Fast food restaurants offer quick, convenient meals with a consistent menu and dine-in or drive-thru options, catering to customers seeking immediate gratification. Ghost kitchens operate exclusively through online orders and delivery services, minimizing overhead costs while maximizing menu variety and customization. Both models reshape the pet food industry by providing fresh, convenient options tailored to busy pet owners' lifestyles.
Table of Comparison
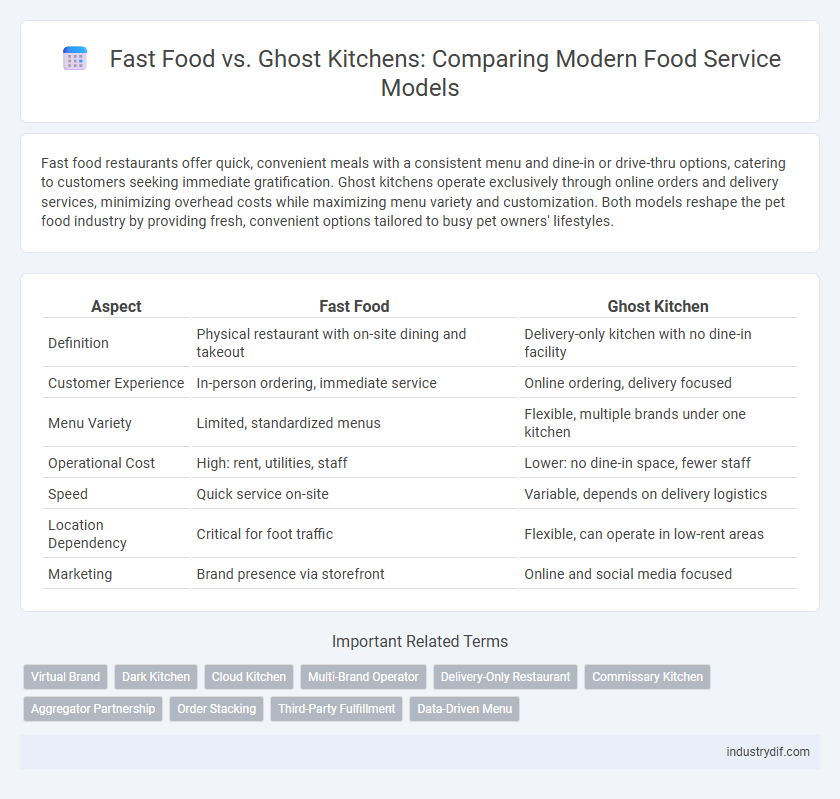
| Aspect | Fast Food | Ghost Kitchen |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Physical restaurant with on-site dining and takeout | Delivery-only kitchen with no dine-in facility |
| Customer Experience | In-person ordering, immediate service | Online ordering, delivery focused |
| Menu Variety | Limited, standardized menus | Flexible, multiple brands under one kitchen |
| Operational Cost | High: rent, utilities, staff | Lower: no dine-in space, fewer staff |
| Speed | Quick service on-site | Variable, depends on delivery logistics |
| Location Dependency | Critical for foot traffic | Flexible, can operate in low-rent areas |
| Marketing | Brand presence via storefront | Online and social media focused |
Defining Fast Food and Ghost Kitchens
Fast food refers to quick-service meals prepared and served in traditional restaurants or outlets, emphasizing convenience and speed with standardized menus and limited table service. Ghost kitchens operate exclusively as delivery-only culinary spaces without dine-in facilities, leveraging digital orders through apps and websites to reduce overhead costs and expand market reach. Both models optimize efficiency but differ in customer interaction and operational structure.
Evolution of the Restaurant Industry
Fast food revolutionized the restaurant industry by introducing quick service, standardized menus, and widespread brand recognition to meet growing urban demand. Ghost kitchens represent the next evolution, leveraging digital platforms and delivery-only models to reduce overhead costs and expand market reach without traditional dine-in spaces. This shift reflects consumer preferences for convenience, technology integration, and diversified food options in a rapidly changing culinary landscape.
Operational Differences Between Fast Food and Ghost Kitchens
Fast food restaurants operate with a physical storefront designed for dine-in, drive-thru, and walk-in customers, integrating front-of-house service and real-time customer interaction. Ghost kitchens function exclusively as delivery-only food preparation facilities without a traditional dining area, optimizing for efficiency and reduced overhead by eliminating the need for customer-facing infrastructure. Operationally, ghost kitchens rely heavily on digital ordering platforms, streamlined kitchen workflows, and third-party delivery partnerships to fulfill orders, contrasting with the multi-channel service model of fast food outlets.
Menu Innovation and Customization
Fast food chains often rely on standardized, limited menus to ensure quick service and operational efficiency, restricting opportunities for customization. Ghost kitchens leverage digital ordering platforms to experiment with diverse, innovative menu options tailored to niche customer preferences, enabling rapid iteration based on real-time data. This flexibility allows ghost kitchens to provide highly customizable dishes, driving greater customer satisfaction and market differentiation.
Delivery Models and Logistics
Fast food relies on traditional brick-and-mortar establishments with drive-thru and walk-in service, focusing on high-speed preparation and immediate customer pick-up. Ghost kitchens operate exclusively through online platforms, optimizing delivery logistics by partnering with third-party apps and using centralized kitchen spaces to streamline order fulfillment. Delivery models in ghost kitchens reduce overhead costs and enable multi-brand operations, contrasting with fast food chains that balance dine-in capacity and delivery efficiency.
