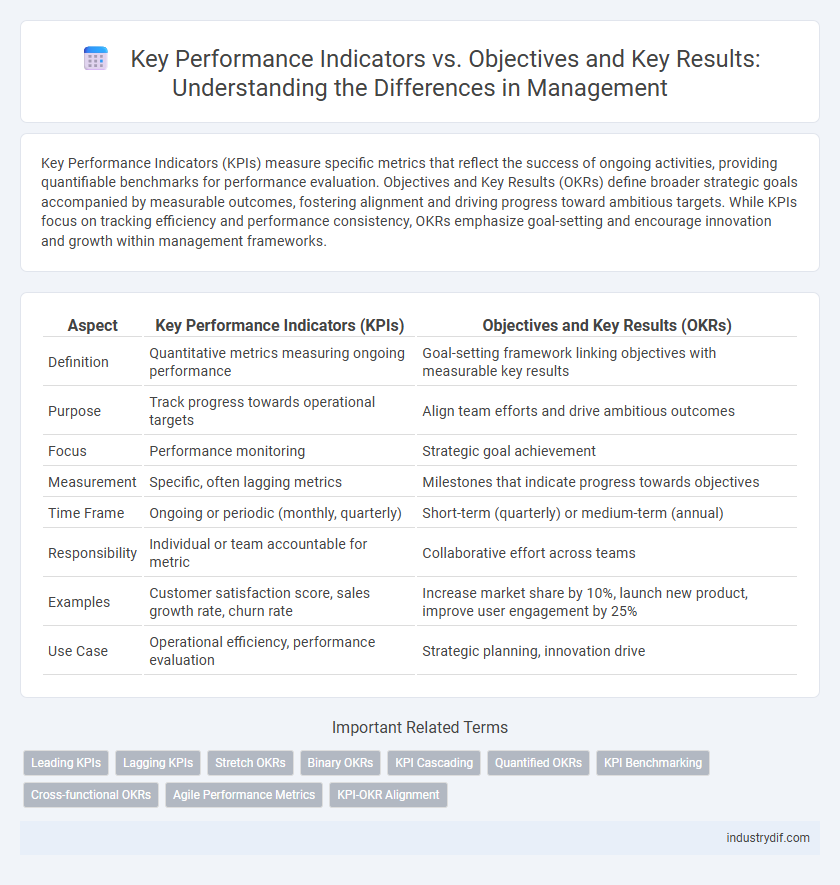
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) measure specific metrics that reflect the success of ongoing activities, providing quantifiable benchmarks for performance evaluation. Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) define broader strategic goals accompanied by measurable outcomes, fostering alignment and driving progress toward ambitious targets. While KPIs focus on tracking efficiency and performance consistency, OKRs emphasize goal-setting and encourage innovation and growth within management frameworks.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) | Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Quantitative metrics measuring ongoing performance | Goal-setting framework linking objectives with measurable key results |
| Purpose | Track progress towards operational targets | Align team efforts and drive ambitious outcomes |
| Focus | Performance monitoring | Strategic goal achievement |
| Measurement | Specific, often lagging metrics | Milestones that indicate progress towards objectives |
| Time Frame | Ongoing or periodic (monthly, quarterly) | Short-term (quarterly) or medium-term (annual) |
| Responsibility | Individual or team accountable for metric | Collaborative effort across teams |
| Examples | Customer satisfaction score, sales growth rate, churn rate | Increase market share by 10%, launch new product, improve user engagement by 25% |
| Use Case | Operational efficiency, performance evaluation | Strategic planning, innovation drive |
Understanding Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are quantifiable metrics that measure the effectiveness of achieving specific business goals, providing ongoing performance tracking and actionable insights. KPIs focus on operational targets such as sales growth, customer retention, or production efficiency, enabling managers to monitor progress and make data-driven decisions. Unlike Objectives and Key Results (OKRs), which emphasize ambitious goal-setting and alignment across teams, KPIs prioritize consistent measurement of critical success factors essential for organizational performance.
Defining Objectives and Key Results (OKRs)
Defining Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) involves setting clear, ambitious goals paired with measurable outcomes that track progress and success. Unlike general Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), OKRs emphasize alignment and focus by linking objectives directly to measurable key results. This structured approach enhances transparency and drives performance by ensuring teams prioritize impactful activities aligned with strategic goals.
Core Differences Between KPIs and OKRs
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) measure specific metrics to track ongoing performance, focusing on quantifiable outcomes that reflect success in business processes. Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) combine qualitative goals with measurable key results to drive strategic initiatives and promote alignment across teams. Unlike KPIs, OKRs emphasize ambition and progress toward broader objectives rather than static performance measurement.
KPIs: Measurement and Tracking Success
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) provide quantifiable metrics that measure progress toward specific business goals, enabling organizations to monitor performance effectively. KPIs focus on critical success factors and deliver real-time data that guide decision-making and operational adjustments. Continuous tracking of KPIs helps identify trends, improve accountability, and ensure alignment with strategic objectives.
OKRs: Setting Ambitious Goals and Outcomes
OKRs (Objectives and Key Results) harness ambitious goal-setting by linking qualitative objectives with measurable outcomes, driving organizational focus and alignment. Unlike traditional Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), which track ongoing performance metrics, OKRs emphasize aspirational targets that encourage innovation and growth. This approach fosters transparency and accountability, enabling teams to push boundaries while clearly defining success through specific, measurable results.
