Homeschooling follows a structured curriculum designed by parents or educators to ensure children meet specific academic standards, while unschooling emphasizes child-led learning based on the child's interests and natural curiosity. Both approaches offer personalized education environments but differ in their levels of flexibility and formal instruction. Families often choose between the two based on their educational philosophy and the child's learning style.
Table of Comparison
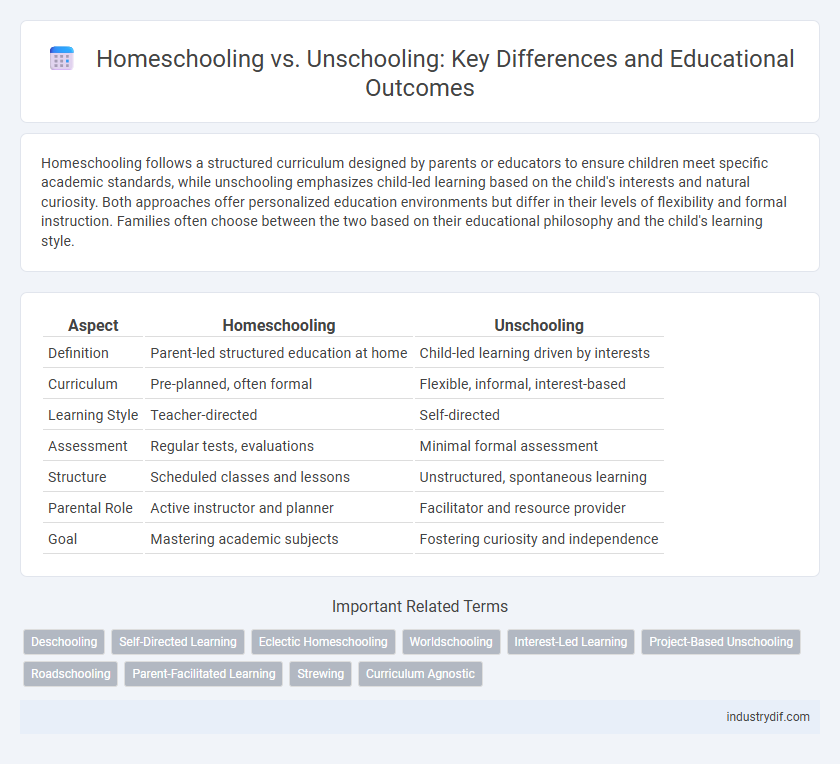
| Aspect | Homeschooling | Unschooling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Parent-led structured education at home | Child-led learning driven by interests |
| Curriculum | Pre-planned, often formal | Flexible, informal, interest-based |
| Learning Style | Teacher-directed | Self-directed |
| Assessment | Regular tests, evaluations | Minimal formal assessment |
| Structure | Scheduled classes and lessons | Unstructured, spontaneous learning |
| Parental Role | Active instructor and planner | Facilitator and resource provider |
| Goal | Mastering academic subjects | Fostering curiosity and independence |
Definition and Core Principles of Homeschooling
Homeschooling is an educational approach where parents design and implement a structured curriculum at home, following state regulations and standardized learning objectives. Core principles of homeschooling emphasize personalized instruction, consistency in academic subjects, and accountability through assessments or portfolio reviews. This method allows flexibility in pacing while maintaining a focus on foundational knowledge across key disciplines such as math, science, language arts, and social studies.
What is Unschooling? Key Concepts Explained
Unschooling is an educational philosophy that emphasizes learner-led, interest-driven learning without a formal curriculum, allowing children to explore subjects at their own pace. Rooted in the belief that natural curiosity fosters deep understanding, unschooling promotes autonomy, creativity, and real-world experiences as primary teaching tools. This approach contrasts with traditional schooling by prioritizing personalized, flexible education tailored to the individual child's interests and developmental readiness.
Legal Requirements: Homeschooling vs Unschooling
Homeschooling typically requires parents to comply with state-specific legal mandates, such as mandatory registration, standardized testing, and curriculum approval, ensuring structured educational accountability. In contrast, unschooling faces more ambiguous legal frameworks, as this learner-driven approach often lacks formal curriculum, making regulatory oversight inconsistent and dependent on local jurisdictions. Understanding these legal distinctions is critical for families choosing between homeschooling and unschooling to ensure compliance and protect their educational choices.
Curriculum Structure: Traditional vs Self-Directed
Homeschooling typically follows a structured curriculum designed to mirror traditional school systems, featuring planned lessons and standardized assessments to ensure comprehensive subject coverage. Unschooling embraces a self-directed learning approach, where students pursue interests at their own pace without predefined curricula or formal evaluations, fostering intrinsic motivation and personalized knowledge acquisition. This fundamental difference in curriculum structure allows homeschooling to maintain consistent academic benchmarks, while unschooling emphasizes experiential learning and adaptability.
Teaching Methodologies and Learning Styles
Homeschooling typically follows a structured curriculum with scheduled lessons, allowing parents to tailor educational content according to their child's academic needs and goals. Unschooling emphasizes learner-driven exploration, where children pursue their interests at their own pace, fostering intrinsic motivation and creativity through real-world experiences. Both methodologies adapt to diverse learning styles, with homeschooling supporting visual and auditory learners through planned instruction, while unschooling benefits kinesthetic and experiential learners by encouraging hands-on activities and self-directed discovery.
