Traditional learning relies heavily on teacher-led instruction during class time, where students passively receive information. In contrast, the flipped classroom model encourages students to engage with lecture materials at home, allowing class time to be used for interactive, hands-on activities that reinforce understanding. This shift promotes active learning and increases student participation, leading to improved retention and application of knowledge.
Table of Comparison
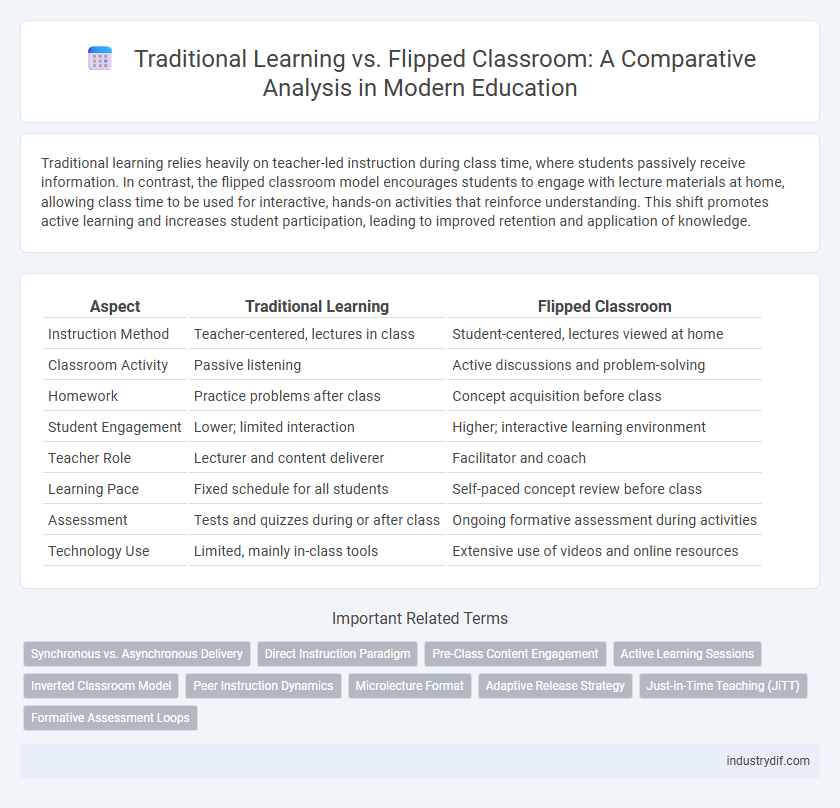
| Aspect | Traditional Learning | Flipped Classroom |
|---|---|---|
| Instruction Method | Teacher-centered, lectures in class | Student-centered, lectures viewed at home |
| Classroom Activity | Passive listening | Active discussions and problem-solving |
| Homework | Practice problems after class | Concept acquisition before class |
| Student Engagement | Lower; limited interaction | Higher; interactive learning environment |
| Teacher Role | Lecturer and content deliverer | Facilitator and coach |
| Learning Pace | Fixed schedule for all students | Self-paced concept review before class |
| Assessment | Tests and quizzes during or after class | Ongoing formative assessment during activities |
| Technology Use | Limited, mainly in-class tools | Extensive use of videos and online resources |
Understanding Traditional Learning Models
Traditional learning models emphasize teacher-centered instruction where educators deliver lectures and students passively receive information in a classroom setting. This approach relies heavily on memorization and standardized assessments to measure student understanding. Despite its widespread use, traditional learning often limits active student engagement and personalized learning opportunities.
Defining the Flipped Classroom Approach
The flipped classroom approach redefines traditional learning by delivering instructional content outside of the classroom, often through video lectures or digital resources, enabling students to engage actively in problem-solving and discussions during class time. This model promotes deeper understanding by shifting passive listening to active participation, fostering collaboration and critical thinking skills. Educational studies highlight increased student engagement and improved academic performance as key benefits of adopting the flipped classroom methodology.
Key Differences Between Traditional and Flipped Classrooms
Traditional learning primarily relies on teacher-centered instruction where students receive lectures in class and complete assignments at home, while flipped classrooms invert this model by having students review instructional content independently before class and engage in interactive, application-based activities during class time. In flipped classrooms, active learning strategies such as collaborative problem-solving and hands-on projects enhance student engagement and comprehension, contrasting with the passive reception of information typical in traditional settings. The shift from passive to active learning environments in flipped classrooms supports deeper understanding, immediate feedback, and personalized teacher support, key differentiators from the conventional lecture-focused approach.
Student Engagement in Both Learning Environments
Traditional learning often limits student engagement to passive listening and note-taking during lectures, which can reduce active participation and critical thinking. In contrast, flipped classrooms enhance engagement by encouraging students to prepare before class and participate in interactive, problem-solving activities during sessions. Research indicates that flipped classrooms foster higher levels of motivation, collaboration, and deeper understanding compared to traditional instructional methods.
Role of Teachers: Facilitator vs Lecturer
In traditional learning environments, teachers primarily act as lecturers who deliver content directly to students through lectures and presentations. In flipped classrooms, the teacher's role shifts to being a facilitator who guides students in active, student-centered learning activities and critical discussions. This transformation enhances personalized support, encourages collaboration, and fosters deeper understanding of the subject matter.
