Linear TV maintains a loyal audience through scheduled programming and familiar viewing habits, offering a reliable platform for entertainment pet content. FAST channels (Free Ad-supported Streaming TV) provide more flexibility with on-demand access and a wide variety of niche pet entertainment options. Both formats cater to different viewer preferences, with Linear TV emphasizing appointment viewing and FAST channels delivering personalized, cost-effective streaming experiences.
Table of Comparison
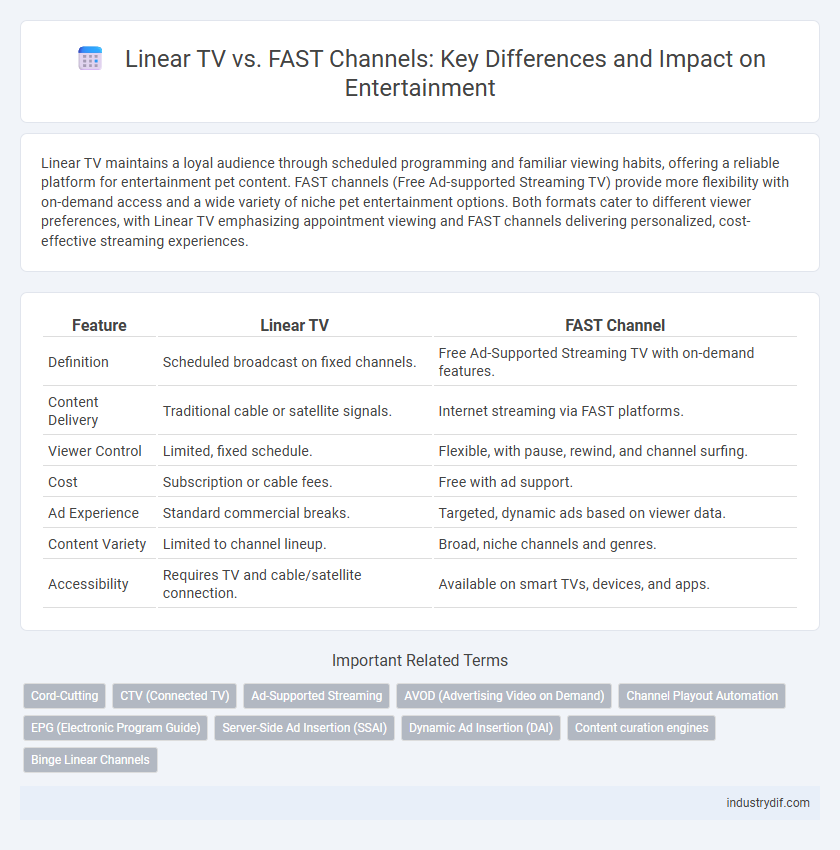
| Feature | Linear TV | FAST Channel |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Scheduled broadcast on fixed channels. | Free Ad-Supported Streaming TV with on-demand features. |
| Content Delivery | Traditional cable or satellite signals. | Internet streaming via FAST platforms. |
| Viewer Control | Limited, fixed schedule. | Flexible, with pause, rewind, and channel surfing. |
| Cost | Subscription or cable fees. | Free with ad support. |
| Ad Experience | Standard commercial breaks. | Targeted, dynamic ads based on viewer data. |
| Content Variety | Limited to channel lineup. | Broad, niche channels and genres. |
| Accessibility | Requires TV and cable/satellite connection. | Available on smart TVs, devices, and apps. |
Defining Linear TV: Traditional Broadcasting Explained
Linear TV refers to traditional broadcasting where programming is delivered on scheduled channels with viewers tuning in at specific times. This format relies on cable, satellite, or over-the-air signals to provide a curated lineup of shows and live events. Unlike FAST channels, Linear TV does not offer on-demand content and limits viewer control over what and when to watch.
What Are FAST Channels? Understanding the Basics
FAST channels, or Free Ad-Supported Streaming Television channels, provide viewers with a linear TV experience through internet streaming without subscription fees. Unlike traditional Linear TV, which broadcasts scheduled programming via cable or satellite, FAST channels deliver curated content on demand, supported by advertisements. This emerging model combines the simplicity of channel surfing with the accessibility of streaming, making it a cost-effective alternative for audiences and advertisers alike.
Key Differences Between Linear TV and FAST Channels
Linear TV operates on scheduled programming with fixed broadcast times, while FAST (Free Ad-Supported Streaming TV) channels provide on-demand streaming of curated content without user subscription fees. FAST channels leverage internet delivery, allowing personalized ad targeting and flexible viewing, contrasting with the traditional broadcast model's one-to-many distribution. The shift from Linear TV to FAST reflects changing consumer preferences for convenience, customization, and cost-effective entertainment options.
Audience Engagement: Linear TV vs FAST Channel Viewership
Linear TV maintains strong audience engagement through scheduled programming that appeals to traditional viewers seeking consistent content timing. FAST channels attract diverse viewers by offering ad-supported, on-demand streaming with personalized recommendations enhancing user interaction. Studies show FAST platforms report higher viewer retention rates due to flexible, genre-specific channels tailored to individual preferences.
Content Delivery Models: Scheduled vs On-Demand
Linear TV operates on a scheduled content delivery model, broadcasting programs at predetermined times, which offers viewers a fixed viewing experience. FAST channels, or Free Ad-Supported Streaming TV, utilize an on-demand delivery approach that allows audiences to access a diverse range of content instantly without a traditional schedule. This shift enhances viewer flexibility and personalization, driving significant growth in digital entertainment consumption.
