Hospital-at-home programs provide acute medical care in the comfort of a pet's home, reducing stress and exposure to hospital-acquired infections compared to traditional hospital stays. Advanced telemedicine and skilled veterinary support enable timely interventions and monitoring, ensuring pets receive high-quality treatment while recovering in familiar environments. This approach can lead to faster recovery times, improved pet comfort, and reduced overall healthcare costs.
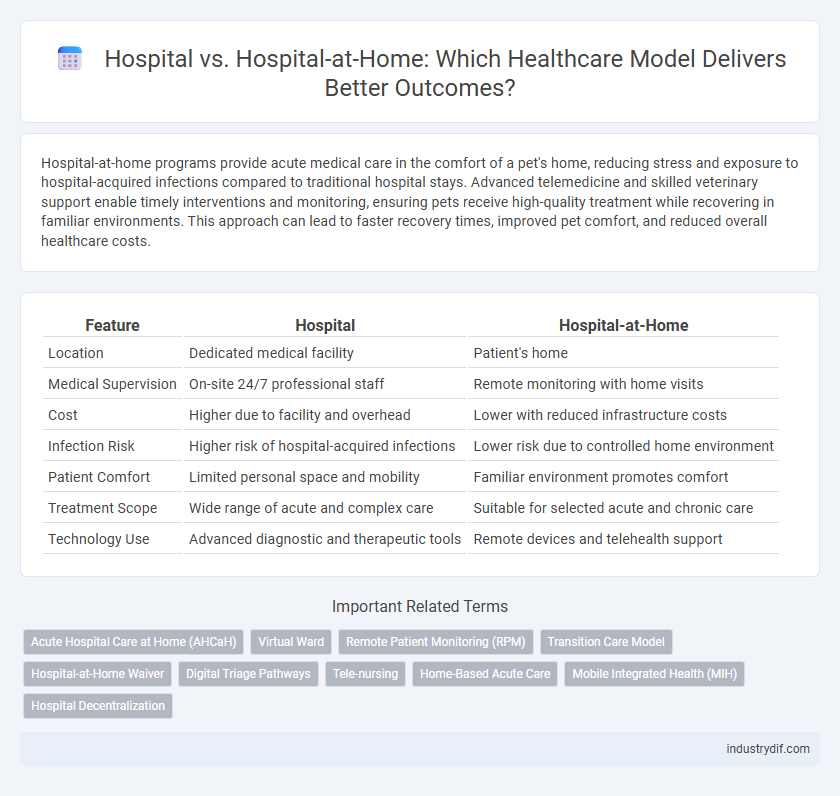
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hospital | Hospital-at-Home |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Dedicated medical facility | Patient's home |
| Medical Supervision | On-site 24/7 professional staff | Remote monitoring with home visits |
| Cost | Higher due to facility and overhead | Lower with reduced infrastructure costs |
| Infection Risk | Higher risk of hospital-acquired infections | Lower risk due to controlled home environment |
| Patient Comfort | Limited personal space and mobility | Familiar environment promotes comfort |
| Treatment Scope | Wide range of acute and complex care | Suitable for selected acute and chronic care |
| Technology Use | Advanced diagnostic and therapeutic tools | Remote devices and telehealth support |
Overview of Hospital and Hospital-at-Home Care
Hospital care involves patients receiving medical treatment within a traditional brick-and-mortar facility, where they have access to specialized equipment, continuous monitoring, and onsite healthcare professionals. Hospital-at-Home care delivers acute and post-acute healthcare services in a patient's residence, leveraging telehealth technologies and mobile medical teams to provide personalized, convenient treatments. Both models aim to improve patient outcomes, but Hospital-at-Home emphasizes reduced hospital stays, lower infection risks, and enhanced comfort while maintaining clinical oversight.
