Broadcast TV offers scheduled programming with broad audience reach, delivering content through traditional airwaves, while FAST Channels (Free Ad-Supported Streaming TV) provide on-demand, internet-based streaming with a diverse range of niche entertainment options. FAST Channels attract viewers seeking personalized and flexible viewing experiences without subscription fees, leveraging targeted advertising to generate revenue. Both platforms serve the entertainment pet industry by showcasing pet-related content, but FAST Channels enable more dynamic and specialized programming to engage pet enthusiasts.
Table of Comparison
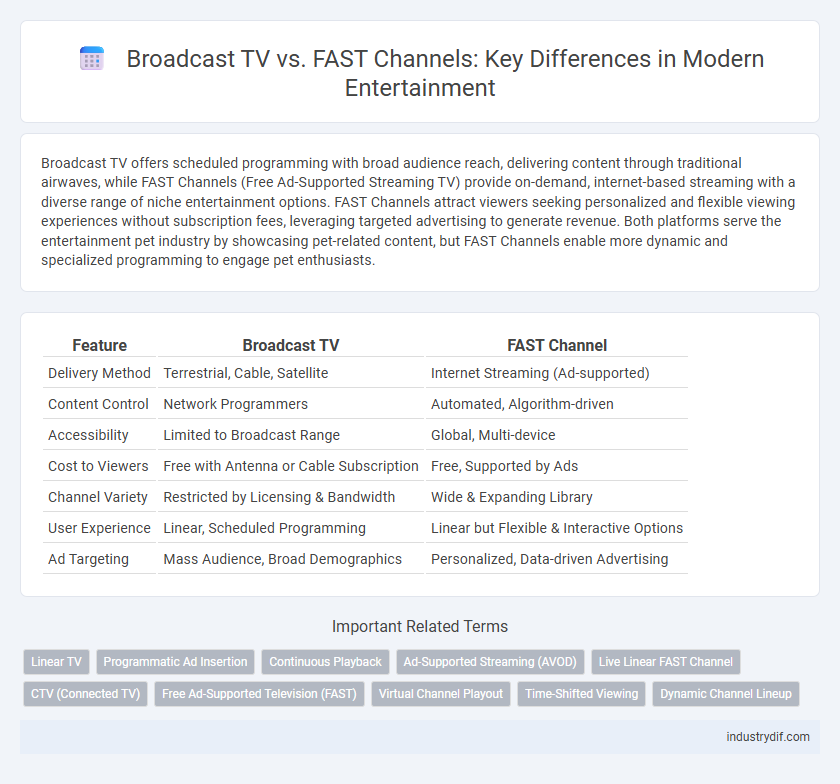
| Feature | Broadcast TV | FAST Channel |
|---|---|---|
| Delivery Method | Terrestrial, Cable, Satellite | Internet Streaming (Ad-supported) |
| Content Control | Network Programmers | Automated, Algorithm-driven |
| Accessibility | Limited to Broadcast Range | Global, Multi-device |
| Cost to Viewers | Free with Antenna or Cable Subscription | Free, Supported by Ads |
| Channel Variety | Restricted by Licensing & Bandwidth | Wide & Expanding Library |
| User Experience | Linear, Scheduled Programming | Linear but Flexible & Interactive Options |
| Ad Targeting | Mass Audience, Broad Demographics | Personalized, Data-driven Advertising |
Broadcast TV vs FAST Channel: Key Differences
Broadcast TV delivers scheduled content through traditional over-the-air signals, offering wide accessibility without internet dependency, whereas FAST (Free Ad-Supported Streaming TV) channels provide on-demand streaming via internet platforms, integrating targeted advertising for personalized viewer experiences. Broadcast TV relies on geographic-specific programming and fixed time slots, while FAST channels offer flexible, diverse content libraries with algorithm-driven recommendations. The primary distinction lies in Broadcast TV's linear model versus FAST's digital, interactive format catering to evolving consumer preferences for convenience and choice.
