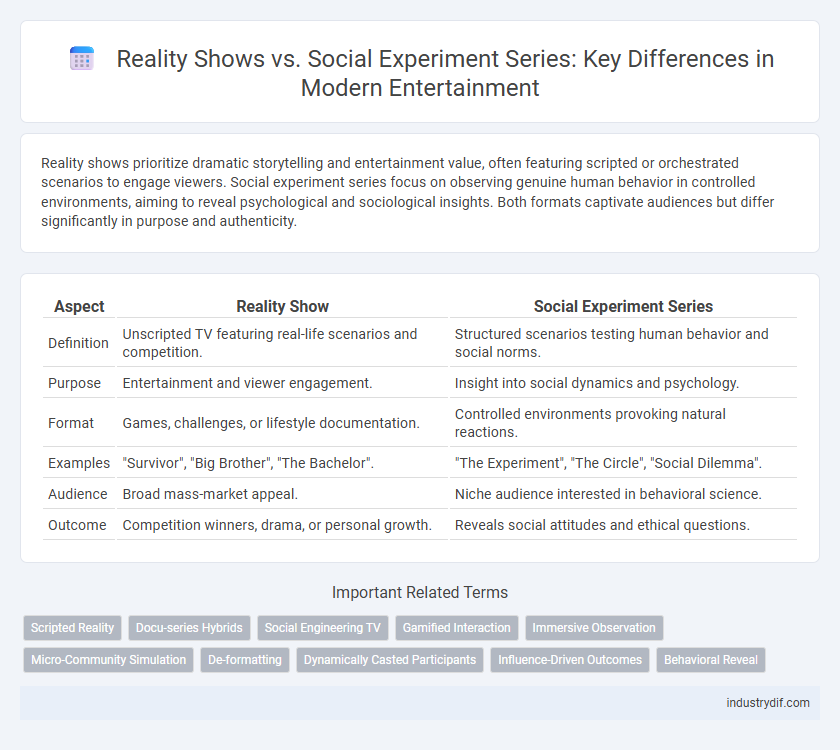
Reality shows prioritize dramatic storytelling and entertainment value, often featuring scripted or orchestrated scenarios to engage viewers. Social experiment series focus on observing genuine human behavior in controlled environments, aiming to reveal psychological and sociological insights. Both formats captivate audiences but differ significantly in purpose and authenticity.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Reality Show | Social Experiment Series |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unscripted TV featuring real-life scenarios and competition. | Structured scenarios testing human behavior and social norms. |
| Purpose | Entertainment and viewer engagement. | Insight into social dynamics and psychology. |
| Format | Games, challenges, or lifestyle documentation. | Controlled environments provoking natural reactions. |
| Examples | "Survivor", "Big Brother", "The Bachelor". | "The Experiment", "The Circle", "Social Dilemma". |
| Audience | Broad mass-market appeal. | Niche audience interested in behavioral science. |
| Outcome | Competition winners, drama, or personal growth. | Reveals social attitudes and ethical questions. |
Defining Reality Shows in Modern Entertainment
Reality shows in modern entertainment are unscripted television programs that capture real-life situations, often featuring competition, personal drama, or lifestyle scenarios to engage viewers. These shows prioritize entertainment value and audience engagement through carefully edited content that emphasizes conflict, emotion, and interpersonal dynamics. Unlike social experiment series, which aim to study human behavior under controlled conditions, reality shows focus on entertainment-driven narratives with varying degrees of authenticity.
What Constitutes a Social Experiment Series?
A social experiment series investigates human behavior by placing participants in controlled environments to observe authentic reactions and social dynamics, often revealing insights about societal norms and psychological responses. Unlike typical reality shows that prioritize entertainment and competitive elements, social experiments emphasize the study of social interactions, ethical dilemmas, and behavioral patterns in real-time scenarios. Key features include participant consent, ethical oversight, and a focus on genuine social phenomena rather than scripted or manipulated outcomes.
Origin and Evolution of Reality TV
Reality TV originated in the 1940s with candid camera shows, evolving through the 1990s with groundbreaking series like "The Real World," which prioritized real-life situations and personal interactions. Social experiment series emerged as a subgenre, focusing on psychological and sociological outcomes by placing participants in controlled, often challenging environments to observe behavioral changes. The evolution of reality TV reflects shifting audience interests towards authenticity, social dynamics, and interactive storytelling through diverse formats and technology-driven engagement.
Key Elements of Social Experiment Formats
Social experiment series focus on authentic human behavior by placing participants in controlled environments to observe natural reactions and social dynamics. Key elements include ethical considerations, transparency about the experiment's purpose, and creating scenarios that reveal underlying societal issues or psychological traits. Unlike reality shows that emphasize drama and entertainment, social experiments prioritize genuine insights into human nature and social interactions.
Audience Engagement: Reality Shows vs Social Experiments
Reality shows thrive on high audience engagement through emotional storytelling, competition, and relatable personalities that drive viewer loyalty and social media interaction. Social experiment series engage viewers by provoking thought and debate on societal issues, creating a deeper intellectual connection and encouraging active discussion within niche communities. The difference in audience engagement lies in reality shows leveraging entertainment and drama, while social experiments focus on reflection and social consciousness to captivate viewers.
