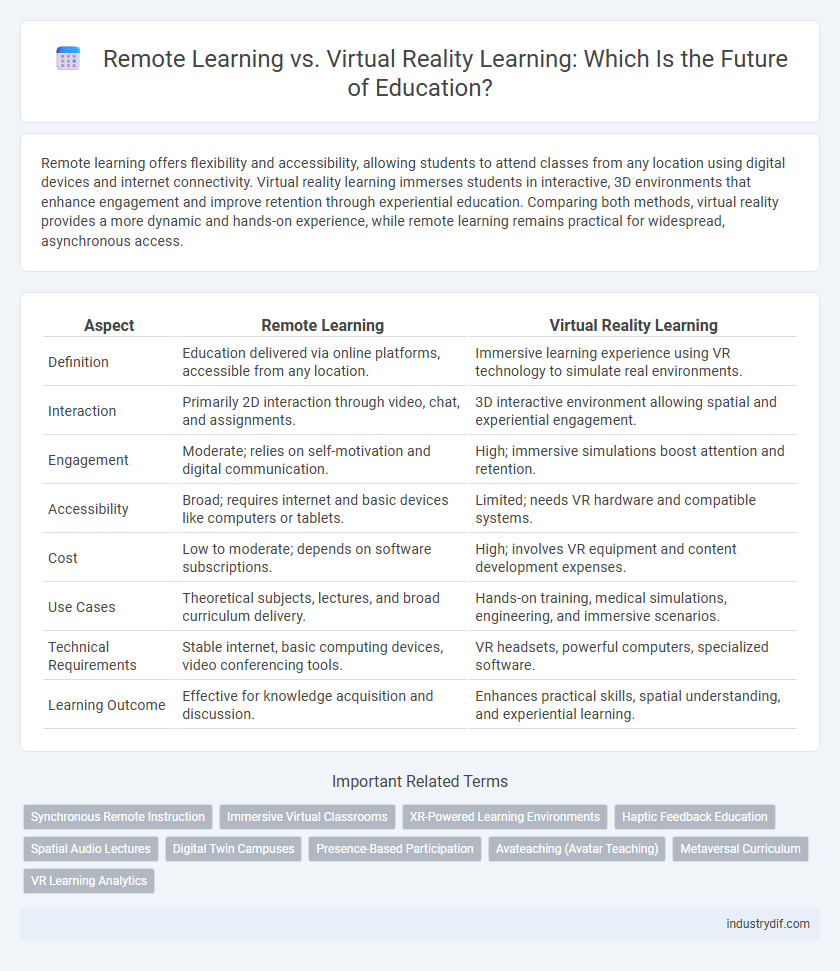
Remote learning offers flexibility and accessibility, allowing students to attend classes from any location using digital devices and internet connectivity. Virtual reality learning immerses students in interactive, 3D environments that enhance engagement and improve retention through experiential education. Comparing both methods, virtual reality provides a more dynamic and hands-on experience, while remote learning remains practical for widespread, asynchronous access.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Remote Learning | Virtual Reality Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Education delivered via online platforms, accessible from any location. | Immersive learning experience using VR technology to simulate real environments. |
| Interaction | Primarily 2D interaction through video, chat, and assignments. | 3D interactive environment allowing spatial and experiential engagement. |
| Engagement | Moderate; relies on self-motivation and digital communication. | High; immersive simulations boost attention and retention. |
| Accessibility | Broad; requires internet and basic devices like computers or tablets. | Limited; needs VR hardware and compatible systems. |
| Cost | Low to moderate; depends on software subscriptions. | High; involves VR equipment and content development expenses. |
| Use Cases | Theoretical subjects, lectures, and broad curriculum delivery. | Hands-on training, medical simulations, engineering, and immersive scenarios. |
| Technical Requirements | Stable internet, basic computing devices, video conferencing tools. | VR headsets, powerful computers, specialized software. |
| Learning Outcome | Effective for knowledge acquisition and discussion. | Enhances practical skills, spatial understanding, and experiential learning. |
Introduction to Remote Learning and Virtual Reality Learning
Remote learning utilizes digital platforms to deliver education beyond traditional classrooms, enabling access through internet-connected devices such as laptops and tablets. Virtual reality learning immerses students in interactive, 3D environments that simulate real-world or conceptual scenarios, enhancing engagement and retention through experiential learning. Both methods leverage technology to expand educational opportunities, with remote learning emphasizing accessibility and virtual reality focusing on immersive experience.
Key Differences Between Remote and VR Learning
Remote learning primarily relies on video conferencing and digital platforms to facilitate education, offering flexibility and accessibility from any location with internet access. Virtual Reality (VR) learning immerses students in interactive, 3D environments that simulate real-world scenarios for experiential learning and enhanced engagement. Unlike remote learning's passive content delivery, VR promotes active participation and spatial understanding, which can improve retention and practical skills acquisition.
Technological Requirements for Each Modality
Remote learning primarily relies on stable internet connections, computers or tablets, and video conferencing software such as Zoom or Microsoft Teams, ensuring accessibility for most students. Virtual reality learning demands more advanced technology including VR headsets like Oculus Quest, powerful computers with high processing capabilities, and specialized software to create immersive educational experiences. Both modalities require technical support and user training, but VR learning's hardware and software needs are significantly more complex and costly.
Engagement Levels in Remote vs. VR Learning
Remote learning often faces challenges in maintaining student engagement due to limited interaction and passive content delivery. Virtual reality learning significantly enhances engagement levels by providing immersive, interactive experiences that stimulate multiple senses and promote active participation. Studies show VR environments boost attention span and information retention, making them more effective for deep learning compared to traditional remote methods.
