Mainstream cinema emphasizes fast-paced storytelling, frequent plot twists, and high-budget effects to captivate wide audiences quickly, shaping entertainment into a dynamic, immersive experience. Slow cinema, by contrast, prioritizes minimalistic narratives, extended takes, and contemplative pacing that invite deep emotional and philosophical engagement. This artistic divergence highlights the evolving landscape of film entertainment, catering to viewers seeking either instant excitement or profound reflection.
Table of Comparison
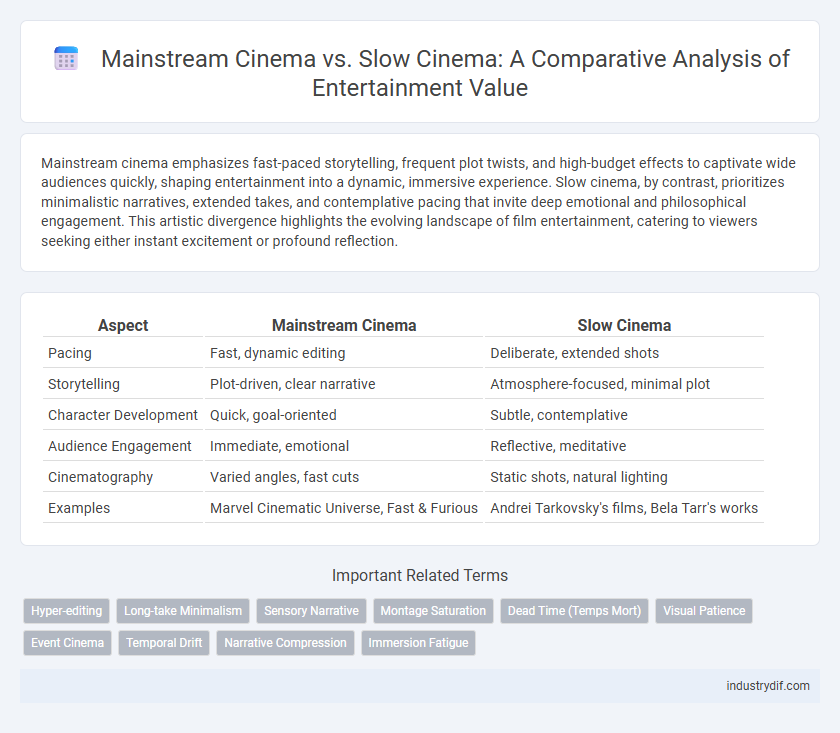
| Aspect | Mainstream Cinema | Slow Cinema |
|---|---|---|
| Pacing | Fast, dynamic editing | Deliberate, extended shots |
| Storytelling | Plot-driven, clear narrative | Atmosphere-focused, minimal plot |
| Character Development | Quick, goal-oriented | Subtle, contemplative |
| Audience Engagement | Immediate, emotional | Reflective, meditative |
| Cinematography | Varied angles, fast cuts | Static shots, natural lighting |
| Examples | Marvel Cinematic Universe, Fast & Furious | Andrei Tarkovsky's films, Bela Tarr's works |
Defining Mainstream Cinema and Slow Cinema
Mainstream cinema is characterized by fast-paced narratives, high-budget productions, and a focus on clear plotlines and commercial appeal, often featuring widespread distribution and popular genres such as action, comedy, and drama. Slow cinema emphasizes minimalistic storytelling with long takes, sparse dialogue, and deliberate pacing, prioritizing mood, atmosphere, and visual composition over plot-driven narratives. Key figures in slow cinema include directors like Bela Tarr and Andrei Tarkovsky, whose films challenge conventional cinematic timing and invite deep contemplation.
Historical Origins and Evolution
Mainstream cinema emerged in the early 20th century with Hollywood's rise, characterized by fast-paced storytelling, clear narratives, and commercial appeal, while slow cinema evolved in the 1960s and 1970s as a reaction to conventional filmmaking, emphasizing prolonged shots, minimalistic dialogue, and contemplative pacing. Influential slow cinema directors like Andrei Tarkovsky and Michelangelo Antonioni reshaped film language by prioritizing atmosphere and visual storytelling over plot-driven structures. The evolution of these two paradigms reflects divergent approaches to audience engagement and narrative complexity within the film industry.
