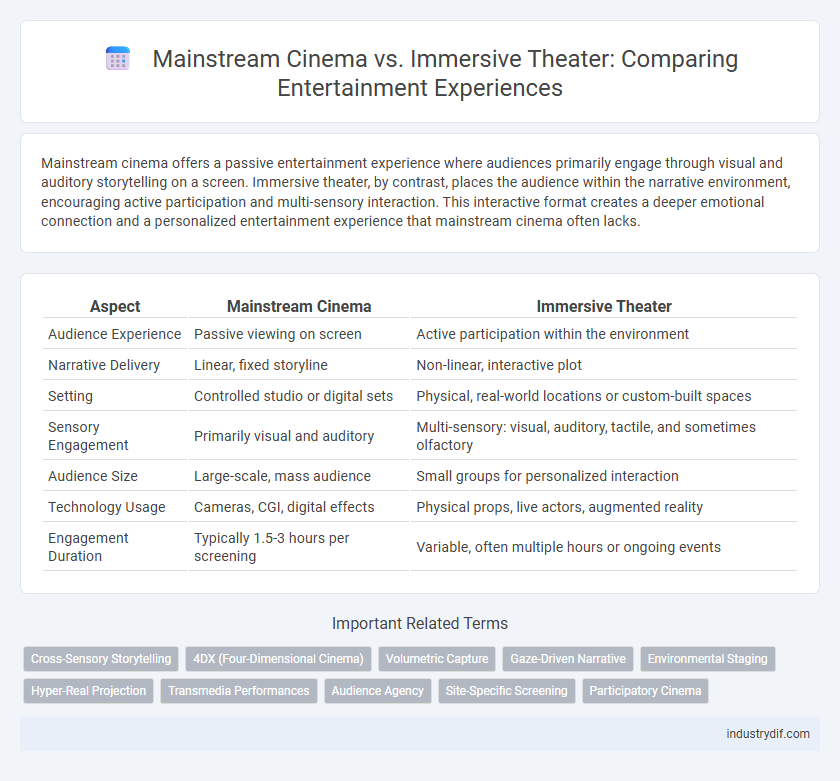
Mainstream cinema offers a passive entertainment experience where audiences primarily engage through visual and auditory storytelling on a screen. Immersive theater, by contrast, places the audience within the narrative environment, encouraging active participation and multi-sensory interaction. This interactive format creates a deeper emotional connection and a personalized entertainment experience that mainstream cinema often lacks.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Mainstream Cinema | Immersive Theater |
|---|---|---|
| Audience Experience | Passive viewing on screen | Active participation within the environment |
| Narrative Delivery | Linear, fixed storyline | Non-linear, interactive plot |
| Setting | Controlled studio or digital sets | Physical, real-world locations or custom-built spaces |
| Sensory Engagement | Primarily visual and auditory | Multi-sensory: visual, auditory, tactile, and sometimes olfactory |
| Audience Size | Large-scale, mass audience | Small groups for personalized interaction |
| Technology Usage | Cameras, CGI, digital effects | Physical props, live actors, augmented reality |
| Engagement Duration | Typically 1.5-3 hours per screening | Variable, often multiple hours or ongoing events |
Defining Mainstream Cinema in the Entertainment Industry
Mainstream cinema refers to big-budget films produced by major studios aimed at wide audiences, featuring conventional storytelling, star actors, and advanced special effects. It dominates the entertainment industry through wide theatrical releases, extensive marketing campaigns, and high box office revenues globally. This sector contrasts with immersive theater by emphasizing passive audience viewing over interactive or participatory experiences.
What Sets Immersive Theater Apart from Traditional Formats
Immersive theater stands apart from mainstream cinema by dissolving the barrier between audience and performer, actively involving viewers in the narrative through multisensory experiences and dynamic spatial design. Unlike traditional film screenings that offer passive consumption, immersive performances engage multiple senses--sight, sound, touch, and sometimes smell--creating a deeply personalized and interactive environment. This format transforms storytelling into an exploratory journey, fostering emotional connections and heightened engagement beyond the linear constraints of conventional cinema.
Audience Engagement: Passive Viewing vs. Active Participation
Mainstream cinema typically offers passive viewing where audiences engage through visual and auditory stimuli without direct interaction, fostering a controlled narrative experience. Immersive theater prioritizes active participation, inviting audiences to influence story progression and environments, resulting in personalized and dynamic engagement. This shift from passive to active involvement enhances emotional connection and memorability in entertainment experiences.
Narrative Structure: Linear Plots vs. Interactive Storytelling
Mainstream cinema typically follows linear plots with a fixed narrative structure, guiding audiences through a predetermined sequence of events that emphasize character development and resolution. Immersive theater disrupts this linearity by incorporating interactive storytelling, allowing audiences to influence the narrative and explore multiple storylines simultaneously within a dynamic environment. This shift from passive viewing to active participation enhances emotional engagement and personal connection to the story.
Technological Innovations in Cinema and Immersive Theater
Technological innovations in mainstream cinema, such as advanced CGI, high frame rates, and 3D projection, have revolutionized visual storytelling by enhancing realism and spectacle on large screens. Immersive theater integrates cutting-edge tools like augmented reality (AR), spatial audio, and motion tracking to create interactive environments where audiences actively participate in the narrative. These innovations blur the lines between viewer and performer, pushing the boundaries of conventional entertainment experiences.
