Degrees provide comprehensive, formal education recognized worldwide, offering in-depth knowledge and credibility in a specific field. Digital badges represent targeted skills and achievements, offering flexible, easily shareable proof of competencies that can complement traditional degrees. Employers increasingly value the combination of both, as badges demonstrate continuous learning and adaptability alongside foundational qualifications.
Table of Comparison
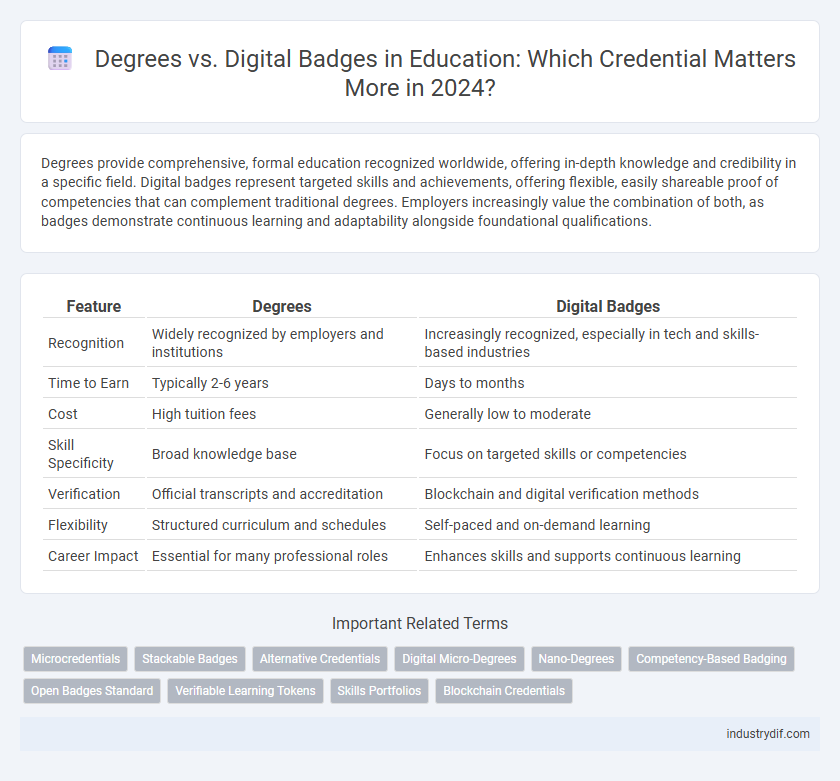
| Feature | Degrees | Digital Badges |
|---|---|---|
| Recognition | Widely recognized by employers and institutions | Increasingly recognized, especially in tech and skills-based industries |
| Time to Earn | Typically 2-6 years | Days to months |
| Cost | High tuition fees | Generally low to moderate |
| Skill Specificity | Broad knowledge base | Focus on targeted skills or competencies |
| Verification | Official transcripts and accreditation | Blockchain and digital verification methods |
| Flexibility | Structured curriculum and schedules | Self-paced and on-demand learning |
| Career Impact | Essential for many professional roles | Enhances skills and supports continuous learning |
Understanding Degrees and Digital Badges
Degrees represent comprehensive academic achievements validated by accredited institutions, offering in-depth knowledge and recognized qualifications across various fields. Digital badges signify targeted skills or competencies earned through shorter, often online, programs that provide flexible and verifiable proof of specific abilities. Both degrees and digital badges serve distinct roles in education, with degrees emphasizing broad expertise and digital badges highlighting specialized skills.
Key Differences Between Degrees and Digital Badges
Degrees represent formal, extensive academic achievements typically awarded by accredited institutions after completing multi-year programs, while digital badges signify specific skills or competencies demonstrated through shorter, targeted learning experiences. Degrees carry widespread recognition and often serve as prerequisites for professional certifications or advanced education, whereas digital badges provide flexible, verifiable credentials that enhance resumes and support continuous skill development. Employers increasingly value digital badges for their ability to showcase up-to-date expertise, complementing traditional degrees in hiring and career advancement processes.
Recognition and Credibility in the Job Market
Degrees often hold extensive recognition and credibility in the job market due to their rigorous academic standards and institutional reputation. Digital badges provide a flexible, verifiable way to showcase specific skills and achievements, gaining traction among employers seeking targeted competencies. Both forms of credentialing complement each other, with degrees establishing foundational knowledge and digital badges highlighting specialized expertise.
Speed and Flexibility of Earning Credentials
Digital badges offer faster credentialing compared to traditional degrees, enabling learners to showcase specific skills or competencies without the lengthy time commitment required for degree programs. These badges provide flexibility by allowing individuals to earn and stack multiple credentials at their own pace, often through online platforms and microlearning units. Consequently, digital badges accelerate career advancement and continuous learning in a rapidly changing job market.
Cost Comparison: Degrees vs Digital Badges
Traditional degrees typically involve significant financial investment, often ranging from $20,000 to over $100,000 depending on the institution and program length. Digital badges offer a cost-effective alternative, usually costing between $50 and $500, making them accessible for skill-specific certifications and micro-credentials. Unlike degrees, digital badges allow for incremental learning without incurring large student debt or long-term financial commitments.
