The studio system dominates entertainment pet films with high budgets, professional crews, and extensive distribution networks, ensuring polished productions and mass appeal. Microbudget filmmaking offers creative freedom, allowing indie creators to experiment with unique stories and raw authenticity that resonate deeply with niche audiences. Both approaches shape the entertainment pet genre, balancing commercial success and artistic innovation.
Table of Comparison
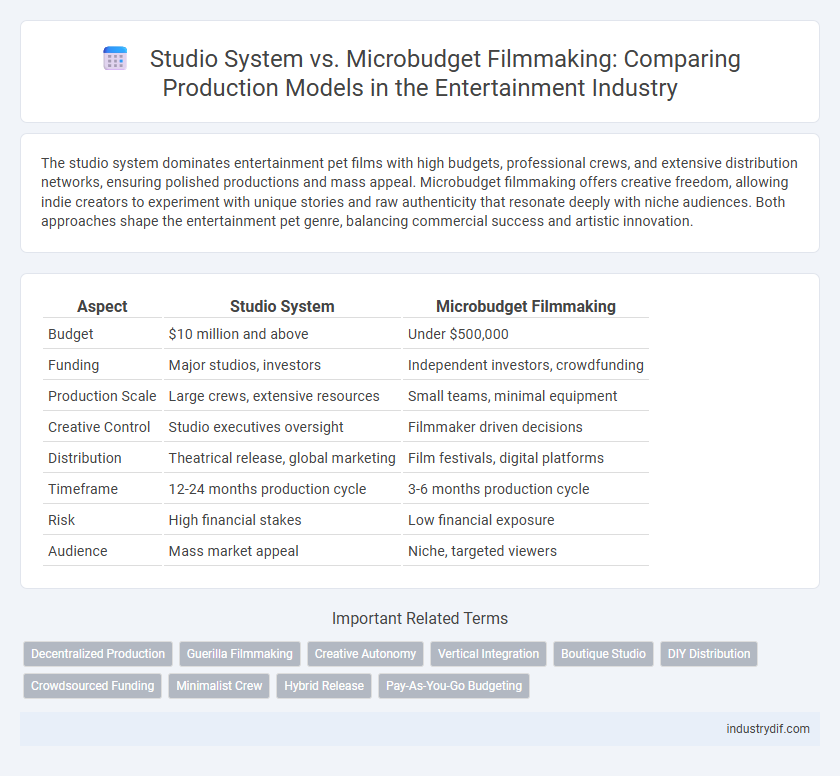
| Aspect | Studio System | Microbudget Filmmaking |
|---|---|---|
| Budget | $10 million and above | Under $500,000 |
| Funding | Major studios, investors | Independent investors, crowdfunding |
| Production Scale | Large crews, extensive resources | Small teams, minimal equipment |
| Creative Control | Studio executives oversight | Filmmaker driven decisions |
| Distribution | Theatrical release, global marketing | Film festivals, digital platforms |
| Timeframe | 12-24 months production cycle | 3-6 months production cycle |
| Risk | High financial stakes | Low financial exposure |
| Audience | Mass market appeal | Niche, targeted viewers |
Overview of the Studio System
The studio system, dominating Hollywood from the 1920s to the 1950s, centralized control over film production, distribution, and exhibition within major studios like MGM, Warner Bros., and Paramount. This vertically integrated model facilitated large-scale budgets, extensive resources, and star contracts, enabling high production values and market reach. Unlike microbudget filmmaking, the studio system's hierarchical structure prioritized efficiency, genre formulas, and mass appeal, shaping mainstream cinema's golden age.
Defining Microbudget Filmmaking
Microbudget filmmaking is characterized by extremely low production costs, often under $100,000, enabling creative storytelling without extensive financial backing or studio support. This approach relies heavily on resourcefulness, minimal crew, locations with limited fees, and digital technology to reduce expenses while maintaining creative control. Microbudget films prioritize narrative strength and innovation over high-end special effects or star power, contrasting sharply with the high investment and scale typical of studio system productions.
Historical Evolution of Film Production Models
The historical evolution of film production models reveals a shift from studio systems dominating Hollywood's Golden Age with vertically integrated production, distribution, and exhibition to the rise of microbudget filmmaking emphasizing creative autonomy and cost-efficiency. Studio systems provided large-scale financial resources, star power, and controlled distribution channels, while microbudget productions leverage digital technology and crowdfunding to bypass traditional gatekeepers. This transition reflects changing audience demands and technological advancements reshaping the entertainment industry landscape.
Funding and Financing Strategies
Studio system filmmaking relies heavily on substantial funding from major studios, leveraging extensive budgets and institutional financing to ensure high production values and wide distribution. Microbudget filmmaking depends on alternative financing strategies such as crowdfunding, private investors, and personal funds, prioritizing cost-efficiency and creative control. These divergent funding approaches significantly impact project scope, marketing reach, and risk management within the entertainment industry.
Creative Control and Decision-Making
Studio system filmmaking often limits creative control as major decisions are influenced by executives prioritizing commercial viability, whereas microbudget filmmaking offers filmmakers significant autonomy to make artistic choices without studio interference. In microbudget projects, directors and creators manage casting, scripting, and post-production decisions, enabling a more personal and innovative approach to storytelling. This independence fosters unique narratives and experimental techniques that are typically constrained within the structured studio environment.