Evolution of Entertainment: From Broadcast to FAST
Broadcast TV traditionally dominated entertainment with scheduled programming and limited viewer control, relying heavily on network advertising revenue. FAST (Free Ad-Supported Streaming TV) channels have evolved by offering on-demand, personalized content with seamless streaming experiences, integrating advanced data analytics for targeted advertising. This shift reflects a broader industry trend toward digital consumption, enhanced user engagement, and flexible monetization strategies.
Content Delivery Methods Compared
Broadcast TV transmits content via terrestrial, satellite, or cable signals directly to viewers, offering scheduled programming to a broad audience with high reliability and reach. FAST (Free Ad-Supported Streaming TV) channels deliver content through internet streaming platforms, leveraging on-demand access and targeted advertising to engage viewers with personalized experiences. While broadcast TV relies on traditional infrastructure and fixed schedules, FAST channels optimize content delivery by harnessing adaptive bitrates and user data analytics for dynamic programming.
Audience Reach: Traditional TV vs FAST Channels
Traditional broadcast TV maintains a substantial audience reach with millions tuning in daily through established cable and satellite subscriptions. FAST (Free Ad-Supported Streaming TV) channels rapidly expand access by leveraging internet connectivity, attracting cord-cutters and younger demographics seeking cost-free content. The convergence of digital accessibility with varied programming on FAST channels challenges traditional TV's dominance in audience engagement and market penetration.
Monetization Models: Ad-Supported vs Scheduled Programming
Broadcast TV monetizes primarily through scheduled programming with fixed ad slots sold to advertisers, generating consistent revenue based on viewer ratings and time slots. FAST (Free Ad-supported Streaming TV) channels leverage dynamic ad insertion and targeted advertising, optimizing monetization by delivering personalized ads in real-time to niche audiences. This model enhances ad revenue potential through data-driven strategies and flexible programming schedules, differentiating FAST from traditional broadcast TV monetization.
Content Discovery and User Experience
Broadcast TV offers limited content discovery with scheduled programming and minimal personalization, often leading to passive viewing. FAST Channels (Free Ad-Supported Streaming TV) enhance user experience by providing on-demand access, curated content libraries, and algorithm-driven recommendations that facilitate active content exploration. These advanced discovery features in FAST Channels create a more engaging and user-centric entertainment environment compared to traditional broadcast television.
Licensing and Distribution in Broadcast vs FAST
Broadcast TV licensing typically involves complex, territory-specific rights and long-term contracts with content owners, ensuring exclusive distribution over linear channels. FAST (Free Ad-Supported Streaming TV) channels leverage more flexible, often global digital licenses, allowing for on-demand and ad-supported streaming models with broader distribution reach. This shift in licensing and distribution models enables FAST channels to rapidly expand content libraries while minimizing traditional broadcasting restrictions.
Data Analytics: Measuring Success across Platforms
Broadcast TV relies on traditional ratings systems such as Nielsen to measure viewer engagement, focusing on average viewership numbers and demographic breakdowns. FAST channels leverage advanced data analytics, using real-time metrics like viewer retention, interaction rates, and targeted ad performance to optimize content delivery and revenue streams. Integrating cross-platform data provides broadcasters with a comprehensive understanding of audience behavior, enhancing strategic programming and advertising decisions.
Opportunities for Content Creators
Broadcast TV offers content creators access to broad, established audiences and reliable revenue streams through traditional advertising and syndication deals. FAST Channels (Free Ad-supported Streaming Television) provide opportunities for niche targeting, flexible content formats, and expanded digital monetization via programmatic ads and direct-to-consumer access. Combining broadcast reach with FAST's data-driven insights enables creators to optimize content distribution and maximize audience engagement.
The Future of Entertainment: Broadcast TV and FAST Channel Integration
Broadcast TV and FAST (Free Ad-Supported Streaming TV) channels are converging to redefine the entertainment landscape by offering seamless integration of live programming and on-demand content. This fusion leverages traditional broadcast reliability with the personalized, data-driven ad targeting of FAST platforms, enhancing viewer engagement and monetization potential. The future of entertainment lies in hybrid models that combine broad audience reach with digital agility, driving industry innovation and audience retention.