Impact on Learning Outcomes
Traditional learning relies on direct instruction with students passively receiving information, often resulting in lower engagement and retention rates compared to active learning models. Flipped classroom approaches, where students review content independently and use class time for interactive problem-solving, have demonstrated significant improvements in critical thinking skills and knowledge application. Studies report that flipped classrooms increase student performance by up to 30% and foster deeper understanding through collaborative activities.
Technological Integration in Flipped Classrooms
Flipped classrooms leverage advanced technological tools such as educational videos, interactive simulations, and online discussion platforms to enhance student engagement and personalize learning experiences. This integration enables learners to access content at their own pace outside the classroom, fostering deeper understanding and critical thinking during in-person sessions. Compared to traditional learning, where technology use is often limited to occasional presentations, flipped classrooms consistently incorporate digital resources to transform instructional delivery and student collaboration.
Flexibility and Accessibility of Learning
Traditional learning typically follows a fixed schedule and location, limiting flexibility and accessibility for students with diverse needs. The flipped classroom model enhances learning flexibility by allowing students to access instructional content online at their convenience and focus class time on interactive activities. This approach improves accessibility for learners with varying schedules and promotes personalized education experiences.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Model
Traditional learning faces challenges such as limited student engagement and passive knowledge absorption, which can hinder effective understanding and retention. The flipped classroom model struggles with unequal access to technology and digital resources, creating barriers for students without reliable internet or devices. Both models require significant adjustments in teaching strategies and can encounter resistance from educators and learners accustomed to conventional methods.
Future Trends in Educational Delivery Methods
Future trends in educational delivery methods emphasize personalized learning through adaptive technologies, integrating AI-driven platforms to customize content based on student performance. Flipped classrooms leverage these innovations by promoting active, student-centered learning outside traditional lecture formats, enhancing engagement and retention. Traditional learning methods face transformation as hybrid models combine in-person interaction with digital resources, preparing education systems for flexible, scalable, and data-informed instruction.
Related Important Terms
Synchronous vs. Asynchronous Delivery
Traditional learning primarily relies on synchronous delivery, where students engage in real-time instruction and immediate feedback occurs during scheduled class times; this fosters direct interaction but limits flexibility. In contrast, flipped classrooms emphasize asynchronous delivery through pre-recorded lectures and independent study, enabling students to learn at their own pace while reserving synchronous sessions for collaborative discussions and problem-solving activities.
Direct Instruction Paradigm
The Direct Instruction Paradigm centralizes teacher-led explanations and structured lessons, contrasting with the flipped classroom model where content delivery shifts outside class to promote active learning during face-to-face sessions. Traditional learning emphasizes systematic skill acquisition through lectures, while flipped classrooms prioritize student engagement and hands-on application in classroom time.
Pre-Class Content Engagement
Pre-class content engagement in flipped classrooms significantly enhances student preparedness by providing accessible video lectures and interactive materials, promoting active learning before in-person sessions. Traditional learning often limits pre-class interaction, resulting in passive knowledge acquisition and reduced student participation during classroom activities.
Active Learning Sessions
Active learning sessions in flipped classrooms engage students through hands-on activities and real-time problem-solving, enhancing comprehension and retention compared to traditional lecture-based learning. This shift fosters critical thinking and collaboration, making education more interactive and student-centered.
Inverted Classroom Model
The Inverted Classroom Model transforms traditional learning by delivering instructional content online outside of class, allowing face-to-face sessions to focus on interactive, application-based activities that enhance student engagement and comprehension. This approach leverages multimedia resources and peer collaboration, resulting in improved critical thinking skills and higher retention rates compared to conventional lecture-based methods.
Peer Instruction Dynamics
Peer instruction dynamics in traditional learning often rely on teacher-led explanations, limiting student interaction and collaborative problem-solving opportunities. In contrast, flipped classrooms foster active peer engagement by encouraging students to discuss concepts and clarify doubts before class, enhancing deeper understanding and retention.
Microlecture Format
The microlecture format in flipped classrooms enhances student engagement by delivering concise, focused video content prior to in-class activities, allowing for deeper interaction and active learning during face-to-face sessions. Traditional learning often relies on extended lectures that can hinder retention, whereas microlectures optimize cognitive load and accommodate diverse learning paces, improving overall academic performance.
Adaptive Release Strategy
The Adaptive Release Strategy enhances the flipped classroom model by customizing content access based on student performance and engagement, ensuring personalized learning pathways. Traditional learning typically lacks this flexibility, often delivering uniform material without real-time adaptation to individual student needs.
Just-in-Time Teaching (JiTT)
Just-in-Time Teaching (JiTT) enhances flipped classrooms by using pre-class assignments to identify student misconceptions, allowing instructors to tailor in-class activities for deeper understanding and immediate feedback. Unlike traditional learning, which delivers content uniformly, JiTT promotes active engagement and personalized learning, improving knowledge retention and critical thinking skills.
Formative Assessment Loops
Formative assessment loops in traditional learning often rely on periodic quizzes and teacher feedback during lectures, which can delay student progress evaluation. The flipped classroom model integrates continuous, real-time formative assessments through pre-class video quizzes and in-class interactive activities, enabling immediate feedback and personalized learning adjustments.
Traditional Learning vs Flipped Classroom Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com