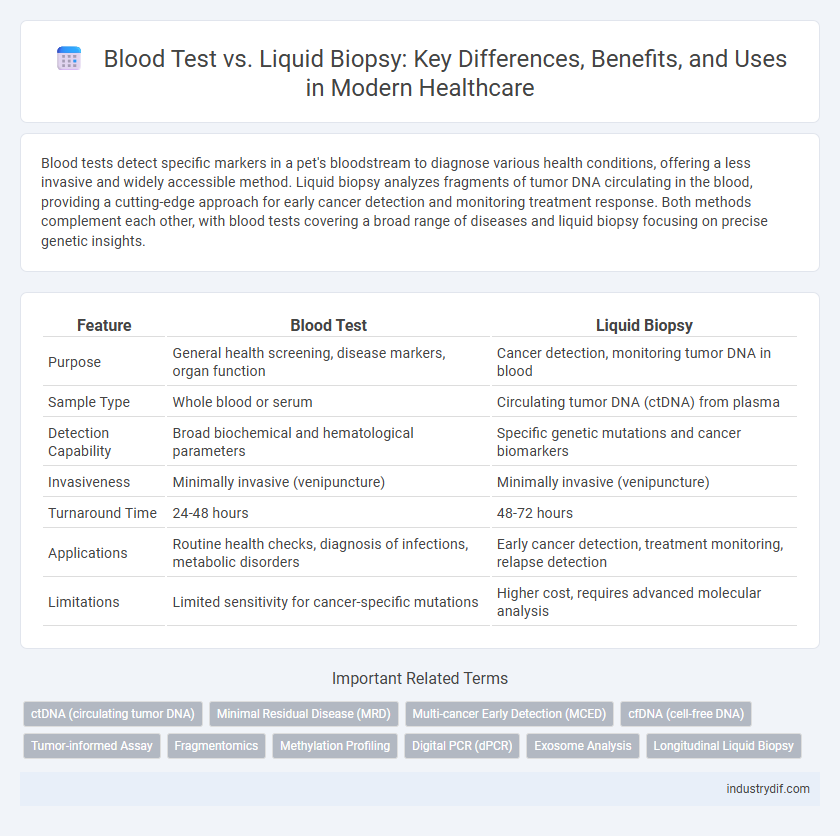
Blood tests detect specific markers in a pet's bloodstream to diagnose various health conditions, offering a less invasive and widely accessible method. Liquid biopsy analyzes fragments of tumor DNA circulating in the blood, providing a cutting-edge approach for early cancer detection and monitoring treatment response. Both methods complement each other, with blood tests covering a broad range of diseases and liquid biopsy focusing on precise genetic insights.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Blood Test | Liquid Biopsy |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | General health screening, disease markers, organ function | Cancer detection, monitoring tumor DNA in blood |
| Sample Type | Whole blood or serum | Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) from plasma |
| Detection Capability | Broad biochemical and hematological parameters | Specific genetic mutations and cancer biomarkers |
| Invasiveness | Minimally invasive (venipuncture) | Minimally invasive (venipuncture) |
| Turnaround Time | 24-48 hours | 48-72 hours |
| Applications | Routine health checks, diagnosis of infections, metabolic disorders | Early cancer detection, treatment monitoring, relapse detection |
| Limitations | Limited sensitivity for cancer-specific mutations | Higher cost, requires advanced molecular analysis |
Overview: Blood Test vs Liquid Biopsy in Modern Healthcare
Blood tests analyze components like cells, proteins, and chemicals in the bloodstream to diagnose and monitor conditions, while liquid biopsies detect circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) and cancer biomarkers for minimally invasive cancer detection. Liquid biopsies offer real-time insights into tumor genetics and dynamics, enabling personalized treatment strategies without surgical tissue extraction. Both methods enhance modern healthcare by improving disease detection, monitoring, and patient outcomes through different yet complementary diagnostic approaches.
