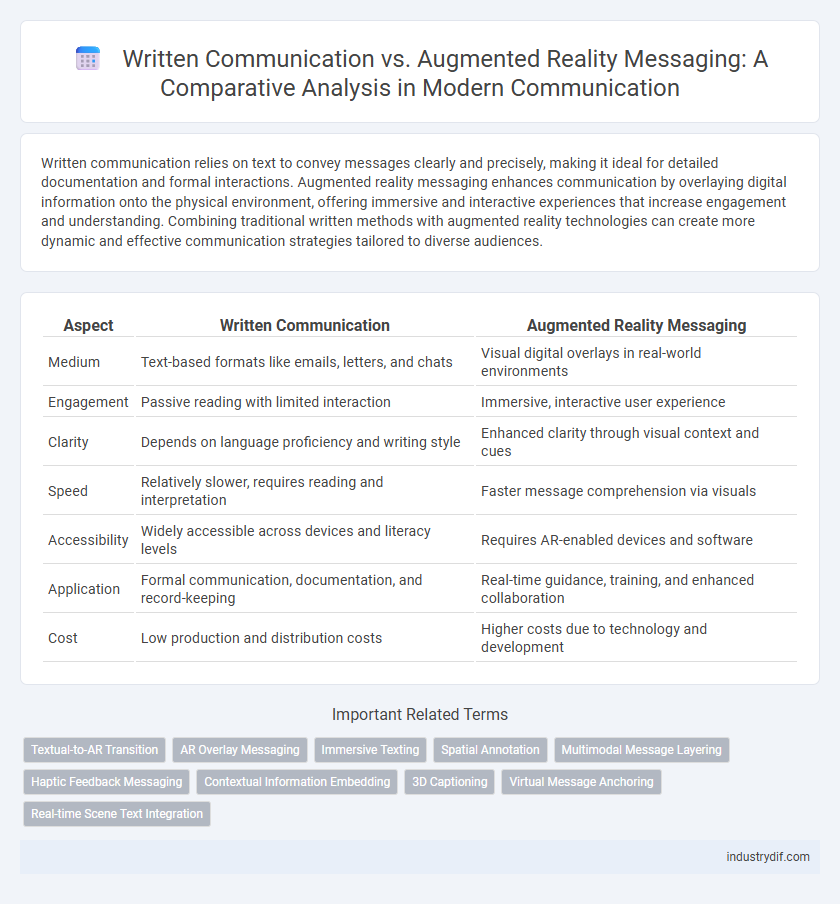
| Aspect | Written Communication | Augmented Reality Messaging |
|---|---|---|
| Medium | Text-based formats like emails, letters, and chats | Visual digital overlays in real-world environments |
| Engagement | Passive reading with limited interaction | Immersive, interactive user experience |
| Clarity | Depends on language proficiency and writing style | Enhanced clarity through visual context and cues |
| Speed | Relatively slower, requires reading and interpretation | Faster message comprehension via visuals |
| Accessibility | Widely accessible across devices and literacy levels | Requires AR-enabled devices and software |
| Application | Formal communication, documentation, and record-keeping | Real-time guidance, training, and enhanced collaboration |
| Cost | Low production and distribution costs | Higher costs due to technology and development |
Introduction to Written Communication and Augmented Reality Messaging
Written communication remains a foundational method for conveying detailed, structured information through text, enabling clarity and formal record-keeping across various digital and physical platforms. Augmented reality (AR) messaging represents an innovative communication form that overlays digital content onto the physical environment, enhancing real-time interaction and contextual understanding. Combining traditional written elements with AR's immersive capabilities offers dynamic potential to transform user engagement and message retention.
Evolution of Communication in the Digital Era
Written communication has evolved from traditional text-based formats to include immersive augmented reality messaging, enhancing user engagement and contextual understanding. Augmented reality messaging integrates visual and spatial elements, allowing real-time interaction and richer information exchange compared to static written messages. This evolution signifies a shift towards more dynamic, multisensory communication methods in the digital era.
Core Principles of Written Communication
Written communication relies on clarity, coherence, and proper structure to convey messages effectively, ensuring the receiver interprets information as intended. It emphasizes grammar, syntax, and vocabulary precision to avoid misunderstandings and maintain professionalism. Unlike augmented reality messaging, written communication depends entirely on textual elements without real-time visual or interactive enhancements.
Fundamentals of Augmented Reality Messaging
Augmented Reality Messaging integrates digital content directly into the physical environment, enhancing interaction beyond traditional text-based written communication. This technology leverages spatial mapping and real-time data rendering to provide immersive and contextually relevant messages. By combining visual, auditory, and sometimes haptic feedback, Augmented Reality Messaging fundamentally transforms how information is perceived and understood.
Key Differences Between Written Communication and AR Messaging
Written communication relies on static text and symbols to convey messages, offering clarity and permanence but limited sensory engagement. Augmented reality (AR) messaging integrates digital content with the physical environment, providing immersive, interactive experiences that enhance understanding through visual and spatial cues. Key differences include the depth of user engagement, real-time contextual adaptation in AR, and the primarily text-based, linear nature of traditional written communication.
