Grading systems assign numerical or letter values to assess student performance, providing clear benchmarks but often creating stress and limiting intrinsic motivation. Ungrading promotes self-assessment and feedback, encouraging deeper learning and critical thinking without the pressure of traditional scores. This approach fosters a growth mindset by prioritizing mastery and personal progress over comparative evaluation.
Table of Comparison
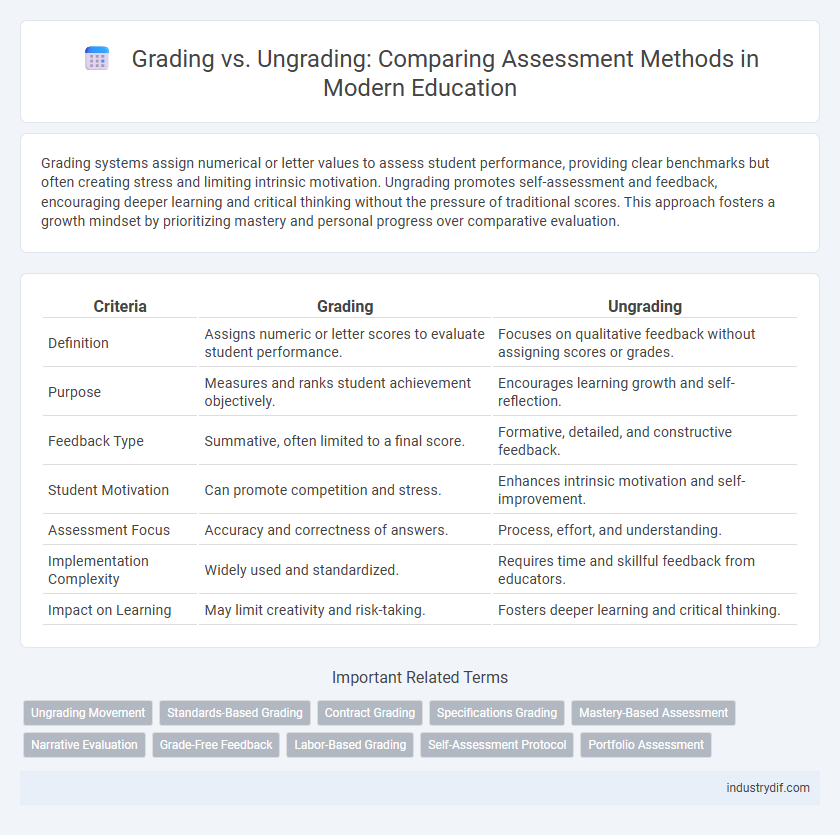
| Criteria | Grading | Ungrading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Assigns numeric or letter scores to evaluate student performance. | Focuses on qualitative feedback without assigning scores or grades. |
| Purpose | Measures and ranks student achievement objectively. | Encourages learning growth and self-reflection. |
| Feedback Type | Summative, often limited to a final score. | Formative, detailed, and constructive feedback. |
| Student Motivation | Can promote competition and stress. | Enhances intrinsic motivation and self-improvement. |
| Assessment Focus | Accuracy and correctness of answers. | Process, effort, and understanding. |
| Implementation Complexity | Widely used and standardized. | Requires time and skillful feedback from educators. |
| Impact on Learning | May limit creativity and risk-taking. | Fosters deeper learning and critical thinking. |
Understanding Grading Systems in Education
Grading systems in education typically assign letters or numbers to represent student performance, which can motivate achievement but may also limit deeper learning by emphasizing scores over comprehension. Ungrading approaches prioritize qualitative feedback and student self-assessment, fostering intrinsic motivation and critical thinking by focusing on mastery rather than numeric or letter grades. Understanding these contrasting methods helps educators design assessments that balance evaluation with meaningful learning experiences.
The Philosophy Behind Ungrading
The philosophy behind ungrading challenges traditional assessment metrics by emphasizing intrinsic motivation, student self-reflection, and personalized learning over standardized scoring systems. It encourages learners to engage deeply with content without the pressure of numerical grades, fostering a growth mindset and critical thinking skills. Educators adopting ungrading aim to create a more equitable and supportive environment that values competence and improvement rather than competition.
Pros and Cons of Traditional Grading
Traditional grading provides a clear, standardized measure of student performance, allowing easy comparison across different learners and institutions. However, it often emphasizes memorization over critical thinking and creativity, potentially causing stress and diminished intrinsic motivation in students. Critics argue that it fails to capture individual growth and diverse learning styles, limiting a holistic understanding of student progress.
Benefits of Ungrading for Student Learning
Ungrading promotes intrinsic motivation by encouraging students to focus on mastery and personal growth instead of external rewards or penalties. This approach reduces anxiety associated with traditional grading systems, fostering a safe environment for experimentation and deeper learning. Research shows ungrading enhances critical thinking and self-assessment skills, leading to improved academic engagement and long-term retention.
Impact on Student Motivation: Grading vs. Ungrading
Grading systems often create competition and anxiety, which can hinder intrinsic motivation and promote surface learning. Ungrading encourages self-assessment and mastery, fostering deeper engagement and a growth mindset in students. Research shows students in ungrading environments demonstrate increased creativity, self-confidence, and sustained motivation compared to traditional graded settings.