Narrative Structures: Fast-Paced vs. Contemplative
Mainstream cinema typically utilizes fast-paced narrative structures characterized by rapid scene transitions and a clear cause-and-effect storyline designed to maintain audience engagement and deliver immediate gratification. In contrast, slow cinema adopts contemplative narratives with extended takes, minimal dialogue, and a focus on subtle visual storytelling that encourages introspection and emotional depth. These divergent approaches influence viewer experience: mainstream films aim for excitement and clarity, while slow cinema fosters patience and a meditative state.
Visual Aesthetics and Cinematic Techniques
Mainstream cinema emphasizes dynamic visual aesthetics with rapid editing, vibrant colors, and complex narrative structures to engage audiences quickly, while slow cinema prioritizes long takes, minimalistic compositions, and natural lighting to evoke contemplation and immersion. Cinematic techniques in slow cinema often include extended shots and restrained camera movements, contrasting sharply with the quick cuts and special effects typical of mainstream films. This divergence in visual style shapes distinct viewer experiences, focusing on sensory stimulation in mainstream films and introspective observation in slow cinema.
Audience Engagement and Reception
Mainstream cinema captivates audiences through fast-paced narratives, clear plotlines, and dynamic characters, leading to widespread commercial success and immediate emotional engagement. Slow cinema, characterized by long takes, minimal dialogue, and contemplative pacing, appeals to niche audiences seeking immersive, reflective viewing experiences that challenge conventional storytelling. Audience reception varies widely; mainstream films often generate broad popular acclaim and high box office returns, while slow cinema garners critical praise and cult followings for its artistic depth and meditative qualities.
Box Office Performance and Distribution
Mainstream cinema dominates global box office revenue with high-budget productions, wide theatrical releases, and extensive marketing campaigns ensuring mass audience appeal and significant profit margins. Slow cinema, characterized by minimalistic storytelling and long takes, generally sees limited box office success due to niche audiences and restricted distribution primarily in festivals and arthouse theaters. Despite lower commercial returns, slow cinema often garners critical acclaim and cultivates dedicated followings through alternative platforms like streaming services and international film circuits.
Notable Directors and Landmark Films
Mainstream cinema features iconic directors such as Steven Spielberg and Ridley Scott, known for blockbuster films like "Jurassic Park" and "Gladiator," which emphasize fast pacing and spectacle. Slow cinema, pioneered by auteurs like Bela Tarr and Tsai Ming-liang with landmark films including "Satantango" and "Stray Dogs," prioritizes long takes, minimal dialogue, and contemplative storytelling. These stylistic differences highlight contrasting approaches to narrative engagement and audience experience in contemporary filmmaking.
Cultural Impact and Global Reach
Mainstream cinema, characterized by fast-paced narratives and commercial appeal, dominates global markets and heavily influences popular culture through widespread distribution and blockbusters. Slow cinema, with its emphasis on minimalism, long takes, and contemplative storytelling, fosters niche audiences and critical acclaim, significantly impacting film culture by challenging conventional viewing habits. While mainstream cinema shapes global entertainment trends and mass cultural consumption, slow cinema enriches cultural diversity and artistic expression within the cinematic landscape.
Critical Reception and Awards Recognition
Mainstream cinema frequently garners widespread critical acclaim and achieves significant awards recognition due to its broad appeal, conventional storytelling, and star-studded casts. Slow cinema, characterized by minimalistic narratives and extended takes, often receives polarized critical reception, praised in niche circles for artistic depth but overlooked by major awards institutions. Films like "The Tree of Life" showcase slow cinema's potential for critical prestige, yet mainstream blockbusters dominate prestigious award categories such as the Oscars and Golden Globes.