Role of Accreditation and Verification
Accreditation ensures that degrees meet established educational standards, providing widespread recognition and trust among employers and institutions. Digital badges offer flexible, skill-based verification but require robust accreditation frameworks to guarantee their credibility and acceptance. Effective verification mechanisms are essential to authenticate both degrees and digital badges, enhancing their value in academic and professional settings.
Impact on Lifelong Learning and Upskilling
Degrees provide comprehensive knowledge with formal recognition that supports long-term career advancement, while digital badges offer targeted skills validation enabling flexible, ongoing upskilling tailored to industry demands. Digital badges promote microlearning and immediate application of new skills, facilitating continuous professional development in fast-evolving fields. Both credentials complement lifelong learning by balancing deep theoretical understanding and agile skill acquisition for evolving job markets.
Employer Perspectives on Credentials
Employers increasingly recognize digital badges as a flexible way to verify specific skills and competencies, complementing traditional degrees in recruitment processes. Digital badges offer detailed metadata that allows employers to assess candidates' practical abilities and continuous learning, enhancing talent evaluation beyond the broad scope of degrees. While degrees remain a standard measure of academic achievement, the rise of digital badges reflects a shift toward skills-based hiring and workforce agility.
Use Cases: When to Choose Degrees or Digital Badges
Degrees are ideal for comprehensive, in-depth education required for professions such as medicine, law, engineering, and academia, where accreditation and formal recognition are essential. Digital badges effectively showcase specific skills, micro-credentials, or professional development achievements, making them suitable for ongoing learning, skill validation, and employer recognition in fast-changing industries like technology and marketing. Choosing between degrees and digital badges depends on the learner's career goals, the industry's credentialing standards, and the need for flexibility or formal accreditation.
Future Trends in Educational Credentials
Degrees continue to represent comprehensive academic achievement recognized globally across industries, but digital badges are rapidly gaining traction as flexible, skill-specific credentials ideal for lifelong learning and micro-credentialing. Future trends indicate a hybrid credential ecosystem where institutions integrate blockchain technology to verify badges and degrees, enhancing transparency and portability. Employers increasingly value digital badges for real-time validation of up-to-date skills in fast-evolving fields like cybersecurity and data science, driving demand for modular, stackable credentials complementing traditional degrees.
Related Important Terms
Microcredentials
Microcredentials offer targeted, skill-specific recognition that complements traditional degrees by providing flexible, stackable learning opportunities tailored to evolving job market demands. Unlike conventional degrees, digital badges enable rapid upskilling and verifiable proof of competencies through blockchain-secured platforms, enhancing employability and lifelong learning pathways.
Stackable Badges
Stackable digital badges offer a flexible alternative to traditional degrees by allowing learners to accumulate verified skills and competencies over time, enhancing employability and personalized career pathways. These modular credentials, recognized by educational institutions and employers, bridge gaps between formal education and practical expertise, promoting continuous professional development in dynamic job markets.
Alternative Credentials
Alternative credentials such as digital badges offer flexible, competency-based recognition that complements traditional degrees by showcasing specific skills and micro-credentials relevant to today's job market. These digital badges enhance lifelong learning and employability, providing verifiable proof of expertise in targeted areas beyond the comprehensive scope of degrees.
Digital Micro-Degrees
Digital micro-degrees offer a flexible, skill-focused alternative to traditional degrees by providing verified, stackable learning credentials that target specific competencies. These digital badges enhance employability through immediate, shareable proof of expertise in emerging fields, aligning education with real-time industry demands.
Nano-Degrees
Nano-degrees offer targeted skill development through short, flexible online courses compared to traditional degrees, providing learners with industry-relevant credentials that enhance employability. Digital badges serve as micro-credentials recognizing specific competencies, while nano-degrees bundle multiple badges into comprehensive, career-focused programs.
Competency-Based Badging
Competency-based badging offers a flexible and verifiable alternative to traditional degrees by validating specific skills and knowledge through digital credentials. These badges enable learners to showcase targeted competencies to employers, enhancing workforce readiness and personalized career development.
Open Badges Standard
Degrees represent traditional, comprehensive academic achievements certified by accredited institutions, while Digital Badges, especially those adhering to the Open Badges Standard, offer verifiable, portable credentials that capture specific skills and competencies gained through informal, non-traditional learning pathways. The Open Badges Standard ensures interoperability and data-rich metadata, enabling recipients to showcase verified achievements across multiple digital platforms and employers.
Verifiable Learning Tokens
Verifiable learning tokens such as digital badges provide a portable and instantly verifiable credential that highlights specific skills and achievements beyond traditional degrees. These tokens enable employers and educators to assess competencies in real time, enhancing transparency and lifelong learning validation.
Skills Portfolios
Skills portfolios provide a versatile way to showcase competencies through digital badges, offering real-time validation of specific abilities compared to traditional degrees. Digital badges enhance employability by highlighting practical skills and micro-credentials that complement or supplement formal education credentials.
Blockchain Credentials
Blockchain credentials offer a secure, verifiable alternative to traditional degrees by providing tamper-proof digital badges that instantly validate skills and achievements. These credentials enhance lifelong learning pathways through transparent, decentralized records accessible to employers and educational institutions worldwide.
Degrees vs Digital Badges Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com