Key Differences Between Inpatient and At-Home Hospitalization
Inpatient hospitalization involves continuous monitoring, advanced diagnostics, and immediate access to specialized medical equipment within a hospital setting, ensuring intensive care for severe conditions. Hospital-at-Home programs provide acute care services in a patient's residence, utilizing telemedicine, remote monitoring devices, and home visits by healthcare professionals, promoting comfort and reducing infection risk. The primary differences lie in the care environment, level of direct supervision, and resource availability, with Hospital-at-Home emphasizing patient-centered convenience and potential cost savings.
Patient Eligibility Criteria and Selection
Patient eligibility criteria for Hospital-at-Home programs typically include stable vital signs, manageable symptoms, and a supportive home environment, ensuring safety and effective care outside traditional hospital settings. Hospitals prioritize patients with acute or complex conditions requiring intensive monitoring and immediate intervention that cannot be provided at home. Selection protocols assess clinical stability, risk of deterioration, and availability of caregiver support to determine the most appropriate care setting.
Clinical Outcomes: Efficacy and Safety Comparison
Hospital-at-Home programs demonstrate comparable efficacy to traditional hospital care by effectively managing acute conditions such as pneumonia and heart failure while reducing hospital-acquired infections and adverse events. Clinical outcomes show similar or improved patient recovery rates, with lower readmission rates and enhanced patient safety profiles due to continuous in-home monitoring and tailored interventions. Studies reveal that Hospital-at-Home models can achieve equivalent or superior safety outcomes by minimizing exposure to nosocomial infections and promoting early mobilization.
Cost Implications and Reimbursement Models
Hospital-at-Home programs reduce healthcare costs by minimizing expenses related to inpatient stays, including room charges and facility fees, while maintaining comparable quality of care. Reimbursement models are evolving to support these services, with Medicare and private insurers increasingly adopting bundled payment approaches and value-based care incentives tailored to home-based acute care. Cost savings combined with flexible reimbursement schemes position Hospital-at-Home as a financially sustainable alternative to traditional hospitalization.
Technology and Remote Monitoring in Hospital-at-Home
Hospital-at-Home leverages advanced technology and remote monitoring tools to deliver acute care outside traditional hospital settings, allowing continuous real-time patient data tracking such as vital signs and oxygen levels through wearable devices. This approach minimizes hospital-acquired infection risks and reduces healthcare costs by enabling healthcare professionals to intervene promptly via telehealth platforms and AI-driven analytics. Remote monitoring facilitates personalized treatment plans and early detection of complications, improving patient outcomes while maintaining hospital-level care in the comfort of patients' homes.
Staffing, Roles, and Workforce Considerations
Hospital settings rely on multidisciplinary teams including physicians, nurses, specialists, and support staff working 24/7 onsite to manage acute patient care, complex diagnostics, and emergency interventions. Hospital-at-Home programs utilize a tailored workforce model combining visiting nurses, telehealth physicians, and home health aides to deliver hospital-level care remotely, requiring specialized training in home-based clinical assessments and patient education. Staffing strategies for Hospital-at-Home emphasize flexibility, cross-functional skills, and coordination to ensure continuity, patient safety, and adherence to treatment protocols in decentralized environments.
Patient Experience and Satisfaction Metrics
Hospital-at-Home programs demonstrate higher patient satisfaction scores compared to traditional hospital stays, with improved comfort and personalized care reported in over 85% of cases. Patients receiving Hospital-at-Home services experience fewer complications and shorter recovery times, which contribute to enhanced overall patient experience metrics. Surveys indicate a 30% reduction in patient-reported stress and anxiety levels when treated at home rather than in an inpatient hospital setting.
Regulatory, Licensing, and Accreditation Challenges
Hospital-at-Home programs face complex regulatory, licensing, and accreditation challenges compared to traditional hospitals, requiring alignment with state health department standards and CMS regulations for reimbursement. Ensuring compliance with HIPAA, patient safety protocols, and quality reporting metrics is essential for accreditation by organizations such as The Joint Commission or ACHC. Navigating varying state licensure requirements and adapting existing hospital policies to a home care setting remain significant hurdles in widespread adoption.