Future Trends in Mainstream and Slow Cinema
Future trends in mainstream cinema emphasize immersive technologies such as virtual reality and augmented reality to enhance audience engagement and storytelling complexity. Slow cinema continues to gain traction through streaming platforms that favor contemplative pacing and minimalist narratives appealing to niche audiences. Integration of AI-driven tools in scriptwriting and editing promises to reshape production workflows across both mainstream and slow cinema sectors.
Related Important Terms
Hyper-editing
Mainstream cinema relies heavily on hyper-editing techniques, featuring rapid cuts and fast-paced sequences that maintain audience engagement through constant visual stimulation. In contrast, slow cinema adopts extended takes and minimal editing to foster contemplative viewing experiences, emphasizing atmosphere and subtle narrative development over frenetic storytelling.
Long-take Minimalism
Mainstream cinema relies on rapid editing and dynamic scene changes to maintain viewer engagement, while slow cinema embraces long-take minimalism, emphasizing extended shots that capture subtle gestures and ambient sound to create immersive, contemplative experiences. Directors like Bela Tarr and Tsai Ming-liang champion long-take minimalism to challenge narrative conventions and evoke deeper emotional and philosophical reflections in audiences.
Sensory Narrative
Mainstream cinema emphasizes fast-paced storytelling with dynamic visuals and sound to engage audiences quickly, while slow cinema prioritizes extended shots and minimalist sound design to cultivate a deep sensory narrative and immersive emotional experience. The sensory narrative in slow cinema relies on subtle visual cues and ambient sounds, encouraging viewers to interpret meaning through atmosphere rather than explicit plot progression.
Montage Saturation
Mainstream cinema often employs rapid montage saturation, featuring fast cuts and dynamic editing to maintain high energy and audience engagement. Slow cinema contrasts this with minimal montage saturation, using long takes and extended scenes to emphasize mood, atmosphere, and contemplation.
Dead Time (Temps Mort)
Dead Time (Temps Mort) in mainstream cinema typically serves as brief transitional moments to maintain narrative momentum, while in slow cinema, it is an essential storytelling device that emphasizes atmosphere, character introspection, and temporal realism. This contrast highlights mainstream films' focus on plot-driven pacing versus slow cinema's deliberate exploration of existential themes and sensory experience.
Visual Patience
Mainstream cinema relies on fast-paced editing and dynamic visual storytelling to maintain audience engagement, emphasizing plot-driven sequences and rapid scene changes. Slow cinema prioritizes visual patience, using extended takes, minimalistic compositions, and deliberate pacing to immerse viewers in contemplative atmospheres and nuanced emotional experiences.
Event Cinema
Mainstream Cinema emphasizes fast-paced narratives and high-budget spectacle, attracting mass audiences through commercial event films like superhero blockbusters and franchises. Slow Cinema, characterized by minimal dialogue and extended takes, contrasts sharply by focusing on contemplative storytelling that challenges traditional event cinema's emphasis on immediacy and spectacle.
Temporal Drift
Mainstream cinema often prioritizes fast-paced editing, clear plot progression, and immediate emotional engagement, whereas slow cinema emphasizes temporal drift through long takes, minimal dialogue, and deliberate pacing to evoke contemplation and a deeper sensory experience. This contrast highlights how temporal manipulation in slow cinema challenges conventional narrative time, encouraging audiences to perceive moments with extended duration and altered rhythm.
Narrative Compression
Mainstream cinema relies heavily on narrative compression to deliver fast-paced, plot-driven stories that prioritize clear cause-and-effect sequences and immediate character motivations, engaging audiences through tightly edited scenes and swift emotional arcs. Slow cinema, by contrast, employs minimal narrative compression, emphasizing extended takes, subtle character exploration, and ambient storytelling that invites viewers to experience time and space more contemplatively.
Immersion Fatigue
Mainstream cinema often relies on fast-paced editing and dynamic storytelling to maintain viewer engagement, which can lead to immersion fatigue by overwhelming the audience with constant stimuli. Slow cinema, characterized by long takes and minimalistic narrative, offers a contrasting experience that reduces sensory overload, allowing viewers to engage more deeply without the exhaustion caused by rapid cinematic techniques.
Mainstream Cinema vs Slow Cinema Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com