Advantages and Limitations of Written Communication
Written communication offers clear documentation and the ability to review messages at any time, which enhances accuracy and accountability in information exchange. It allows for detailed expression and can be widely distributed across multiple channels without real-time constraints, making it useful for formal and legal communications. However, it lacks the immediacy and interactive elements of augmented reality messaging, and may lead to misunderstandings due to the absence of non-verbal cues and contextual immersion.
Benefits and Challenges of Augmented Reality Messaging
Augmented Reality (AR) messaging enhances written communication by providing immersive, interactive experiences that increase engagement and retention through visual and spatial context. Benefits include real-time information overlay, improved clarity in complex instructions, and personalized user interaction, making messages more memorable and impactful. Challenges involve technological accessibility, higher development costs, and potential user distraction or discomfort due to prolonged AR exposure.
Industry Applications of Written and AR Messaging
Industrial sectors increasingly adopt written communication for formal documentation, compliance reporting, and standardized instructions ensuring clarity and legal accountability. Augmented Reality messaging enhances operational efficiency in manufacturing, maintenance, and remote assistance by overlaying real-time data and interactive visual cues directly onto equipment and workspaces. This fusion of traditional written formats with AR technologies drives innovation in training, troubleshooting, and customer support across industries such as automotive, healthcare, and logistics.
Impact on Workplace Collaboration and Engagement
Written communication remains a foundational tool for clear documentation and asynchronous collaboration, ensuring detailed records and thought-out responses in the workplace. Augmented Reality (AR) messaging revolutionizes engagement by enabling immersive, real-time interaction, enhancing spatial understanding and reducing miscommunication during collaborative tasks. Integrating both methods fosters a dynamic communication environment, boosting productivity and team cohesion through complementary strengths.
Future Trends in Communication Technologies
Written communication continues to evolve with integration into digital platforms, enhancing clarity and accessibility across global audiences. Augmented Reality (AR) messaging introduces immersive, context-rich interactions that overlay digital information on physical environments, transforming user engagement. Future trends in communication technologies emphasize seamless blending of written content and AR elements to create dynamic, interactive experiences that redefine information sharing and collaboration.
Related Important Terms
Textual-to-AR Transition
The shift from traditional written communication to augmented reality messaging transforms static text into immersive, interactive content, enhancing user engagement and comprehension. This textual-to-AR transition leverages spatial context and real-time data overlays, offering dynamic communication experiences that surpass conventional written formats.
AR Overlay Messaging
AR overlay messaging transforms written communication by embedding digital text directly onto physical environments, enhancing context and user engagement. This innovative approach increases information retention and immediacy, outperforming traditional written methods by merging real-world visuals with interactive message delivery.
Immersive Texting
Immersive texting through augmented reality messaging enhances written communication by integrating spatial and interactive elements, allowing users to experience messages within a 3D environment that promotes deeper engagement and contextual understanding. Unlike traditional written texts, AR messaging supports real-time visual annotations and gestures, transforming static content into dynamic conversations that bridge the gap between digital and physical communication.
Spatial Annotation
Written communication relies on linear text to convey messages, often lacking spatial context that can enhance understanding; augmented reality messaging integrates spatial annotation by overlaying information directly onto physical environments, improving clarity and engagement. Spatial annotations in AR enable users to interact with dynamic, location-specific content, bridging the gap between traditional written texts and immersive, context-aware communication.
Multimodal Message Layering
Written communication relies heavily on text-based messages that convey meaning through structured language, while augmented reality (AR) messaging integrates visual, auditory, and spatial elements to create immersive multimodal message layering. This combination of semantic, sensory, and contextual cues in AR messaging enhances message clarity and engagement beyond the limitations of traditional written formats.
Haptic Feedback Messaging
Haptic feedback messaging in augmented reality offers immersive, tactile sensations that enhance user engagement beyond traditional written communication, enabling more intuitive and emotionally resonant interactions. This technology leverages precise vibration patterns and force feedback to simulate real-world touch, revolutionizing message delivery by providing sensory depth that text alone cannot convey.
Contextual Information Embedding
Written communication embeds contextual information through structured language and detailed descriptions, enabling clarity and precision in conveying messages. Augmented Reality messaging enhances contextual embedding by layering digital information onto real-world environments, providing immersive, situational awareness that written text alone cannot achieve.
3D Captioning
Written communication relies on text to convey information efficiently, but 3D captioning in augmented reality messaging enhances user engagement by overlaying contextual, spatially anchored text directly within the physical environment. This integration improves comprehension and accessibility, especially in complex scenarios such as technical instructions and real-time collaboration.
Virtual Message Anchoring
Virtual Message Anchoring in augmented reality messaging enhances spatial context and user engagement by overlaying messages onto real-world objects, enabling clearer and more intuitive communication compared to traditional written communication, which lacks this immersive and interactive dimension. The integration of anchoring technology enables dynamic information updates and precise message localization, transforming static written texts into context-aware, real-time communication tools.
Real-time Scene Text Integration
Written communication relies on static text constructs that require interpretation without environmental context, whereas augmented reality messaging integrates real-time scene text to enhance understanding and immediacy. This dynamic overlay of digital information onto physical surroundings facilitates interactive and context-aware dialogue, significantly improving message clarity and engagement.
Written Communication vs Augmented Reality Messaging Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com