Assessment Methods: Letter Grades vs. Feedback
Letter grades provide a standardized metric that simplifies student evaluation but often reduces complex learning processes to a single quantitative score. Feedback-oriented assessment emphasizes qualitative insights, promoting deeper understanding and personal growth by highlighting strengths and areas for improvement. Embracing feedback over letter grades fosters intrinsic motivation and encourages continuous learning beyond traditional score-based measures.
Teacher Perspectives on Grading and Ungrading
Teachers often perceive traditional grading as a clear, standardized method to evaluate student performance but recognize its limitations in capturing individual learning progress and creativity. Many educators advocate for ungrading to foster intrinsic motivation, promote deeper understanding, and reduce anxiety associated with numeric scores. Teacher perspectives highlight that implementing ungrading requires significant shifts in assessment strategies, ongoing student-teacher dialogue, and institutional support to be effective.
Equity and Inclusion in Grading Practices
Grading systems often reinforce inequities by disproportionately impacting marginalized students, while ungrading promotes equity by emphasizing mastery and personalized feedback over numeric scores. Inclusive grading practices prioritize diverse learning styles and reduce biases associated with traditional assessment metrics, fostering a more supportive educational environment. Institutions adopting ungrading methods report increased student engagement and a stronger sense of belonging among underrepresented groups.
Implementing Ungrading: Strategies and Challenges
Implementing ungrading requires clear communication of learning goals and creating criteria that emphasize student growth over numerical scores. Teachers must adopt reflective assessments, peer reviews, and narrative feedback to support deeper understanding and motivation. Challenges include resisting institutional grading norms, addressing student anxiety about undefined evaluations, and ensuring consistent, fair assessment practices across diverse learning environments.
Future Trends in Educational Assessment
Emerging educational assessment trends emphasize ungrading approaches, which prioritize personalized feedback and student reflection over traditional letter grades, fostering deeper learning and intrinsic motivation. Advances in technology enable real-time data analytics and adaptive assessments, supporting competency-based education frameworks that assess mastery rather than completion. Future educational models increasingly integrate qualitative evaluations with digital portfolios, transforming assessment into a dynamic, learner-centered process that aligns with skills needed for the 21st century.
Related Important Terms
Ungrading Movement
The ungrading movement emphasizes student-centered assessment by eliminating traditional numeric or letter grades, fostering intrinsic motivation, deeper learning, and critical thinking skills. This approach prioritizes qualitative feedback and self-assessment, transforming educational practices to support personalized growth and reduce anxiety associated with standardized grading systems.
Standards-Based Grading
Standards-Based Grading (SBG) evaluates student performance by measuring mastery of specific learning goals rather than assigning traditional letter grades, promoting clearer feedback and targeted instruction. This approach enhances student understanding by focusing on competencies aligned with curriculum standards, fostering a growth mindset and personalized learning pathways.
Contract Grading
Contract grading emphasizes clear, student-defined criteria and mutual agreements to assess performance, fostering intrinsic motivation and reducing anxiety compared to traditional grading systems. This method encourages active learning by allowing students to negotiate expectations and focus on mastery rather than competing for points.
Specifications Grading
Specifications grading replaces traditional points-based evaluation with clearly defined criteria, ensuring students meet explicit learning outcomes rather than aiming for partial credit. This method enhances transparency and motivation by aligning assessments directly with course objectives, minimizing grade ambiguity and fostering mastery.
Mastery-Based Assessment
Mastery-based assessment emphasizes students' understanding and skill development over traditional grading scales, promoting personalized learning paths and deeper comprehension. By focusing on demonstrated mastery instead of numeric or letter grades, this approach fosters intrinsic motivation and continuous improvement in educational settings.
Narrative Evaluation
Narrative evaluation emphasizes personalized feedback by detailing students' strengths and areas for improvement, fostering deeper learning without relying on traditional letter grades. This approach contrasts with standard grading systems by promoting intrinsic motivation and a more comprehensive understanding of student progress.
Grade-Free Feedback
Grade-free feedback emphasizes qualitative assessment by providing detailed comments that target student growth and understanding, fostering intrinsic motivation without the pressure of numeric scores. This approach enhances learning by encouraging self-reflection and personalized improvement, contrasting with traditional grading systems that often prioritize ranking over mastery.
Labor-Based Grading
Labor-Based Grading evaluates students strictly on the effort and time invested in their work rather than the accuracy or final product, fostering a learning environment that values process over performance. This approach contrasts traditional grading systems by minimizing anxiety and competition, encouraging consistent engagement and skill development throughout the course.
Self-Assessment Protocol
Self-assessment protocols empower students to critically evaluate their own learning progress, fostering deeper engagement and intrinsic motivation compared to traditional grading systems. This method encourages reflective practices, helping learners identify strengths and areas for improvement without relying on external numeric scores.
Portfolio Assessment
Portfolio assessment emphasizes continuous feedback, critical reflection, and student growth over traditional letter grades, fostering deeper learning and self-awareness. This method allows educators to evaluate a comprehensive body of work, highlighting skills, progress, and creativity rather than isolated test scores.
Grading vs Ungrading Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com