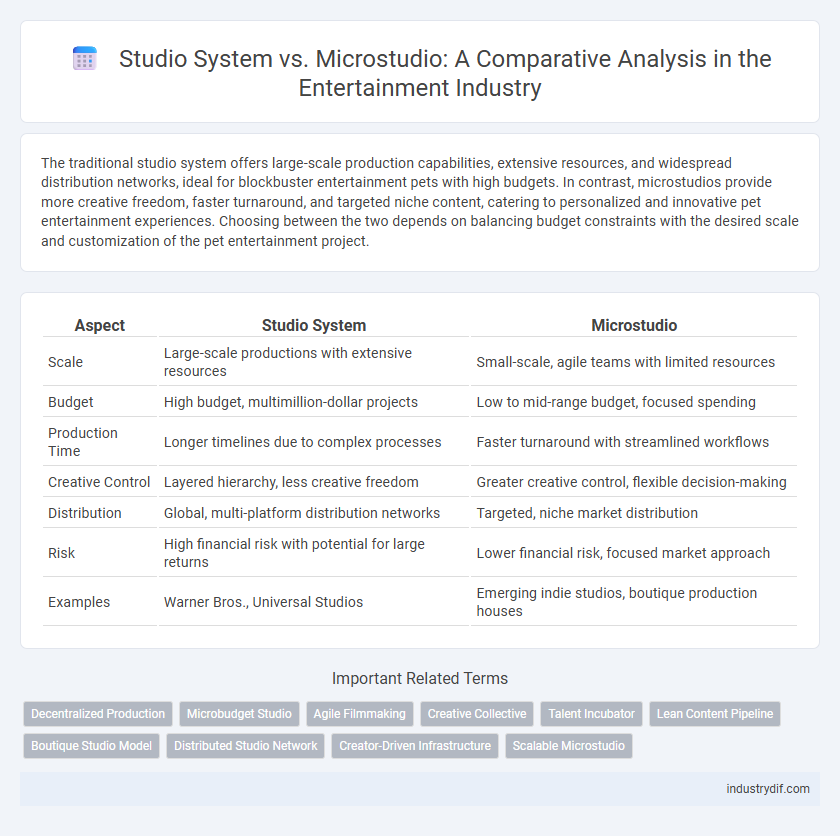
The traditional studio system offers large-scale production capabilities, extensive resources, and widespread distribution networks, ideal for blockbuster entertainment pets with high budgets. In contrast, microstudios provide more creative freedom, faster turnaround, and targeted niche content, catering to personalized and innovative pet entertainment experiences. Choosing between the two depends on balancing budget constraints with the desired scale and customization of the pet entertainment project.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Studio System | Microstudio |
|---|---|---|
| Scale | Large-scale productions with extensive resources | Small-scale, agile teams with limited resources |
| Budget | High budget, multimillion-dollar projects | Low to mid-range budget, focused spending |
| Production Time | Longer timelines due to complex processes | Faster turnaround with streamlined workflows |
| Creative Control | Layered hierarchy, less creative freedom | Greater creative control, flexible decision-making |
| Distribution | Global, multi-platform distribution networks | Targeted, niche market distribution |
| Risk | High financial risk with potential for large returns | Lower financial risk, focused market approach |
| Examples | Warner Bros., Universal Studios | Emerging indie studios, boutique production houses |
Defining the Studio System and Microstudio Model
The Studio System refers to large, vertically integrated entertainment companies that control production, distribution, and exhibition, enabling high-budget films with wide market reach. The Microstudio Model emphasizes smaller-scale production companies focused on niche markets, lower budgets, and faster project turnaround, often leveraging digital platforms for distribution. Both models shape the industry's landscape by balancing mass appeal with targeted, innovative content creation.
Historical Evolution of Entertainment Production
The historical evolution of entertainment production highlights the transition from the dominant studio system, characterized by vertically integrated major studios controlling production, distribution, and exhibition, to the rise of microstudios focused on low-budget, agile filmmaking targeting niche audiences. This shift intensified in the late 20th century with technological advances lowering barriers to entry, enabling independent creators and microstudios to compete effectively against traditional studios. The microstudio model's flexibility and adaptability have reshaped content creation, distribution strategies, and audience engagement within the entertainment industry.
Key Players: Major Studios vs. Independent Microstudios
Major studios like Warner Bros., Disney, and Universal dominate the entertainment industry with massive budgets, extensive distribution networks, and established franchises. Independent microstudios, such as A24 and Blumhouse, excel by producing niche content with lower budgets and innovative storytelling that targets specific audience segments. The competitive landscape is shaped by these key players' contrasting approaches to production scale, marketing strategies, and content diversity.
Funding and Budget Differences
Studio systems typically secure funding through major studio investments, enabling large-scale budgets that support high-profile talent and extensive marketing campaigns. Microstudios rely on limited funding from independent investors or crowdfunding, resulting in smaller budgets focused on niche projects or innovative storytelling. Budget constraints in microstudios often drive creative efficiency, contrasting with the vast financial resources available within traditional studio systems.
Creative Control and Artistic Freedom
Microstudios provide filmmakers with greater creative control and artistic freedom by operating with smaller budgets and fewer executive constraints compared to traditional studio systems. Studio systems often prioritize commercial viability and market trends, which can limit innovative storytelling and experimental projects. Independent microstudios foster diverse narratives and unique visual styles by empowering creators to take risks and explore unconventional ideas.