Cost Structure and Profit Margins
Fast food restaurants typically incur higher fixed costs, including rent for prime locations, in-store staff wages, and extensive equipment maintenance, leading to moderate profit margins averaging around 6-9%. Ghost kitchens, operating without dine-in facilities, benefit from significantly lower overhead expenses such as reduced rent and minimal staffing, which can boost profit margins to approximately 15-20%. The streamlined cost structure of ghost kitchens enables greater financial efficiency, allowing for competitive pricing and quicker adaptation to market demand.
Customer Experience and Engagement
Fast food outlets offer immediate product availability and physical ambiance, enhancing tactile customer experience and spontaneous engagement. Ghost kitchens leverage technology-driven ordering systems and variety, optimizing convenience and personalized digital interactions. Both models prioritize speed but differ in sensory engagement and brand interaction dynamics.
Impact of Technology on Both Models
Fast food chains leverage technology through automated ordering systems, digital menus, and efficient supply chain management to boost speed and consistency. Ghost kitchens operate exclusively online, utilizing data analytics, app integrations, and cloud-based platforms to minimize overhead and optimize delivery routes. Both models rely heavily on advanced technology to enhance customer experience and streamline operations in the competitive food industry.
Sustainability and Environmental Concerns
Fast food chains often generate significant food waste and rely heavily on single-use plastics, contributing to environmental degradation. Ghost kitchens optimize sustainability by minimizing physical infrastructure and reducing energy consumption, while using technology to streamline ingredient sourcing and waste management. This model lowers carbon footprints and supports eco-friendly practices, addressing critical environmental concerns in the food industry.
Future Trends in Fast Food and Ghost Kitchens
Future trends in fast food emphasize technology integration such as AI-driven ordering systems and automated food preparation, boosting efficiency and personalization. Ghost kitchens leverage data analytics and delivery app partnerships to expand reach without traditional storefront costs, driving rapid growth in urban areas. Sustainability initiatives and plant-based menu offerings are becoming critical factors shaping the evolution of both fast food chains and ghost kitchen models.
Related Important Terms
Virtual Brand
Virtual brands operating within ghost kitchens leverage lower overhead costs and flexible menus to rapidly adapt to consumer preferences, outpacing traditional fast food chains in innovation and market reach. These digitally native brands optimize online ordering platforms and delivery logistics, creating a scalable model that maximizes efficiency and profitability in the competitive fast food industry.
Dark Kitchen
Dark kitchens, operating exclusively through online orders without dine-in facilities, revolutionize fast food by reducing overhead costs and maximizing delivery efficiency. This model leverages data-driven menu optimization and location-flexible setups to meet rising consumer demand for quick, convenient meals.
Cloud Kitchen
Cloud kitchens, also known as ghost kitchens, revolutionize fast food by operating solely through online orders without a traditional dine-in space, optimizing delivery efficiency and reducing overhead costs. This model leverages data-driven menu designs and advanced logistics to meet growing consumer demand for convenient, high-quality fast food options.
Multi-Brand Operator
Multi-brand operators leverage ghost kitchens to efficiently manage diverse fast food brands under one roof, optimizing delivery and reducing overhead costs. This strategy enhances scalability and market reach, offering faster service while maintaining distinct brand identities.
Delivery-Only Restaurant
Ghost kitchens operate as delivery-only restaurants, eliminating the need for dine-in space and reducing overhead costs compared to traditional fast food outlets. These kitchens leverage digital platforms to optimize order efficiency and expand menu variety, meeting the rising demand for convenient, contactless food delivery.
Commissary Kitchen
Commissary kitchens serve as centralized spaces for ghost kitchens, offering commercial-grade equipment and strict health compliance, enabling efficient fast food preparation without traditional dine-in facilities. Fast food chains often rely on commissary kitchens to streamline production, reduce overhead costs, and expand delivery-only services through ghost kitchen models.
Aggregator Partnership
Fast food chains rely heavily on aggregator partnerships to maximize order volume and reach a broad customer base quickly, leveraging established brand recognition and physical locations. Ghost kitchens optimize aggregator collaborations to reduce overhead costs and increase menu flexibility, allowing rapid adaptation to demand trends and expanding virtual presence without traditional storefronts.
Order Stacking
Fast food restaurants often struggle with order stacking during peak hours, causing delays and inaccuracies in meal preparation, while ghost kitchens leverage streamlined digital workflows and real-time order management systems to efficiently prioritize and sequence multiple simultaneous orders. By optimizing kitchen layout and utilizing advanced software, ghost kitchens minimize wait times and improve order accuracy compared to traditional fast food chains.
Third-Party Fulfillment
Third-party fulfillment services play a critical role in both fast food and ghost kitchen models by streamlining order processing and expanding delivery reach. Ghost kitchens rely heavily on these external logistics providers to optimize delivery efficiency and minimize overhead costs compared to traditional fast food outlets.
Data-Driven Menu
Data-driven menu optimization in fast food leverages customer purchase patterns and real-time analytics to tailor offerings, enhancing order accuracy and reducing waste. Ghost kitchens utilize advanced data insights from multiple platforms to rapidly adapt menus based on demand trends, maximizing operational efficiency and profit margins.
Fast Food vs Ghost Kitchen Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com