Future Trends and Innovations in Acute Care Delivery
Emerging innovations in acute care delivery emphasize the integration of Hospital-at-Home models, utilizing telemedicine, remote monitoring technologies, and personalized care protocols to reduce hospital admissions and improve patient outcomes. Future trends include advanced AI-driven diagnostics and real-time data analytics that enable proactive interventions and optimized resource allocation outside traditional hospital settings. These approaches promise enhanced patient comfort, lower healthcare costs, and scalable solutions for managing complex acute conditions in decentralized environments.
Related Important Terms
Acute Hospital Care at Home (AHCaH)
Acute Hospital Care at Home (AHCaH) delivers complex hospital-level treatments in the patient's residence, reducing risks of hospital-acquired infections and enhancing patient comfort compared to traditional hospital settings. This model integrates advanced remote monitoring technologies and multidisciplinary clinical teams to provide timely, effective care equivalent to in-hospital services.
Virtual Ward
Virtual Ward in hospital-at-home models leverages remote monitoring technology and telehealth to provide acute care outside traditional hospital settings, improving patient outcomes and reducing readmission rates. This approach integrates continuous data tracking, virtual consultations, and personalized care plans, offering a scalable alternative to inpatient hospitalization while maintaining clinical safety and patient satisfaction.
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) in Hospital-at-Home models leverages wearable sensors and real-time data analytics to track vital signs, enabling early detection of complications and reducing hospital readmissions. In contrast, traditional hospitals rely more on intermittent bedside monitoring, which may delay intervention and increase healthcare costs.
Transition Care Model
The Transition Care Model (TCM) emphasizes coordinated, patient-centered care to reduce hospital readmissions and improve recovery, making Hospital-at-Home a viable alternative by delivering acute-level interventions in a familiar home environment. This approach leverages multidisciplinary teams and telehealth technologies to provide continuous monitoring and personalized treatment, enhancing patient outcomes compared to traditional hospital stays.
Hospital-at-Home Waiver
Hospital-at-Home Waiver allows patients to receive acute-level medical care in their own homes, reducing hospital stays and minimizing infection risks. This program enhances patient comfort and convenience by providing services such as nursing, medication administration, and remote monitoring under physician supervision.
Digital Triage Pathways
Hospital-at-Home programs leverage advanced digital triage pathways to remotely assess patient symptoms, enabling real-time monitoring and personalized care plans, which reduces hospital admissions and improves patient outcomes. These digital triage systems use AI-driven algorithms and telemedicine tools to streamline patient evaluation, ensuring timely interventions and efficient resource allocation compared to traditional hospital settings.
Tele-nursing
Tele-nursing in Hospital-at-Home programs enhances patient care by enabling continuous remote monitoring and timely intervention, reducing hospital readmission rates and healthcare costs. Leveraging advanced telehealth technologies, tele-nurses deliver personalized support and clinical assessments, ensuring improved patient outcomes compared to traditional hospital stays.
Home-Based Acute Care
Home-Based Acute Care delivers hospital-level treatment in the comfort of a patient's residence, reducing risks of hospital-acquired infections and improving patient satisfaction. Hospitals implementing Hospital-at-Home programs utilize advanced telemedicine technology and remote monitoring to provide timely, effective care while lowering overall healthcare costs.
Mobile Integrated Health (MIH)
Mobile Integrated Health (MIH) enhances Hospital-at-Home programs by leveraging mobile healthcare teams to deliver acute and chronic care directly to patients' residences, reducing hospital admissions and improving patient outcomes. This model integrates telehealth, remote monitoring, and community paramedicine to provide cost-effective, personalized care that aligns with hospital standards while minimizing the risk of hospital-associated infections.
Hospital Decentralization
Hospital decentralization through Hospital-at-Home programs enables patients to receive acute care in their own residences, reducing strain on traditional hospital infrastructure and lowering risk of hospital-acquired infections. This shift leverages telemedicine and mobile healthcare teams, improving patient outcomes and optimizing resource allocation across healthcare systems.
Hospital vs Hospital-at-Home Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com