Distribution Channels and Market Reach
Studio systems leverage extensive distribution channels including global theatrical releases, established streaming platforms, and international TV syndication, ensuring vast market reach and brand visibility. Microstudios rely heavily on digital distribution methods such as niche streaming services, social media platforms, and video-on-demand, targeting specific audience segments for focused market penetration. The contrasting approaches allow studio systems to dominate mainstream markets while microstudios excel in agile, targeted content delivery.
Technology Adoption: Traditional vs. Agile Approaches
Studio systems typically rely on established, large-scale production technologies with substantial infrastructure investments, favoring traditional, linear workflows and proprietary software. Microstudios embrace agile technology adoption by utilizing cloud-based tools, modular software, and flexible hardware setups to rapidly iterate and adapt to creative demands. This contrast enables microstudios to innovate faster and reduce costs, while studio systems maintain high production values through robust, stable technologies.
Collaboration and Talent Management
Studio systems leverage extensive collaboration networks and structured talent management to streamline project development, ensuring efficient resource allocation and high-quality output. Microstudios prioritize flexible collaboration models and personalized talent management, fostering innovation through close-knit team dynamics and agile workflows. Both approaches influence production speed and creative control, impacting how projects align with market demands and audience preferences.
Audience Targeting and Content Diversity
Studio systems leverage extensive resources and market research to target broad audiences with diverse content spanning multiple genres and demographics, ensuring wide appeal. Microstudios focus on niche markets by producing specialized, culturally specific, or experimental content, fostering intense audience loyalty and community engagement. This strategic contrast in audience targeting and content diversity allows both studio types to coexist and thrive within the entertainment industry.
Future Trends: The Shifting Landscape of Production Models
The future of entertainment production is increasingly shaped by the rise of microstudios, which offer agile, cost-efficient alternatives to the traditional studio system. Advances in digital technology, virtual production, and streaming platforms empower microstudios to innovate rapidly and target niche audiences with personalized content. This shift is transforming industry dynamics, with major studios adopting hybrid models to stay competitive in an evolving market driven by consumer demand for diverse and immersive experiences.
Related Important Terms
Decentralized Production
Studio systems centralize production resources and decision-making, enabling large-scale film projects with substantial budgets and extensive distribution networks. Microstudios leverage decentralized production models, utilizing digital technologies and remote collaboration to reduce costs, increase creative freedom, and accelerate project timelines.
Microbudget Studio
Microbudget studios prioritize lean production models, leveraging digital tools and streamlined workflows to create high-quality content with limited financial resources. These studios capitalize on niche audiences and flexible distribution channels, outpacing traditional studio systems in agility and cost efficiency.
Agile Filmmaking
The Studio System's rigid hierarchy contrasts sharply with Microstudios' lean structures, enabling faster decision-making and greater creative flexibility essential for Agile Filmmaking. Microstudios leverage digital tools and iterative production cycles to rapidly adapt to market trends, reducing costs while enhancing content quality and audience engagement.
Creative Collective
Creative collectives within microstudios often foster more innovative and flexible storytelling compared to traditional studio systems, enabling quicker decision-making and personalized project development. Microstudios prioritize collaborative environments and experimental content, challenging the structured hierarchy and extensive bureaucracy typical of conventional studio systems.
Talent Incubator
Studio systems offer extensive resources and established networks that accelerate talent incubation through structured mentorship, high-budget projects, and broad exposure. Microstudios provide nimble, creative environments fostering personalized development and experimentation, enabling emerging talent to innovate and rapidly adapt within niche markets.
Lean Content Pipeline
The Studio System leverages extensive resources and established distribution channels to produce high-budget content, while Microstudios prioritize agility and efficiency through a lean content pipeline that minimizes production costs and accelerates time-to-market. This lean content pipeline emphasizes rapid iteration, streamlined workflows, and targeted audience engagement to maximize ROI in competitive entertainment markets.
Boutique Studio Model
Boutique studios leverage specialized talent and agile production techniques to deliver high-quality, niche content with lower budgets compared to traditional studio systems. Emphasizing creative control and innovative storytelling, microstudios often outpace larger competitors by rapidly adapting to market trends and audience preferences.
Distributed Studio Network
A Distributed Studio Network leverages interconnected Microstudios to enhance flexibility and reduce overhead compared to traditional centralized Studio Systems, enabling faster content creation and localized production. This decentralized model fosters innovation through collaborative workflows and real-time resource sharing across multiple locations.
Creator-Driven Infrastructure
Creator-driven infrastructure in studio systems emphasizes large-scale resources and established distribution channels, enabling extensive production value and global reach, while microstudios prioritize agility and personalized creative control, fostering innovative content tailored to niche audiences. This shift highlights a trend where creators leverage microstudio models to bypass traditional studio constraints, utilizing digital platforms and direct fan engagement to amplify their artistic vision.
Scalable Microstudio
Scalable microstudios leverage cloud computing and modular workflows to efficiently produce high-quality content with lower overhead compared to traditional studio systems. This model enables rapid adaptation to market trends, fostering creative innovation and cost-effective scalability in the entertainment industry.
Studio System vs Microstudio Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com