Assessment and Progress Tracking
Homeschooling relies on structured assessment methods such as standardized tests, portfolios, and regular progress reports to monitor student learning and ensure curriculum objectives are met. Unschooling emphasizes self-directed learning and often uses informal tracking tools like journals, projects, and observational notes to gauge development and skill acquisition. Both approaches prioritize personalized progress tracking but differ in their reliance on formal evaluation versus experiential documentation.
Socialization Opportunities and Peer Interaction
Homeschooling offers structured socialization opportunities through organized group activities, co-ops, and extracurricular programs, allowing children to interact with diverse peers in planned settings. Unschooling emphasizes organic socialization, encouraging children to engage with community members and pursue interests freely, fostering peer interaction in real-world environments. Both approaches support social development but differ in how they facilitate peer engagement and social skills growth.
Parental Involvement and Role Differences
Parental involvement in homeschooling typically requires structured lesson planning, direct teaching, and consistent assessment, ensuring curriculum alignment with educational standards. In contrast, unschooling emphasizes a parent's role as a facilitator and resource provider, supporting child-led learning driven by the student's interests and intrinsic motivation. These role differences shape the educational environment, with homeschooling parents often acting as primary educators and unschooling parents serving as mentors and guides.
Advantages and Challenges of Homeschooling
Homeschooling offers personalized learning experiences tailored to a child's unique pace, strengths, and interests, fostering academic growth and family bonding. It provides flexibility in curriculum choices and schedules, allowing for a more adaptive and child-centered education. Challenges include the significant time commitment from parents, potential socialization concerns, and the need for access to diverse educational resources and expertise.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Unschooling
Unschooling fosters a child-led learning environment that encourages creativity, independence, and real-world problem-solving skills, often resulting in higher intrinsic motivation compared to traditional homeschooling. However, the lack of structured curriculum and standardized assessment can lead to gaps in foundational knowledge and challenges in socialization or transitioning to formal education settings. Parents must carefully balance freedom with guidance to ensure comprehensive skill development and academic progress.
Related Important Terms
Deschooling
Deschooling serves as a critical transitional phase in both homeschooling and unschooling, allowing learners to disengage from traditional educational structures and develop personalized learning rhythms. This process fosters autonomy, reduces academic pressure, and emphasizes experiential, interest-driven education essential for effective unschooling.
Self-Directed Learning
Homeschooling provides a structured yet flexible environment where parents guide curriculum choices, fostering self-directed learning through tailored educational plans aligned with a child's needs and interests. Unschooling emphasizes learner autonomy by allowing children to explore subjects organically, promoting intrinsic motivation and critical thinking skills through real-world experiences without formal curricula.
Eclectic Homeschooling
Eclectic homeschooling combines structured curriculum elements with flexible teaching methods, allowing parents to tailor education based on their child's interests and learning style. This approach blends traditional subjects with unschooling principles, fostering both academic rigor and self-directed exploration for a balanced learning experience.
Worldschooling
Worldschooling integrates the flexibility of homeschooling with experiential learning across diverse cultures, enriching children's education through real-world experiences. This approach fosters global awareness, adaptability, and personalized education that unschooling emphasizes, but with the added dimension of immersive travel and cultural exposure.
Interest-Led Learning
Interest-led learning in homeschooling allows students to explore subjects driven by personal curiosity, fostering deep engagement and intrinsic motivation. Unschooling amplifies this approach by eliminating formal curricula and schedules, encouraging learners to pursue knowledge through everyday experiences and self-directed projects.
Project-Based Unschooling
Project-based unschooling emphasizes learner-driven projects that integrate real-world skills and interests, fostering critical thinking and creativity outside traditional curricula. This approach contrasts with homeschooling by prioritizing experiential learning over structured lessons, enabling personalized educational pathways tailored to each child's passions and developmental pace.
Roadschooling
Roadschooling combines homeschooling's structured curriculum with unschooling's experiential learning by using travel as a dynamic classroom, fostering adaptability and cultural immersion. Families engaging in roadschooling access diverse educational resources on-the-go, promoting real-world skills and global awareness beyond traditional classroom settings.
Parent-Facilitated Learning
Parent-facilitated learning in homeschooling involves structured guidance and curated curriculum to achieve specific educational goals, while unschooling emphasizes child-led exploration with parents serving as facilitators rather than traditional instructors. This approach in unschooling nurtures intrinsic motivation and personalized growth, contrasting with the more directed and outcome-based strategies found in homeschooling frameworks.
Strewing
In homeschooling, strewing involves deliberately placing educational materials in accessible areas to spark children's curiosity and encourage self-directed learning, enhancing engagement through planned exposure. Unschooling relies heavily on strewing as a core practice, organically offering diverse resources that align with a child's interests, fostering intrinsic motivation without structured curricula.
Curriculum Agnostic
Homeschooling offers a structured approach with customizable curricula tailored by parents, while unschooling is curriculum agnostic, emphasizing child-led learning without formal lesson plans. Both methods prioritize flexibility, but unschooling fosters self-directed exploration, making it distinct in its rejection of standardized educational frameworks.
Homeschooling vs Unschooling Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com