Diet plays a crucial role in maintaining pet health, but nutrigenomics offers a personalized approach by analyzing how an individual pet's genes interact with specific nutrients. Understanding genetic variations allows pet owners to tailor diets that optimize metabolism, immune response, and overall well-being. This synergy between diet and nutrigenomics enhances the effectiveness of nutritional plans, promoting longevity and disease prevention in pets.
Table of Comparison
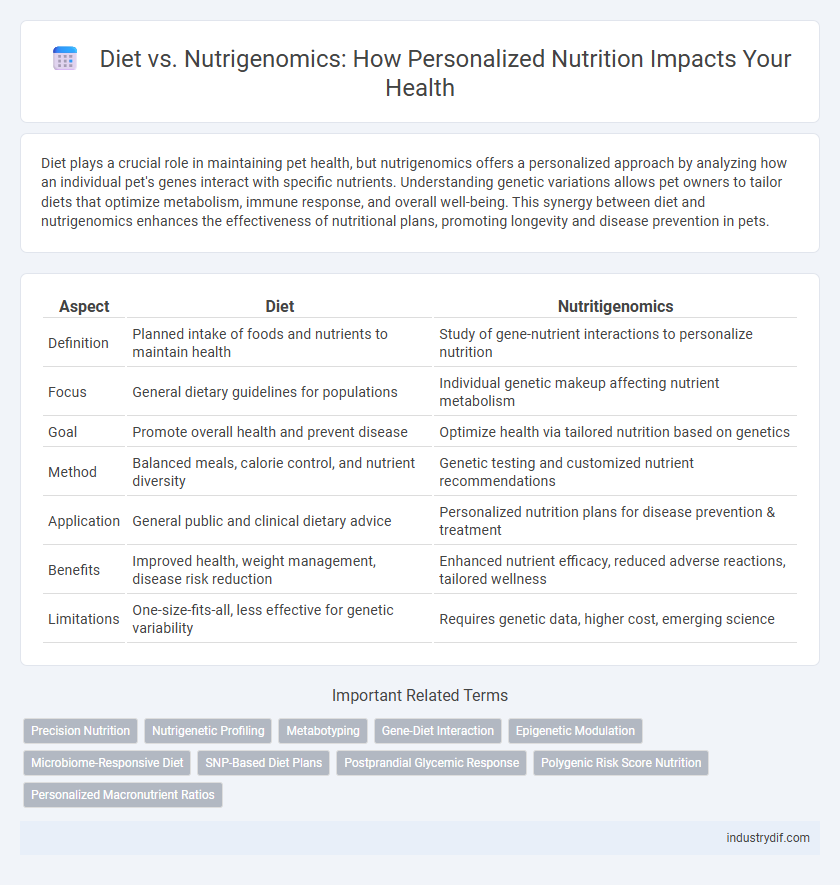
| Aspect | Diet | Nutritigenomics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Planned intake of foods and nutrients to maintain health | Study of gene-nutrient interactions to personalize nutrition |
| Focus | General dietary guidelines for populations | Individual genetic makeup affecting nutrient metabolism |
| Goal | Promote overall health and prevent disease | Optimize health via tailored nutrition based on genetics |
| Method | Balanced meals, calorie control, and nutrient diversity | Genetic testing and customized nutrient recommendations |
| Application | General public and clinical dietary advice | Personalized nutrition plans for disease prevention & treatment |
| Benefits | Improved health, weight management, disease risk reduction | Enhanced nutrient efficacy, reduced adverse reactions, tailored wellness |
| Limitations | One-size-fits-all, less effective for genetic variability | Requires genetic data, higher cost, emerging science |
Understanding Diet: Traditional Approaches to Nutrition
Traditional diet approaches focus on balanced macronutrient intake and calorie management based on general population guidelines, emphasizing whole foods, portion control, and nutrient density. These methods rely on standardized recommendations such as the Mediterranean diet or Dietary Guidelines for Americans to promote health and prevent chronic diseases. While effective for many, traditional diets lack personalization based on genetic variability, which is a key limitation addressed by nutrigenomics.
What is Nutrigenomics? A New Frontier in Health
Nutrigenomics explores how individual genetic makeup interacts with diet to influence health outcomes, offering personalized nutrition strategies that optimize disease prevention and wellness. This emerging field analyzes gene expression changes triggered by nutrients, enabling targeted dietary recommendations that go beyond one-size-fits-all guidelines. By understanding genetic variations affecting nutrient metabolism, nutrigenomics paves the way for precision nutrition, enhancing the effectiveness of dietary interventions in managing conditions like obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases.
Key Differences: Diet vs Nutrigenomics
Diet primarily focuses on general food intake and nutrition guidelines to maintain health, emphasizing calorie balance and macronutrient distribution. Nutrigenomics investigates how individual genetic variations influence nutrient metabolism and dietary responses, enabling personalized nutrition plans. Understanding nutrigenomics allows for tailored dietary interventions that optimize health outcomes based on genetic profiles.
How Genes Influence Nutrient Metabolism
Genes play a crucial role in nutrient metabolism by influencing how individuals absorb, process, and utilize various dietary components. Nutrigenomics explores these genetic variations to tailor diets that optimize health outcomes based on an individual's genetic makeup. Understanding gene-nutrient interactions can enhance personalized nutrition strategies, improving metabolic efficiency and reducing disease risk.
Personalized Nutrition: The Role of Nutrigenomics
Nutrigenomics enables personalized nutrition by analyzing an individual's genetic makeup to tailor dietary recommendations that optimize health and prevent disease. Unlike generic diet plans, this approach considers gene-nutrient interactions that influence metabolism, nutrient absorption, and susceptibility to chronic conditions. Implementing nutrigenomic data enhances dietary precision, promoting improved metabolic responses and long-term wellness.