Ethics and Controversies in Both Genres
Reality shows often face criticism for prioritizing sensationalism over participant well-being, raising ethical concerns regarding manipulation and exploitation. Social experiment series, while aiming to explore human behavior, can blur ethical boundaries by exposing subjects to psychological stress without adequate consent or support. Both genres grapple with controversies surrounding informed consent, participant privacy, and the potential harm caused by public exposure and editing practices.
Impact on Society and Viewer Behavior
Reality shows often prioritize entertainment value and dramatization, influencing viewer behavior by promoting aspirational lifestyles and sensationalism, which can sometimes distort social norms. Social experiment series provide a more analytical perspective by exposing human behavior and societal issues, encouraging critical thinking and empathy among audiences. The impact on society differs as reality shows typically drive consumerism and celebrity culture, while social experiments foster awareness and dialogue around social dynamics and ethical concerns.
Notable Examples: Reality Show Hits and Social Experiment Breakthroughs
Reality show hits like "Survivor" and "Big Brother" captivate audiences with competitive challenges and personal drama, driving high viewership and cultural trends. Notable social experiment breakthroughs such as "The Experiment" and "Black Mirror's" interactive episodes push boundaries by exploring human behavior and societal norms in controlled settings. Both formats influence entertainment by blending unscripted content with psychological and social insights, shaping viewer expectations and media trends.
Production Techniques: Scripting vs Genuine Reactions
Reality shows often employ detailed scripting and staged scenarios to enhance drama and ensure consistent viewer engagement, utilizing multiple camera setups and controlled lighting for cinematic quality. Social experiment series prioritize genuine reactions by minimizing producer interference and capturing spontaneous interactions, often using hidden cameras or unobtrusive filming techniques to maintain authenticity. Production teams balance these approaches by adjusting editing styles; reality shows favor polished narratives while social experiments highlight raw, unscripted human behavior.
Future Trends in Unscripted Entertainment
Reality shows are increasingly integrating social experiment elements to boost viewer engagement and authenticity, reflecting a shift towards more immersive and psychologically driven content. Advances in AI and data analytics enable producers to tailor experiences and outcomes, predicting audience preferences and enhancing interactive participation. Future trends in unscripted entertainment emphasize hybridity, with formats blending real-life social dynamics and competitive storytelling to maintain relevance in a digital-first landscape.
Related Important Terms
Scripted Reality
Scripted reality shows blend real-life scenarios with scripted dialogue to enhance drama and viewer engagement, often blurring the lines between authentic behavior and planned interactions. In contrast, social experiment series prioritize genuine reactions and social dynamics by placing participants in controlled, thought-provoking situations to explore human behavior.
Docu-series Hybrids
Reality shows prioritize entertainment through scripted challenges and contestant interactions, while social experiment series focus on authentic human behavior under controlled conditions; docu-series hybrids blend these elements by combining real-life situations with structured narrative arcs to engage audiences and provoke social reflection. This hybrid format leverages unscripted emotional responses and thematic storytelling, enhancing viewer investment through relatable characters and socially relevant scenarios.
Social Engineering TV
Social Engineering TV leverages psychological manipulation and behavioral science to create immersive social experiment series that reveal authentic human responses and societal dynamics. Unlike traditional reality shows that prioritize dramatization and entertainment, social experiment series focus on ethical observation and the impact of environmental variables on participant behavior.
Gamified Interaction
Reality shows emphasize competitive gamified interactions where contestants participate in challenges to win prizes, driving viewer engagement through strategic gameplay and social dynamics. Social experiment series prioritize authentic human behavior observation in controlled environments, using gamified elements to subtly influence participants' decisions and reactions.
Immersive Observation
Reality shows emphasize competitive or personal drama within structured scenarios, while social experiment series prioritize immersive observation of participant behavior in real-life or simulated societal contexts. The immersive observation in social experiments captures authentic reactions and social dynamics, providing deeper insights into human interaction compared to the often scripted nature of reality shows.
Micro-Community Simulation
Reality shows emphasize dramatic interactions for entertainment, often exaggerating conflicts within micro-communities to captivate viewers. Social experiment series focus on authentic behavior and social dynamics by simulating micro-communities to study human interaction and societal patterns.
De-formatting
Reality shows often rely on scripted scenarios and editing techniques to maintain viewer engagement, while social experiment series emphasize unscripted, authentic interactions to de-format traditional television structures. This shift challenges conventional entertainment by prioritizing genuine human behavior and unpredictable outcomes over manufactured drama.
Dynamically Casted Participants
Reality shows often feature dynamically casted participants selected for their diverse personalities and dramatic potential to enhance viewer engagement, while social experiment series prioritize individuals chosen based on specific social traits or scenarios to authentically explore human behavior. The strategic casting in reality shows aims to maximize entertainment value, whereas social experiment series emphasize realistic interactions and outcomes through carefully curated participant dynamics.
Influence-Driven Outcomes
Reality shows prioritize entertainment through scripted drama and competitive challenges, often manipulating participant behavior for higher viewer engagement. Social experiment series focus on authentic human interactions and behavioral changes, aiming to reveal genuine psychological and social dynamics with influence-driven outcomes rooted in real-life scenarios.
Behavioral Reveal
Reality shows emphasize entertainment through dramatized scenarios and competition, often prioritizing audience engagement over authentic behavior. Social experiment series aim to uncover genuine human reactions by placing participants in controlled environments that reveal true behavioral patterns and social dynamics.
Reality Show vs Social Experiment Series Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com