Span of control determines the number of direct reports a manager can effectively oversee, impacting decision-making efficiency and communication clarity. Agile squads operate with a smaller, focused span of control to enhance collaboration, autonomy, and rapid delivery within cross-functional teams. Balancing span of control with agile principles fosters empowered squads that adapt quickly and maintain high productivity.
Table of Comparison
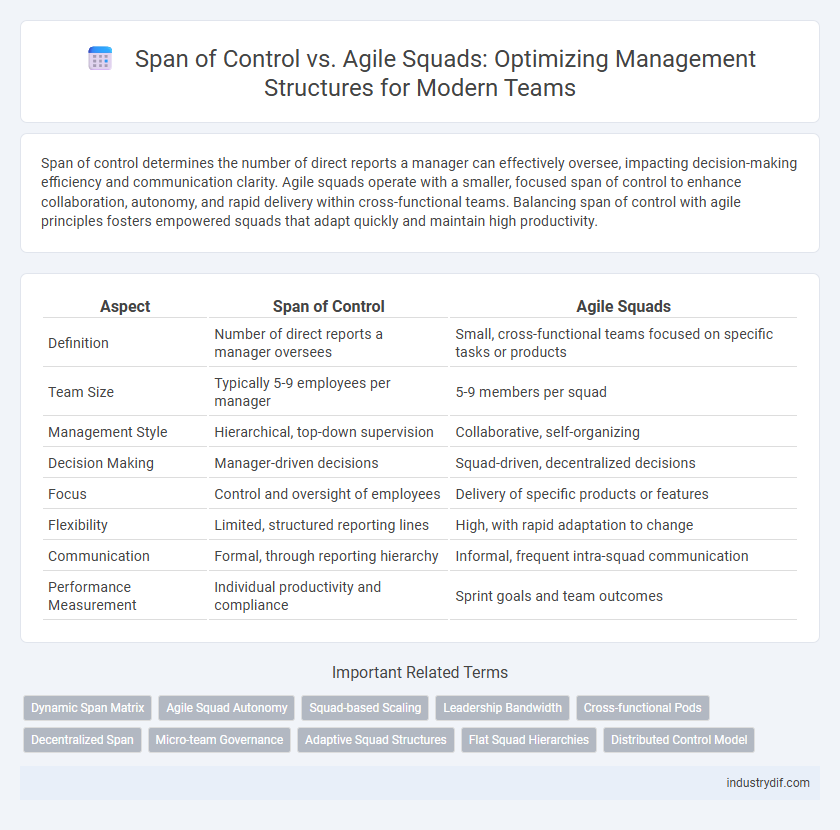
| Aspect | Span of Control | Agile Squads |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Number of direct reports a manager oversees | Small, cross-functional teams focused on specific tasks or products |
| Team Size | Typically 5-9 employees per manager | 5-9 members per squad |
| Management Style | Hierarchical, top-down supervision | Collaborative, self-organizing |
| Decision Making | Manager-driven decisions | Squad-driven, decentralized decisions |
| Focus | Control and oversight of employees | Delivery of specific products or features |
| Flexibility | Limited, structured reporting lines | High, with rapid adaptation to change |
| Communication | Formal, through reporting hierarchy | Informal, frequent intra-squad communication |
| Performance Measurement | Individual productivity and compliance | Sprint goals and team outcomes |
Understanding Span of Control in Traditional Management
Understanding span of control in traditional management involves analyzing the number of direct reports a manager can effectively supervise, typically ranging from five to ten employees. This structure emphasizes clear hierarchy and centralized decision-making, ensuring consistent communication and accountability within the team. In contrast, agile squads operate with smaller, cross-functional teams that promote decentralized authority and rapid adaptability.
Defining Agile Squads in Modern Organizations
Agile squads in modern organizations consist of small, cross-functional teams empowered to make decisions independently, enabling rapid adaptation and increased innovation. Unlike traditional span of control models that emphasize hierarchical supervision, agile squads prioritize collaboration and autonomy, breaking down silos to enhance responsiveness. This approach aligns with dynamic market demands by promoting flexibility and accountability within decentralized team structures.
Key Differences: Span of Control vs Agile Squads
Span of Control defines the number of direct reports a manager supervises, emphasizing hierarchical oversight and centralized decision-making, while Agile Squads operate as cross-functional, self-managed teams with decentralized authority fostering collaboration and adaptability. Span of Control prioritizes clear command chains and workload balance, whereas Agile Squads focus on flexibility, continuous delivery, and iterative problem-solving within dynamic environments. These key differences highlight traditional organizational structure versus modern agile frameworks designed to enhance responsiveness and innovation.
Impact on Decision-Making Authority
A narrow span of control centralizes decision-making authority, enabling managers to closely monitor and guide team members, which can slow down responsiveness in dynamic environments. Agile squads operate with decentralized decision-making, granting teams autonomy to make swift choices, enhancing adaptability and innovation. Balancing span of control with agile principles improves organizational agility by empowering squads while maintaining necessary managerial oversight.
Team Structure and Communication Flow
Span of control directly influences team structure by determining the number of direct reports a manager can effectively supervise, which contrasts with Agile squads designed for cross-functional collaboration and autonomous decision-making. Agile squads emphasize decentralized communication flow, enabling rapid feedback loops and adaptability, whereas traditional spans of control rely on hierarchical communication channels that may slow information exchange. Optimizing team structure involves balancing manageable spans of control with the dynamic, networked communication practices intrinsic to Agile squads to enhance responsiveness and productivity.
