Traditional classrooms rely on teacher-led instruction where students absorb information during class and complete assignments at home, which can limit active engagement and personalized learning. Flipped classrooms reverse this model by having students review lecture materials independently before class, allowing in-person sessions to focus on interactive activities and collaborative problem-solving. This approach enhances student participation, deeper understanding, and accommodates diverse learning paces.
Table of Comparison
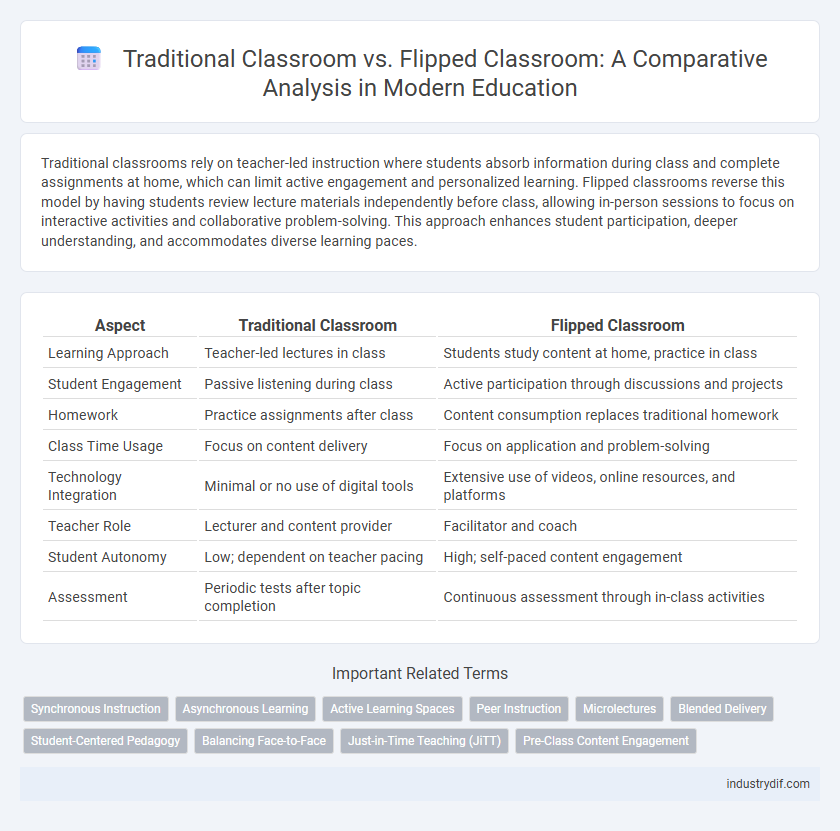
| Aspect | Traditional Classroom | Flipped Classroom |
|---|---|---|
| Learning Approach | Teacher-led lectures in class | Students study content at home, practice in class |
| Student Engagement | Passive listening during class | Active participation through discussions and projects |
| Homework | Practice assignments after class | Content consumption replaces traditional homework |
| Class Time Usage | Focus on content delivery | Focus on application and problem-solving |
| Technology Integration | Minimal or no use of digital tools | Extensive use of videos, online resources, and platforms |
| Teacher Role | Lecturer and content provider | Facilitator and coach |
| Student Autonomy | Low; dependent on teacher pacing | High; self-paced content engagement |
| Assessment | Periodic tests after topic completion | Continuous assessment through in-class activities |
Overview of Traditional Classroom Methods
Traditional classroom methods rely on teacher-centered instruction, where educators deliver lectures and students passively absorb information during class time. This approach emphasizes direct teaching, rote memorization, and standardized assessments to evaluate student understanding. Despite criticism for limited student engagement, traditional classrooms remain prevalent in many educational institutions worldwide due to their structured environment and predictable routines.
Flipped Classroom: A Modern Educational Approach
Flipped classroom methods enhance student engagement by delivering instructional content online outside of class, allowing in-person sessions to focus on interactive activities and personalized support. This modern educational approach leverages technology to foster active learning, critical thinking, and collaboration among students. Studies show that flipped classrooms improve academic performance and increase student motivation compared to traditional lecture-based models.
Key Differences Between Traditional and Flipped Classrooms
Traditional classrooms emphasize direct instruction from teachers with students passively receiving information during class time, while flipped classrooms invert this model by delivering instructional content, often via video lectures, outside of class for self-paced learning. In flipped classrooms, class time is dedicated to interactive activities, problem-solving, and personalized support, promoting active student engagement and collaboration. This approach contrasts with the traditional model's focus on lectures, allowing flipped classrooms to better accommodate diverse learning styles and foster deeper understanding.
Instructional Delivery Techniques
Traditional classrooms rely on direct instruction where teachers deliver lectures and students passively receive information. Flipped classrooms invert this approach by providing instructional content online for students to study before class, allowing in-person time to focus on interactive activities and personalized support. This shift enhances engagement, deepens understanding, and encourages active learning through collaborative problem-solving and discussion.
Student Engagement and Participation
Traditional classrooms often limit student engagement to passive listening and note-taking, resulting in lower participation levels. Flipped classrooms enhance student involvement by assigning pre-class content review, which allows in-class time to focus on interactive activities and collaborative problem-solving. Research indicates that flipped learning models increase student motivation and active participation, leading to improved academic performance and deeper understanding.