Principles of Blood Tests and Liquid Biopsies
Blood tests analyze components such as cells, proteins, and chemicals in the bloodstream to assess overall health and detect conditions like infections or anemia. Liquid biopsies focus on detecting circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) or other biomarkers from cancer cells shed into the blood, enabling early cancer diagnosis and monitoring. Both methods rely on blood sampling but differ fundamentally in their targets: traditional blood tests assess general physiological markers while liquid biopsies provide molecular insights into cancer genetics.
Key Differences Between Blood Tests and Liquid Biopsies
Blood tests primarily analyze blood components such as cells, enzymes, and chemicals to assess general health or diagnose conditions, while liquid biopsies detect circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) and other biomarkers for cancer diagnosis and monitoring. Blood tests are widely used for routine screening, detecting infections, or monitoring organ function, whereas liquid biopsies provide a minimally invasive method to identify genetic mutations and tumor dynamics in oncology. Sensitivity and specificity differ as blood tests offer broad analysis, but liquid biopsies deliver targeted insights for personalized cancer treatment.
Diagnostic Applications in Oncology
Liquid biopsy offers a minimally invasive method to detect circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA), enabling real-time monitoring of cancer progression and treatment response. Traditional blood tests measure biomarkers such as tumor markers but lack the specificity and sensitivity of liquid biopsies for detecting genetic mutations and tumor heterogeneity. Liquid biopsy enhances personalized oncology by guiding targeted therapies through precise molecular profiling, improving diagnostic accuracy and patient outcomes.
Accuracy and Sensitivity Comparison
Blood tests and liquid biopsies differ significantly in accuracy and sensitivity when detecting medical conditions such as cancer. Liquid biopsies offer higher sensitivity by detecting circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) at very low concentrations, improving early diagnosis compared to traditional blood panels. Studies show liquid biopsies can detect mutations with over 85% sensitivity and 90% specificity, surpassing many conventional blood tests' performance metrics.
Patient Experience and Sample Collection
Blood tests typically require a standard blood draw, which is quick and minimally invasive, causing only minor discomfort for patients. Liquid biopsies use similar blood samples but offer a less invasive alternative to traditional tissue biopsies, reducing the risk of complications and enhancing patient comfort. Both methods provide efficient sample collection, but liquid biopsy improves patient experience by enabling easier, repeatable testing with faster turnaround times.
Cost Implications and Accessibility
Liquid biopsy offers a less invasive alternative to traditional blood tests but typically comes at a higher cost due to advanced technology and specialized analysis. Blood tests are widely accessible and more affordable, making them the preferred choice for routine health screenings across diverse healthcare settings. Cost implications may deter widespread liquid biopsy use despite its growing potential for early cancer detection and personalized treatment monitoring.
Clinical Impact on Early Disease Detection
Liquid biopsy offers a minimally invasive alternative to traditional blood tests by analyzing circulating tumor DNA, enabling earlier detection of cancers at a molecular level. This advanced technique improves clinical outcomes by facilitating timely intervention and personalized treatment plans compared to conventional blood tests that primarily detect established biomarkers. Integration of liquid biopsy into routine diagnostics enhances sensitivity and specificity in early disease detection, transforming patient care and prognosis.
Technological Innovations Shaping Liquid Biopsy
Technological innovations in liquid biopsy leverage cutting-edge techniques like next-generation sequencing (NGS) and digital PCR to detect genetic mutations and circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) with high sensitivity and specificity, surpassing traditional blood tests. These advancements enable real-time monitoring of cancer progression and treatment response, offering a non-invasive alternative for early cancer detection and personalized therapy adjustments. Integration of AI-driven data analysis further enhances the accuracy and speed of liquid biopsy results, transforming disease diagnostics and patient management in oncology.