When to Use KPIs vs OKRs in Management
KPIs measure ongoing performance against specific targets, making them ideal for monitoring efficiency and operational success in stable environments. OKRs drive strategic alignment and ambitious growth by setting challenging goals with measurable outcomes, suitable for dynamic or transformational phases. Use KPIs for tracking routine processes and OKRs for fostering innovation and organizational change.
Integrating KPIs and OKRs for Optimal Performance
Integrating Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) creates a cohesive framework that aligns measurable outcomes with strategic goals, enhancing organizational performance. KPIs track specific metrics to monitor ongoing efficiency, while OKRs set ambitious, time-bound objectives that drive transformational progress. Combining these tools ensures continuous performance assessment and agile goal adjustment, fostering a culture of accountability and sustained growth.
Common Pitfalls in Implementing KPIs and OKRs
Common pitfalls in implementing Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) include setting unclear or misaligned goals that fail to drive meaningful progress, relying too heavily on quantitative metrics without qualitative context, and neglecting regular review and adaptation processes. Overemphasis on vanity metrics can distort performance insights, while lack of stakeholder buy-in undermines engagement and accountability. Successful implementation requires clear communication, relevance to strategic priorities, and continuous monitoring to ensure KPIs and OKRs truly reflect organizational objectives and foster growth.
Industry Best Practices for KPI and OKR Alignment
Industry best practices for KPI and OKR alignment emphasize setting clear, measurable KPIs that directly support the achievement of strategic OKRs, ensuring organizational focus and accountability. Effective integration involves periodic reviews where KPI outcomes are analyzed to refine OKRs, promoting agility and continuous improvement. Leveraging data-driven dashboards enhances transparency, enabling real-time tracking of both KPIs and OKRs to drive performance excellence.
Choosing the Right Framework for Your Organization
Selecting the appropriate management framework depends on organizational goals and operational dynamics, with Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) offering precise metrics to monitor performance and Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) fostering alignment through ambitious goal setting and measurable outcomes. KPIs excel in tracking ongoing processes and maintaining efficiency, while OKRs drive transformative initiatives by encouraging innovation and stretch targets. Understanding the distinct purposes of KPIs and OKRs ensures strategic clarity and maximizes performance impact within diverse organizational environments.
Related Important Terms
Leading KPIs
Leading Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) provide early signals of future performance and are essential for proactive management, whereas Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) align broader organizational goals with measurable outcomes. Leading KPIs drive agile decision-making by highlighting trends before lagging metrics reveal results, enabling real-time adjustments to achieve strategic objectives effectively.
Lagging KPIs
Lagging Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) measure outcomes and final results, reflecting past performance and helping organizations assess the success of their strategic initiatives. In contrast, Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) combine ambitious goals with measurable milestones, often relying on leading indicators to drive progress before lagging KPIs confirm the achieved impact.
Stretch OKRs
Stretch OKRs drive ambitious growth by setting challenging targets that exceed standard Key Performance Indicators, promoting innovation and continuous improvement. Unlike static KPIs, stretch OKRs emphasize aspirational goals with measurable outcomes, fostering greater motivation and strategic alignment across teams.
Binary OKRs
Binary OKRs simplify performance tracking by focusing on clear, measurable outcomes with a yes/no status, enhancing clarity compared to traditional Key Performance Indicators that often require continuous metric evaluation. This approach drives decisive progress assessment and aligns team efforts with organizational goals through unambiguous completion signals.
KPI Cascading
KPI cascading ensures alignment by breaking down Key Performance Indicators from top-level strategic goals to individual tasks, enabling precise tracking of performance across all organizational layers. Unlike OKRs, which emphasize ambitious goal-setting and measurable outcomes, KPIs focus on continuous performance metrics that drive operational efficiency through a structured cascade process.
Quantified OKRs
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) measure specific metrics to gauge ongoing performance, while Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) focus on setting ambitious goals with clearly quantified key results to drive strategic progress. Quantified OKRs emphasize measurable outcomes, enabling precise tracking of objective achievement and alignment across teams.
KPI Benchmarking
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) provide quantifiable metrics essential for KPI benchmarking, enabling organizations to measure performance against industry standards or competitors effectively. Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) complement this by defining strategic goals and tracking progress through specific outcomes, ensuring alignment with overall business priorities.
Cross-functional OKRs
Cross-functional OKRs drive collaboration across departments by setting measurable, transparent goals aligned with overall business strategy, enhancing agility and accountability. Unlike traditional KPIs that track isolated performance metrics, OKRs foster integrated team efforts and continuous progress evaluation.
Agile Performance Metrics
Agile performance metrics emphasize Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) by aligning team goals with measurable outcomes, enhancing adaptability and focus in fast-paced environments. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) provide consistent benchmarks for ongoing processes but may lack the dynamic flexibility required for continuous improvement in agile frameworks.
KPI-OKR Alignment
Effective management requires aligning Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) with Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) to ensure measurable progress toward strategic goals. This alignment enhances organizational focus by linking specific metrics to broader outcomes, facilitating transparent performance tracking and agile decision-making.
Key Performance Indicators vs Objectives and Key Results Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com