Teacher’s Role: Facilitator vs. Instructor
In a traditional classroom, the teacher primarily acts as an instructor, delivering lectures and directing the learning process to ensure content comprehension. In contrast, the flipped classroom positions the teacher as a facilitator, guiding students through interactive activities and personalized support based on pre-class preparation. This shift enhances student engagement and encourages active learning by promoting collaboration and critical thinking skills.
Assessment Methods and Feedback
Traditional classroom assessment methods primarily rely on periodic quizzes, exams, and in-class participation, providing feedback mainly through graded assignments and teacher commentary. Flipped classroom models emphasize formative assessments such as interactive quizzes, peer evaluations, and real-time feedback during in-class activities, fostering continuous improvement. The flipped approach enhances personalized feedback by leveraging technology to track student progress and tailor instruction accordingly.
Technology Integration in Education
Technology integration in education transforms traditional classrooms by incorporating digital tools that enhance interactive learning and real-time feedback. Flipped classrooms leverage technology to deliver instructional content online, allowing class time to focus on collaborative activities and personalized support. This approach promotes student engagement and fosters deeper understanding through multimedia resources and digital collaboration platforms.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Both Models
Traditional classrooms offer structured environments with direct teacher-led instruction, promoting discipline and immediate feedback, but they can limit student engagement and personalized learning. Flipped classrooms enhance active learning by allowing students to review content at their own pace outside of class, fostering collaboration and critical thinking during in-person sessions, though they require reliable technology access and strong self-motivation. Both models present trade-offs between consistency and flexibility, making the choice dependent on specific educational goals and learner needs.
Future Trends in Classroom Learning
Emerging trends in classroom learning emphasize the integration of technology to create hybrid models that blend traditional classroom instruction with flipped classroom approaches. Data shows that flipped classrooms enhance student engagement by enabling personalized learning experiences through pre-class video lectures and interactive in-class activities. Future educational environments are expected to further leverage artificial intelligence and adaptive learning platforms to optimize curriculum delivery and improve learning outcomes.
Related Important Terms
Synchronous Instruction
Synchronous instruction in traditional classrooms involves real-time teacher-led lectures where all students participate simultaneously, allowing immediate feedback and direct interaction. In flipped classrooms, synchronous sessions focus on active learning activities such as discussions and problem-solving, maximizing the use of live class time for deeper engagement rather than passive content delivery.
Asynchronous Learning
Asynchronous learning in flipped classrooms allows students to engage with instructional videos and materials at their own pace, promoting deeper understanding compared to traditional classrooms where learning happens synchronously. This approach enhances flexibility, supports diverse learning styles, and improves student retention by shifting direct instruction outside of class time.
Active Learning Spaces
Active learning spaces in traditional classrooms often limit student interaction due to fixed seating arrangements and teacher-centered instruction, whereas flipped classrooms transform these spaces into dynamic environments that promote collaboration, critical thinking, and hands-on activities. By reallocating class time for interactive exercises, flipped classrooms enhance student engagement and deepen understanding through peer discussions and practical application.
Peer Instruction
Peer instruction in traditional classrooms typically involves occasional group discussions led by the instructor, whereas flipped classrooms embed peer instruction more deeply by having students engage in collaborative problem-solving before class. This shift enhances active learning, improves conceptual understanding, and fosters critical thinking skills through continuous peer interaction.
Microlectures
Microlectures in flipped classrooms compress essential content into brief, focused segments, enhancing student engagement and comprehension compared to extended traditional lectures. This approach leverages multimedia resources and active learning strategies to improve knowledge retention and allow in-class time for collaborative problem-solving and personalized instruction.
Blended Delivery
Blended delivery in education combines traditional classroom methods with flipped classroom strategies, enhancing student engagement and personalized learning by integrating face-to-face instruction with digital resources. This approach promotes active learning and enables educators to tailor content delivery based on student needs, improving comprehension and retention rates.
Student-Centered Pedagogy
Student-centered pedagogy in traditional classrooms emphasizes teacher-led instruction with limited student autonomy, while flipped classrooms prioritize active learning by having students engage with instructional content at home and participate in collaborative, problem-solving activities during class time. Research shows flipped classrooms enhance student engagement, critical thinking, and retention by fostering a more personalized and interactive learning environment.
Balancing Face-to-Face
Balancing face-to-face interaction in traditional classrooms allows for direct teacher guidance and immediate feedback, fostering student engagement and collaborative learning. Flipped classrooms maximize in-person time by shifting lectures online, dedicating class sessions to hands-on activities and personalized support, enhancing active learning and deeper comprehension.
Just-in-Time Teaching (JiTT)
Just-in-Time Teaching (JiTT) enhances the flipped classroom model by using pre-class assignments to identify student misconceptions and tailor in-class activities for immediate clarification, improving engagement and comprehension. Unlike traditional classrooms where content delivery dominates, JiTT fosters active learning through timely feedback and interaction, optimizing classroom time for deeper understanding.
Pre-Class Content Engagement
In traditional classrooms, pre-class content engagement is minimal as students primarily receive foundational knowledge during in-person lectures. Flipped classrooms enhance pre-class engagement by requiring students to interact with instructional videos, quizzes, and readings beforehand, fostering better preparedness and active participation in subsequent discussions.
Traditional Classroom vs Flipped Classroom Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com