Leadership Roles in Span of Control and Agile Squads
Leadership roles in span of control emphasize hierarchical supervision, where managers directly oversee a defined number of subordinates to maintain clear accountability and streamlined decision-making. In contrast, agile squads operate with decentralized leadership, empowering cross-functional team members to self-organize and adapt quickly within their roles. The shift from span of control to agile squads reflects a move toward flexibility, fostering innovation and faster response times by distributing leadership responsibilities across the team.
Adaptability to Organizational Change
Span of control traditionally limits manager oversight to a fixed number of subordinates, often slowing adaptability during organizational change. Agile squads operate with decentralized decision-making and cross-functional teams, enhancing responsiveness and flexibility in dynamic environments. This model supports rapid iteration and continuous feedback, critical for managing change in fast-paced markets.
Performance Measurement: Efficiency vs Agility
Span of control emphasizes efficiency by limiting the number of direct reports for streamlined decision-making and standardized performance metrics, enhancing control and accountability. Agile squads prioritize agility through cross-functional teams empowered to adapt rapidly, using iterative feedback and dynamic KPIs that capture innovation speed and customer responsiveness. Balancing these approaches requires integrating quantitative efficiency indicators with qualitative agility metrics to optimize overall organizational performance.
Challenges in Transitioning from Span of Control to Agile Squads
Transitioning from traditional Span of Control to Agile Squads presents challenges in redefining leadership roles and decision-making autonomy, often causing confusion in accountability and communication flows. Managers must adapt to decentralized control, empowering squads to self-organize while maintaining alignment with organizational goals. Resistance to change and the need for continuous coaching hinder seamless adoption, requiring tailored strategies to bridge cultural and operational gaps.
Best Practices for Integrating Span of Control with Agile Methods
Optimizing span of control in Agile squads requires limiting the number of direct reports to enhance team autonomy and communication flow. Effective integration involves keeping squad sizes typically between 5 to 9 members, enabling swift decision-making aligned with Agile principles. Emphasizing cross-functional roles and clear leadership within each squad ensures balanced oversight while preserving the flexibility central to Agile methodologies.
Related Important Terms
Dynamic Span Matrix
Dynamic Span Matrix enhances management effectiveness by adjusting span of control in real-time based on Agile squads' workload, skill diversity, and project complexity. This adaptive approach ensures optimal leader-to-team ratios, boosting responsiveness and collaboration within Agile frameworks.
Agile Squad Autonomy
Agile squads operate with a high degree of autonomy, enabling faster decision-making and adaptability compared to traditional span of control models that emphasize hierarchical oversight. This autonomy empowers teams to self-organize, prioritize tasks, and respond swiftly to changing project requirements, driving innovation and efficiency in dynamic management environments.
Squad-based Scaling
Span of control in traditional management limits the number of direct reports per leader, whereas agile squads adopt a flat structure with small, cross-functional teams to enhance responsiveness and collaboration. Squad-based scaling prioritizes decentralized decision-making and continuous feedback loops to improve adaptability and accelerate delivery in complex projects.
Leadership Bandwidth
Leadership bandwidth in Span of Control limits the number of direct reports a manager can effectively supervise, typically ranging between 5 to 9 employees, ensuring focused guidance and decision-making. In Agile Squads, leadership bandwidth is optimized through decentralized autonomy and cross-functional teams, enabling faster decision cycles and enhanced adaptability without overburdening any single leader.
Cross-functional Pods
Cross-functional pods in Agile squads optimize span of control by fostering decentralized decision-making and enhancing team autonomy, enabling faster adaptation to change and improved collaboration. This structure contrasts traditional hierarchical spans by integrating diverse expertise within pods, reducing management layers and increasing efficiency.
Decentralized Span
Decentralized span of control in agile squads enhances autonomy by distributing decision-making authority across team members, fostering faster responsiveness and innovation. This model supports fluid team structures, minimizing hierarchical bottlenecks and enabling adaptive management aligned with agile principles.
Micro-team Governance
Span of control impacts micro-team governance by determining how many Agile squad members a manager can effectively oversee, influencing decision-making speed and team autonomy. Optimizing span of control enhances Agile squad performance by balancing oversight with empowerment, fostering adaptability and collaborative innovation.
Adaptive Squad Structures
Adaptive squad structures enable dynamic span of control adjustments by promoting decentralized decision-making and flexible team sizes, optimizing responsiveness in Agile environments. This approach enhances collaboration and speeds up project delivery by tailoring management layers to squad capabilities and project complexity.
Flat Squad Hierarchies
Flat squad hierarchies in agile teams maximize efficiency by reducing span of control, enabling managers to oversee fewer team members directly, which fosters rapid decision-making and enhanced collaboration. This streamlined structure supports adaptive workflows and accelerates project delivery by empowering squads with greater autonomy and accountability.
Distributed Control Model
The Distributed Control Model enhances Span of Control by decentralizing decision-making across Agile Squads, enabling faster responsiveness and increased autonomy within teams. This approach reduces management bottlenecks, fostering collaboration and empowering squads to innovate while maintaining alignment with organizational goals.
Span of Control vs Agile Squads Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com