Accessibility and Inclusivity Considerations
Remote learning enables broad accessibility by allowing students from diverse geographic locations and socioeconomic backgrounds to participate without the need for physical presence. Virtual reality learning enhances inclusivity by providing immersive, interactive environments tailored to different learning styles and needs, including those with disabilities. However, VR systems may present accessibility challenges related to cost, hardware requirements, and potential usability barriers for students with certain impairments.
Pedagogical Approaches in Both Learning Environments
Remote learning primarily relies on asynchronous content delivery and synchronous video conferencing, emphasizing self-paced study and real-time interaction to accommodate diverse learning styles. Virtual reality learning incorporates immersive, experiential approaches that enhance engagement through simulated environments, promoting active learning and spatial understanding. Both methods integrate constructivist principles but differ in sensory input and interaction depth, influencing cognitive load and knowledge retention.
Cost Comparison: Remote Learning vs Virtual Reality
Remote learning incurs lower upfront costs, relying mainly on internet access and basic devices, while virtual reality learning requires substantial investment in VR headsets and compatible hardware. Maintenance and software updates for VR environments add to ongoing expenses, contrasting with the minimal technical support often needed for remote learning platforms. Despite higher costs, VR learning offers immersive experiences that can enhance engagement and comprehension beyond remote learning's traditional video and text methods.
Real-World Applications and Case Studies
Remote learning enables access to education across diverse geographic locations, exemplified by platforms like Coursera and Khan Academy that support millions of learners worldwide. Virtual reality learning offers immersive experiences demonstrated by case studies such as medical training simulations at Stanford University, which improve practical skills in a controlled environment. Real-world applications highlight VR's potential to enhance hands-on learning while remote learning excels in scalability and accessibility.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Method
Remote learning often faces challenges such as limited student engagement, technological disparities, and reduced hands-on interaction, which can hinder effective comprehension. Virtual reality learning, despite offering immersive educational experiences, encounters limitations including high costs, accessibility issues, and potential motion sickness among users. Both methods require significant infrastructure and training investments, posing barriers to widespread adoption in diverse educational settings.
Future Trends in Digital Education Technology
Remote learning continues to evolve with advancements in AI-driven platforms that personalize educational content to individual student needs, improving engagement and retention. Virtual reality learning offers immersive, interactive experiences that enhance comprehension and practical skills through simulated environments, making it particularly effective for complex subjects like medicine and engineering. Future trends indicate an integration of remote learning's accessibility with VR's experiential benefits, supported by 5G connectivity and augmented reality tools to create hybrid, adaptive educational ecosystems.
Related Important Terms
Synchronous Remote Instruction
Synchronous remote instruction utilizes live video conferencing tools such as Zoom and Microsoft Teams to facilitate real-time interaction between educators and students, ensuring immediate feedback and engagement. Virtual reality learning enhances this experience by immersing students in interactive 3D environments, promoting experiential learning and improving knowledge retention compared to traditional remote classrooms.
Immersive Virtual Classrooms
Immersive virtual classrooms enhance remote learning by providing students with interactive 3D environments that simulate real-world classroom experiences, improving engagement and knowledge retention. Unlike traditional remote learning, virtual reality integrates spatial audio, gesture recognition, and real-time collaboration tools to create a more dynamic and personalized educational setting.
XR-Powered Learning Environments
XR-powered learning environments integrate augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and mixed reality (MR) to create immersive educational experiences that enhance engagement and retention compared to traditional remote learning platforms. These technologies provide interactive simulations and real-time feedback, enabling personalized skill development and deeper conceptual understanding across diverse subjects.
Haptic Feedback Education
Haptic feedback education enhances remote learning by delivering tactile experiences that simulate real-world interactions, improving student engagement and knowledge retention. Virtual reality learning with integrated haptic technology offers immersive, hands-on practice environments, making complex subjects like anatomy and engineering more accessible and effective.
Spatial Audio Lectures
Spatial audio lectures in remote learning environments enhance auditory immersion, allowing students to perceive sound direction and distance, which improves focus and retention. Virtual reality learning integrates spatial audio with 3D visuals, creating a multisensory experience that fosters deeper engagement and realistic understanding of complex educational content.
Digital Twin Campuses
Remote learning offers flexibility and accessibility through online platforms, while virtual reality learning leverages immersive Digital Twin Campuses to simulate real-world educational environments, enhancing student engagement and spatial understanding. Digital Twin Campuses create accurate, interactive replicas of physical schools, enabling immersive simulations that support collaborative learning and practical training in a controlled virtual space.
Presence-Based Participation
Presence-based participation in remote learning often relies on video conferencing and chat interactions, which can limit the sense of engagement and immersion. Virtual reality learning enhances presence by creating interactive, three-dimensional environments that simulate real-world contexts, fostering deeper cognitive involvement and active collaboration.
Avateaching (Avatar Teaching)
Remote learning leverages online platforms to deliver education flexibly, while virtual reality learning, such as Avateaching, immerses students in interactive 3D environments using avatars to enhance engagement and retention. Avateaching combines the benefits of avatar-based instruction with real-time feedback, enabling personalized learning experiences that simulate classroom interaction in a virtual space.
Metaversal Curriculum
Remote learning relies on digital platforms to deliver traditional coursework, while virtual reality learning immerses students in interactive, 3D environments that enhance engagement and retention. The metaversal curriculum integrates VR technology to create adaptive, experiential learning paths that personalize education and foster collaboration across global classrooms.
VR Learning Analytics
Virtual Reality Learning Analytics provide immersive data insights by tracking student interactions, engagement levels, and real-time cognitive responses within 3D environments, outperforming traditional remote learning metrics. These analytics enable personalized adaptive learning pathways, enhancing knowledge retention and skill acquisition through precise behavioral and performance analysis.
Remote Learning vs Virtual Reality Learning Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com