Future Prospects in Diagnostic Medicine
Liquid biopsy represents a revolutionary advancement in diagnostic medicine, offering non-invasive, rapid, and highly sensitive detection of cancer-related biomarkers from circulating tumor DNA, unlike traditional blood tests that primarily analyze general blood components. Emerging technologies in liquid biopsy enable real-time monitoring of tumor dynamics and personalized treatment adjustments, paving the way for precision oncology and early disease detection. Innovations in molecular profiling and artificial intelligence integration are expected to enhance the accuracy and clinical utility of liquid biopsies, positioning them as a transformative tool in future healthcare diagnostics.
Related Important Terms
ctDNA (circulating tumor DNA)
Liquid biopsy using circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) offers a minimally invasive alternative to traditional blood tests for cancer detection, enabling real-time monitoring of tumor dynamics and treatment response. Unlike conventional blood tests, ctDNA analysis provides high sensitivity in identifying specific genetic mutations and tumor burden, improving personalized oncology care.
Minimal Residual Disease (MRD)
Liquid biopsy offers a highly sensitive method for detecting Minimal Residual Disease (MRD) by analyzing circulating tumor DNA in the bloodstream, providing real-time insights into cancer recurrence and treatment response. Traditional blood tests measure general biomarkers but lack the precision of liquid biopsies in identifying MRD at a molecular level, crucial for personalized cancer management.
Multi-cancer Early Detection (MCED)
Liquid biopsy offers a groundbreaking approach for Multi-cancer Early Detection (MCED) by analyzing circulating tumor DNA, enhancing sensitivity compared to traditional blood tests that primarily detect specific biomarkers. This non-invasive method allows for earlier diagnosis across multiple cancer types, improving treatment outcomes and patient survival rates.
cfDNA (cell-free DNA)
Liquid biopsy analyzes cell-free DNA (cfDNA) circulating in the bloodstream to detect genetic mutations and monitor tumor dynamics with high sensitivity, offering a non-invasive alternative to traditional blood tests which primarily measure biochemical markers. Unlike conventional blood tests, cfDNA-based liquid biopsy provides real-time molecular profiling crucial for early cancer detection, treatment response assessment, and minimal residual disease monitoring.
Tumor-informed Assay
Tumor-informed assays in liquid biopsies provide a highly sensitive method for detecting minimal residual disease by analyzing tumor-specific genetic mutations in circulating tumor DNA, surpassing traditional blood tests in precision. Liquid biopsy enables real-time monitoring of cancer progression and treatment response, offering a personalized and non-invasive alternative to invasive tissue biopsies.
Fragmentomics
Fragmentomics analyzes cell-free DNA fragmentation patterns in blood tests and liquid biopsies to detect cancer-specific signatures with higher sensitivity. Liquid biopsy offers a non-invasive method for real-time cancer monitoring by capturing fragmented DNA shed from tumor cells, enhancing early diagnosis compared to traditional blood tests.
Methylation Profiling
Methylation profiling in blood tests enables detection of specific DNA methylation patterns associated with various diseases, providing insights into epigenetic changes. Liquid biopsy enhances this approach by analyzing circulating tumor DNA methylation profiles, offering a minimally invasive method for early cancer detection and monitoring.
Digital PCR (dPCR)
Digital PCR (dPCR) enhances the sensitivity and precision of liquid biopsy by quantifying low-abundance circulating tumor DNA fragments, offering a less invasive alternative to traditional blood tests. This cutting-edge technology supports early cancer detection and real-time treatment monitoring through highly accurate molecular profiling.
Exosome Analysis
Exosome analysis in liquid biopsy offers a non-invasive alternative to traditional blood tests by isolating extracellular vesicles that carry tumor-derived genetic material, enabling early cancer detection and monitoring with higher sensitivity. Unlike conventional blood tests, liquid biopsy captures dynamic molecular changes in real-time, improving precision in personalized treatment strategies.
Longitudinal Liquid Biopsy
Longitudinal liquid biopsy enables real-time monitoring of tumor dynamics by analyzing circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) over multiple time points, offering greater sensitivity and less invasiveness than traditional blood tests. This approach allows for early detection of treatment resistance and disease progression, improving personalized cancer management and outcome prediction.
Blood Test vs Liquid Biopsy Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com