Advertising Strategies: Linear TV Versus FAST Monetization
Linear TV advertising relies on scheduled commercial breaks with broad audience targeting, offering advertisers guaranteed reach but limited flexibility and measurability. FAST (Free Ad-supported Streaming TV) channels utilize programmatic advertising and dynamic ad insertion, enabling precise audience segmentation and real-time campaign adjustments for higher monetization efficiency. Brands favor FAST channels for cost-effective, data-driven advertising strategies that maximize ROI compared to traditional Linear TV buys.
Platform Accessibility: Devices and Reach Comparison
Linear TV remains widely accessible through traditional cable and satellite devices, ensuring broad household penetration across urban and rural areas. FAST channels (Free Ad-Supported Streaming TV) leverage internet-connected devices like smart TVs, streaming sticks, and mobile apps, expanding reach to cord-cutters and younger, tech-savvy audiences. While Linear TV dominates in device ubiquity, FAST channels offer greater platform flexibility and global accessibility through OTT ecosystems.
Cost Structure for Viewers: Subscription vs Free Streaming
Linear TV typically requires viewers to pay monthly subscription fees or cable packages, leading to higher overall costs. FAST (Free Ad-Supported Streaming TV) channels offer free access to content supported by advertisements, eliminating subscription expenses for viewers. This model reduces the financial barrier while providing similar entertainment options, especially appealing to cost-conscious audiences.
Industry Trends: The Shift from Linear TV to FAST Channels
The entertainment industry is experiencing a significant shift as viewers increasingly favor FAST (Free Ad-Supported Streaming TV) channels over traditional linear TV, driven by the demand for on-demand accessibility and diverse content. FAST channels offer a cost-effective model for both consumers and advertisers, leveraging targeted advertising that outperforms the broad reach of linear TV. Industry trends indicate that media companies are investing heavily in FAST platforms to capture cord-cutters and capitalize on streaming growth, signaling a gradual decline in traditional linear TV viewership.
Future Outlook: Evolving Roles in the Entertainment Landscape
Linear TV is anticipated to maintain a steady presence, particularly among older demographics who value scheduled programming and traditional broadcast experiences. FAST (Free Ad-supported Streaming TV) channels are rapidly expanding, driven by increasing consumer demand for on-demand, cost-free content with targeted advertising. The future entertainment landscape will likely see a hybrid model where Linear TV coexists with FAST services, leveraging advancements in data analytics and personalized content delivery to optimize viewer engagement and monetization.
Related Important Terms
Cord-Cutting
Linear TV faces significant decline as cord-cutting accelerates, with viewers shifting to FAST channels that offer free, ad-supported streaming tailored to on-demand preferences. FAST platforms capitalize on reduced subscription costs and personalized content, challenging traditional cable's dominance in the evolving entertainment landscape.
CTV (Connected TV)
Connected TV (CTV) integrates both Linear TV and Free Ad-supported Streaming TV (FAST) channels, offering viewers access to scheduled programming alongside on-demand content through internet-connected devices. FAST channels leverage CTV's targeted advertising capabilities, enhancing viewer engagement and ROI compared to traditional linear broadcasting.
Ad-Supported Streaming
Linear TV remains a dominant force in ad-supported streaming due to its scheduled programming and broad audience reach, while FAST (Free Ad-Supported Streaming TV) channels gain rapid popularity by offering on-demand content and targeted advertising, enhancing viewer engagement. Advertisers increasingly invest in FAST channels for precise audience segmentation and cost efficiency, leveraging real-time data analytics to optimize ad placements compared to traditional Linear TV's fixed slots.
AVOD (Advertising Video on Demand)
FAST channels leverage AVOD to deliver curated, linear-style content streams that maximize viewer engagement through targeted ads, offering a cost-effective alternative to traditional linear TV. Unlike traditional linear TV's fixed schedules and limited interactivity, AVOD on FAST platforms provides on-demand access with personalized advertising, driving higher monetization and viewer retention.
Channel Playout Automation
Linear TV channel playout automation relies on scheduled broadcasting systems that enable seamless content delivery with minimal manual intervention, ensuring consistent viewer experience across fixed time slots. FAST channel playout automation leverages advanced algorithms and real-time data analytics to dynamically insert targeted ads and optimize content distribution for enhanced audience engagement and monetization.
EPG (Electronic Program Guide)
Linear TV relies heavily on traditional EPGs for scheduled content navigation, offering real-time program listings that audiences expect for appointment viewing. FAST Channels integrate dynamic EPG experiences with algorithm-driven recommendations, enhancing content discovery by blending live programming with on-demand features.
Server-Side Ad Insertion (SSAI)
Server-Side Ad Insertion (SSAI) enhances viewer experience in both Linear TV and FAST channels by seamlessly integrating targeted ads without buffering or ad blockers, increasing ad effectiveness and revenue. FAST channels leverage SSAI to deliver personalized, dynamic ad content at scale, surpassing traditional Linear TV's static ad insertion capabilities.
Dynamic Ad Insertion (DAI)
Dynamic Ad Insertion (DAI) enhances FAST Channels by allowing precise, real-time ad targeting based on viewer data, surpassing traditional Linear TV's static ad slots that lack personalization. This advanced technology boosts monetization efficiency and viewer engagement by delivering relevant ads during live streaming on FAST platforms.
Content curation engines
Content curation engines in Linear TV rely on traditional scheduling algorithms and genre-based categorization, limiting personalization and real-time adaptability. FAST Channels leverage advanced AI-driven content curation engines that analyze viewer behavior and preferences, delivering dynamic, personalized programming to enhance user engagement and retention.
Binge Linear Channels
Binge Linear Channels on Linear TV provide scheduled, curated content blocks that mimic traditional viewing habits, contrasting FAST Channels which offer on-demand, algorithm-driven streams without fixed schedules. These binge channels capitalize on nostalgia and appointment viewing, enhancing audience retention through thematic programming consistent with classic TV consumption patterns.
Linear TV vs FAST Channel Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com