Distribution Channels and Market Reach
Studio system films benefit from extensive distribution channels including global theatrical releases, major streaming platforms, and international TV networks, ensuring wide market reach and significant promotional resources. Microbudget filmmaking often relies on film festivals, niche streaming services, and direct-to-consumer digital platforms, targeting specific audiences with tailored marketing strategies. The distribution model for microbudget films emphasizes agility and cost-effectiveness, contrasting with the studio system's broad, high-investment approach to market penetration.
Impact on Talent and Crew Opportunities
Studio system productions offer extensive resources and established networks, providing talent and crew with higher budgets, advanced equipment, and professional development opportunities. Microbudget filmmaking fosters creative freedom and hands-on experience, allowing emerging artists to take on multiple roles and build versatile portfolios in a highly collaborative environment. This contrast shapes career trajectories, as studio projects emphasize specialization and scale, while microbudget films encourage innovation and adaptability among talent and crew.
Technological Innovations and Accessibility
Technological innovations such as advanced digital cameras, affordable editing software, and online distribution platforms have dramatically lowered barriers, enabling microbudget filmmaking to flourish outside traditional studio systems. Studios rely on high-end, proprietary technology and extensive resources, while independent filmmakers leverage accessible tools to produce and distribute content with limited budgets. This democratization of technology fosters creative freedom and diverse storytelling, challenging the historical dominance of studio-driven entertainment production.
Audience Engagement and Marketing
Studio system films leverage extensive marketing budgets and star power to create wide-reaching audience engagement, employing data-driven strategies to target diverse demographics and maximize box office returns. Microbudget filmmaking relies heavily on grassroots marketing, social media platforms, and niche communities to foster authentic connections and viral potential despite limited promotional resources. Both approaches aim to optimize audience engagement, but studio systems prioritize mass appeal while microbudget films focus on tailored, intimate viewer experiences.
Future Trends in Film Production Paradigms
Studio systems continue to dominate with expansive budgets, advanced technology, and extensive distribution networks, shaping blockbuster releases. Microbudget filmmaking leverages affordable digital tools and streaming platforms, enabling diverse voices and experimental narratives to flourish. Future trends indicate a hybrid model where studios adopt agile, cost-effective strategies while independent creators gain amplified reach through evolving digital infrastructures.
Related Important Terms
Decentralized Production
Decentralized production in microbudget filmmaking leverages local talent, affordable technology, and flexible schedules to bypass the hierarchical constraints and high costs intrinsic to studio systems. This approach enables creators to maintain creative control, rapidly adapt to changes, and distribute content through digital platforms, fostering innovation and niche audience engagement.
Guerilla Filmmaking
Guerrilla filmmaking thrives within microbudget filmmaking by leveraging minimal resources, unconventional locations, and a small crew to produce authentic, raw cinematic experiences often unattainable in traditional studio systems. This approach prioritizes creative freedom and improvisation, contrasting sharply with the high-cost, highly controlled environments typical of studio productions.
Creative Autonomy
Studio system filmmaking often involves multiple layers of creative control from executives, limiting director autonomy to align with commercial goals, whereas microbudget filmmaking empowers creators with full artistic freedom and flexible storytelling choices. Independent microbudget productions leverage minimal resources to maximize originality and personal vision, contrasting with studio projects that prioritize market-tested formulas and high production values.
Vertical Integration
Studio systems benefit from vertical integration by controlling production, distribution, and exhibition, maximizing revenue streams and ensuring consistent quality. Microbudget filmmaking often lacks this integration, relying on external distributors and digital platforms, which limits control but increases flexibility and creative freedom.
Boutique Studio
Boutique studios in the entertainment industry specialize in producing high-quality, artistically driven films with budgets typically ranging between $5 million and $50 million, striking a balance between the expansive resources of a studio system and the creative freedom of microbudget filmmaking. These studios emphasize unique storytelling and niche audience appeal, leveraging strategic marketing and targeted distribution to maximize returns without the overhead constraints of major studio operations.
DIY Distribution
Microbudget filmmaking leverages DIY distribution through digital platforms, social media, and grassroots marketing to reach niche audiences cost-effectively, bypassing traditional studio-controlled release windows. Studio systems rely on established theatrical, streaming, and international distribution networks, focusing on large-scale marketing campaigns and wide-release strategies that require significant financial investment.
Crowdsourced Funding
Crowdsourced funding has transformed microbudget filmmaking by enabling independent creators to bypass traditional studio systems and directly engage audiences for financial support, fostering creative freedom and niche storytelling. Studio systems typically rely on large-scale investments and controlled funding, limiting grassroots innovation and audience-driven project development.
Minimalist Crew
Microbudget filmmaking thrives on a minimalist crew, maximizing efficiency and creativity by reducing personnel to essential roles, which significantly lowers production costs compared to studio systems. This lean approach fosters intimate collaboration and faster decision-making, contrasting with the extensive, specialized teams typical of large studio productions.
Hybrid Release
Hybrid release strategies blend traditional studio system distribution with microbudget filmmaking's flexibility, optimizing market reach and audience engagement. This approach leverages digital platforms and limited theatrical runs, increasing profitability while maintaining creative control typical of microbudget productions.
Pay-As-You-Go Budgeting
Pay-As-You-Go budgeting in microbudget filmmaking offers flexible, real-time expense management, contrasting sharply with the rigid, pre-allocated funds typical of studio systems. This approach empowers filmmakers to dynamically allocate resources based on immediate production needs, optimizing creativity while minimizing financial risk.
Studio System vs Microbudget Filmmaking Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com