Production Scale: Mass Distribution vs. Intimate Experiences
Mainstream cinema emphasizes mass distribution with large-scale production budgets, aiming to reach global audiences through multiplexes and streaming platforms. Immersive theater focuses on intimate experiences, utilizing smaller venues and interactive storytelling to create personalized audience engagement. The contrast lies in cinema's broad accessibility versus theater's tailored, sensory-rich environments.
Accessibility and Venue Differences
Mainstream cinema offers widespread accessibility through multiplexes and streaming platforms, enabling audiences to watch films conveniently worldwide. Immersive theater is typically limited to specialized venues with controlled environments, providing intimate, interactive experiences but restricting audience size and geographic reach. Venue differences highlight cinema's scalability versus immersive theater's focused engagement and physical presence.
Economic Models: Box Office vs. Ticketed Experiences
Mainstream cinema relies heavily on box office revenue, generating significant income through mass ticket sales and international distribution deals. Immersive theater adopts a ticketed experience model, often with limited audience capacity and premium pricing to enhance exclusivity and engagement. Economic sustainability in immersive theater depends on diversified revenue streams like merchandise and sponsorships, contrasting with mainstream cinema's focus on volume and wide audience reach.
Evolving Audience Expectations in Modern Entertainment
Mainstream cinema continues to attract large audiences through high-budget productions and blockbuster franchises, while immersive theater appeals to viewers seeking participatory and multi-sensory experiences that challenge traditional storytelling. The evolution of audience expectations highlights a growing demand for personalization and emotional engagement, driving entertainment providers to innovate beyond passive consumption. Technologies such as virtual reality and interactive sets exemplify the shift towards immersive environments that blur the line between spectator and performer.
The Future Landscape: Blending Cinema and Immersive Theater
The future landscape of entertainment envisions a seamless fusion between mainstream cinema and immersive theater, leveraging advanced technologies such as virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) to create interactive storytelling experiences. This blending enhances audience engagement by allowing viewers to actively participate in narrative environments traditionally limited to passive observation. Industry leaders like Netflix and immersive theater companies such as Punchdrunk are pioneering hybrid productions that redefine entertainment boundaries through multi-sensory and multi-dimensional storytelling techniques.
Related Important Terms
Cross-Sensory Storytelling
Mainstream cinema primarily relies on visual and auditory stimuli to convey narratives, whereas immersive theater engages multiple senses, including touch, smell, and spatial awareness, to create a holistic storytelling experience. Cross-sensory storytelling in immersive theater enhances audience emotional connection and memory retention through interactive environments that extend beyond traditional screen-based formats.
4DX (Four-Dimensional Cinema)
4DX technology in mainstream cinema enhances traditional film viewing by incorporating motion seats, environmental effects like wind, rain, and scents, creating a multi-sensory experience that simulates on-screen action. Immersive theater, by contrast, offers live, interactive performances where audiences engage physically and emotionally in shared spaces, emphasizing presence over the technologically-driven sensory stimuli found in 4DX cinemas.
Volumetric Capture
Volumetric capture transforms immersive theater by enabling 3D holographic performances that engage audiences with interactive, lifelike experiences beyond traditional screens. Mainstream cinema remains limited to 2D and 3D projections, whereas volumetric technology enhances storytelling by blending physical space and digital actors, revolutionizing audience immersion.
Gaze-Driven Narrative
Mainstream cinema utilizes a fixed camera perspective to guide the audience's gaze and control narrative focus, creating a passive viewing experience. In contrast, immersive theater encourages an active gaze-driven narrative where audience members explore multiple viewpoints, influencing their personal interpretation and engagement with the story.
Environmental Staging
Mainstream cinema relies on controlled visual framing and edited sequences to create immersive narratives, while immersive theater utilizes environmental staging by transforming physical spaces and allowing audiences to interact with live performers, fostering a multi-sensory experience. This approach in immersive theater enhances engagement by integrating set design, lighting, sound, and spatial movement to blur the boundary between spectators and the story.
Hyper-Real Projection
Hyper-real projection in mainstream cinema enhances visual storytelling through advanced CGI and large-scale screens, creating polished, immersive visuals that captivate wide audiences. Immersive theater utilizes hyper-real projection to blend digital environments with physical space, fostering interactive experiences that engage viewers on a multisensory level beyond traditional cinematic presentation.
Transmedia Performances
Mainstream cinema relies on linear storytelling and passive audience engagement, whereas immersive theater employs transmedia performances that integrate multiple platforms such as live acting, virtual reality, and interactive digital content to create a multidimensional narrative experience. These transmedia elements in immersive theater foster active participation, allowing audiences to influence story outcomes and deepen emotional connections beyond traditional cinematic boundaries.
Audience Agency
Mainstream cinema offers a passive audience experience where viewers consume a fixed narrative, limiting personal interaction with the story. In contrast, immersive theater grants audience agency by enabling participants to influence plot directions and engage directly with performers, creating a dynamic and personalized storytelling environment.
Site-Specific Screening
Site-specific screenings in immersive theater transform traditional viewing by integrating the environment into the narrative, creating a multi-sensory experience that engages audiences beyond the passive role typical of mainstream cinema. This approach utilizes real-world locations to heighten emotional impact and foster deeper audience connection, contrasting with the fixed settings and detached spectatorship of conventional film theaters.
Participatory Cinema
Participatory cinema transforms audiences from passive viewers into active contributors, blending elements of mainstream cinema's narrative scope with immersive theater's interactive environment. This hybrid form leverages technology and live performance techniques to create personalized story experiences, enhancing engagement beyond traditional film screenings.
Mainstream Cinema vs Immersive Theater Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com