Related Important Terms
Linear TV
Broadcast TV delivers scheduled programming via terrestrial signals, ensuring wide accessibility without internet dependency, while FAST channels offer free ad-supported streaming on-demand content through internet-connected devices. Linear TV remains essential in broadcast for real-time event viewing, but FAST channels increasingly attract audiences seeking flexible, digital-first viewing experiences.
Programmatic Ad Insertion
Programmatic ad insertion in Broadcast TV relies on linear scheduling with limited targeting, whereas FAST channels leverage dynamic, data-driven ad placement for hyper-targeted viewer engagement. FAST's programmatic capabilities enable real-time optimization and personalized advertising, significantly enhancing monetization opportunities compared to traditional broadcast methods.
Continuous Playback
Broadcast TV offers scheduled programming with fixed airtime slots, limiting viewer control over continuous playback, whereas FAST (Free Ad-Supported Streaming TV) channels provide seamless continuous playback with on-demand access, enhancing viewer convenience through uninterrupted content streaming. FAST channels leverage advanced streaming technology to deliver zero-lag transitions between shows, optimizing user engagement compared to traditional broadcast TV's linear format.
Ad-Supported Streaming (AVOD)
Broadcast TV maintains a broad audience reach with traditional linear programming, while FAST Channels leverage Ad-Supported Streaming (AVOD) models to deliver targeted, data-driven ads that maximize viewer engagement and advertiser ROI. AVOD on FAST platforms offers real-time metrics and dynamic ad insertion, enhancing personalization and monetization beyond the capabilities of conventional broadcast television.
Live Linear FAST Channel
Live Linear FAST Channels deliver real-time, scheduled programming over the internet without subscription fees, combining the familiarity of traditional broadcast TV with the flexibility of streaming. These channels leverage ad-supported streaming technology to reach audiences seeking live sports, news, and entertainment, optimizing viewer engagement compared to conventional cable broadcasts.
CTV (Connected TV)
Broadcast TV reaches traditional audiences through over-the-air signals, while FAST channels leverage Connected TV devices to deliver ad-supported streaming content directly to smart TVs, enhancing viewer engagement with targeted, real-time ads. Connected TV's integration with FAST channels provides advertisers access to granular user data, enabling precision marketing and interactive experiences beyond conventional broadcast capabilities.
Free Ad-Supported Television (FAST)
Free Ad-Supported Television (FAST) channels offer viewers a cost-effective alternative to traditional Broadcast TV by delivering a wide range of on-demand and linear content without subscription fees. As FAST platforms leverage targeted advertising technology, they provide advertisers with enhanced audience segmentation and measurable engagement metrics compared to conventional broadcast networks.
Virtual Channel Playout
Broadcast TV relies on traditional over-the-air signals with fixed virtual channel playouts tied to specific frequencies, while FAST channels use adaptive virtual channel playout that dynamically assembles content streams for internet-delivered linear viewing. FAST platforms optimize virtual channel playout through programmatic ad insertion and real-time content curation, enhancing viewer engagement beyond the static scheduling of broadcast TV.
Time-Shifted Viewing
Broadcast TV offers limited time-shifted viewing options, primarily through DVR or scheduled recordings, whereas FAST (Free Ad-Supported Streaming TV) channels provide seamless on-demand access with extensive time-shifted content available anytime. FAST channels leverage cloud-based streaming technology to enhance viewer flexibility, allowing audiences to watch programs at their convenience without the constraints of traditional broadcast schedules.
Dynamic Channel Lineup
Broadcast TV offers a static channel lineup with fixed programming schedules, limiting viewer flexibility. FAST channels feature a dynamic channel lineup that adapts in real-time to audience preferences and trending content, enhancing user engagement through personalized viewing experiences.
Broadcast TV vs FAST Channel Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com