Benefits and Limitations of Standard Diets
Standard diets provide generalized nutritional guidelines based on population-level data, offering simplicity and ease of adherence for improving overall health outcomes. However, these diets often overlook individual genetic variations that influence nutrient metabolism and disease risk, potentially limiting their effectiveness. NutriGenomics addresses these limitations by tailoring dietary recommendations to one's unique genetic profile, optimizing nutrient intake and minimizing adverse health effects.
Advancements in Nutrigenomic Testing
Advancements in nutrigenomic testing have revolutionized personalized diet plans by analyzing individuals' genetic variations to optimize nutrient intake and metabolic responses. Cutting-edge technologies, including next-generation sequencing and bioinformatics, enable precise identification of gene-diet interactions that influence susceptibility to chronic diseases and weight management. These innovations empower tailored nutritional interventions that enhance overall health and prevent diet-related disorders more effectively than traditional diet approaches.
Practical Applications: Tailoring Diet Based on Genetic Profiles
Tailoring diet based on genetic profiles enhances personalized nutrition strategies by identifying individual variations in nutrient metabolism and sensitivities. Nutrigenomics enables targeted dietary recommendations to optimize health outcomes, prevent chronic diseases, and improve metabolic function. Integrating genetic data with dietary planning allows health professionals to design highly customized nutrition plans that align with unique genetic markers.
Ethical and Privacy Considerations in Nutrigenomics
Nutrigenomics raises critical ethical and privacy considerations related to genetic data handling and informed consent for personalized dietary recommendations. Protecting individual genetic information from misuse or discrimination is essential to maintain trust and promote responsible research practices. Transparent data policies and robust security measures must be implemented to safeguard privacy while advancing personalized nutrition science.
The Future of Nutrition: Integrating Diet with Genomic Science
Nutrigenomics explores how individual genetic variations influence nutrient metabolism, allowing personalized dietary recommendations that optimize health outcomes. Diet plans tailored to one's genome can prevent chronic diseases, improve metabolic efficiency, and enhance nutrient absorption. Integrating diet with genomic science drives the future of nutrition, promoting precision health by aligning nutrition strategies with genetic profiles.
Related Important Terms
Precision Nutrition
Precision nutrition harnesses nutrigenomics to tailor dietary recommendations based on an individual's genetic makeup, optimizing health outcomes by targeting specific metabolic pathways and nutrient interactions. This personalized approach surpasses traditional diet plans by considering genetic variations that influence nutrient absorption, metabolism, and risk factors for chronic diseases.
Nutrigenetic Profiling
Nutrigenetic profiling tailors dietary recommendations based on an individual's genetic makeup, enhancing personalized nutrition by identifying gene variants that affect nutrient metabolism and disease risk. Unlike generic diet plans, this approach optimizes nutrient intake to improve health outcomes and prevent chronic conditions through targeted genetic insights.
Metabotyping
Metabotyping, a key component of nutrigenomics, classifies individuals based on metabolic profiles to tailor diet recommendations for improved health outcomes. Unlike generic diet plans, metabotyping leverages genetic and metabolic data to optimize nutrient intake and personalized disease prevention.
Gene-Diet Interaction
Gene-diet interaction explores how individual genetic variations influence the body's response to specific nutrients, highlighting the personalized approach of nutrigenomics compared to general diet plans. Understanding these interactions enables tailored nutrition strategies that optimize health outcomes by targeting genetic predispositions and metabolic pathways.
Epigenetic Modulation
Diet influences epigenetic modulation by altering DNA methylation and histone modification patterns, impacting gene expression related to metabolic health and disease risk. Nutrigenomics investigates individual genetic responses to dietary components, enabling personalized nutrition strategies that optimize epigenetic regulation for improved health outcomes.
Microbiome-Responsive Diet
Microbiome-responsive diets tailor nutrient intake based on an individual's gut microbiota composition, enhancing metabolic health and reducing inflammation. Unlike traditional diets, nutrigenomics leverages genetic data to optimize diet, but microbiome-based approaches offer dynamic insights into real-time dietary impacts on microbial balance and overall wellness.
SNP-Based Diet Plans
SNP-based diet plans leverage individual genetic variations, particularly single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), to tailor nutrition strategies that optimize metabolic responses and disease risk reduction. This precision approach outperforms generic diet recommendations by addressing how specific gene variants influence nutrient absorption, metabolism, and overall health outcomes.
Postprandial Glycemic Response
Postprandial glycemic response varies significantly between individuals due to genetic factors influencing nutrient metabolism, making nutrigenomics a critical tool for personalized diet planning. Unlike standard diet guidelines, nutrigenomics tailors carbohydrate intake to optimize blood glucose control and reduce the risk of metabolic diseases by analyzing gene-diet interactions.
Polygenic Risk Score Nutrition
Polygenic Risk Score Nutrition leverages genetic data to tailor dietary recommendations that reduce the risk of chronic diseases by addressing individual polygenic risk factors. Unlike traditional diet approaches, this method integrates genomics to optimize nutrient intake based on inherited genetic variations influencing metabolism and disease susceptibility.
Personalized Macronutrient Ratios
Personalized macronutrient ratios in nutrigenomics tailor protein, carbohydrate, and fat intake based on an individual's genetic profile to optimize metabolism and reduce disease risk. Unlike traditional diets with fixed macronutrient guidelines, nutrigenomics-driven plans enhance nutrient absorption and metabolic efficiency by accounting for genetic variations in nutrient processing.
Diet vs Nutritigenomics Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com