Teamwork involves coordinated efforts where each member has defined roles contributing to a common goal, ensuring structured collaboration and accountability. Swarming, in contrast, is a dynamic, rapid response approach where team members collectively address an urgent issue without predetermined roles, allowing flexibility and immediate problem-solving. Both methods enhance productivity, but choosing between them depends on task complexity and the need for speed versus organization.
Table of Comparison
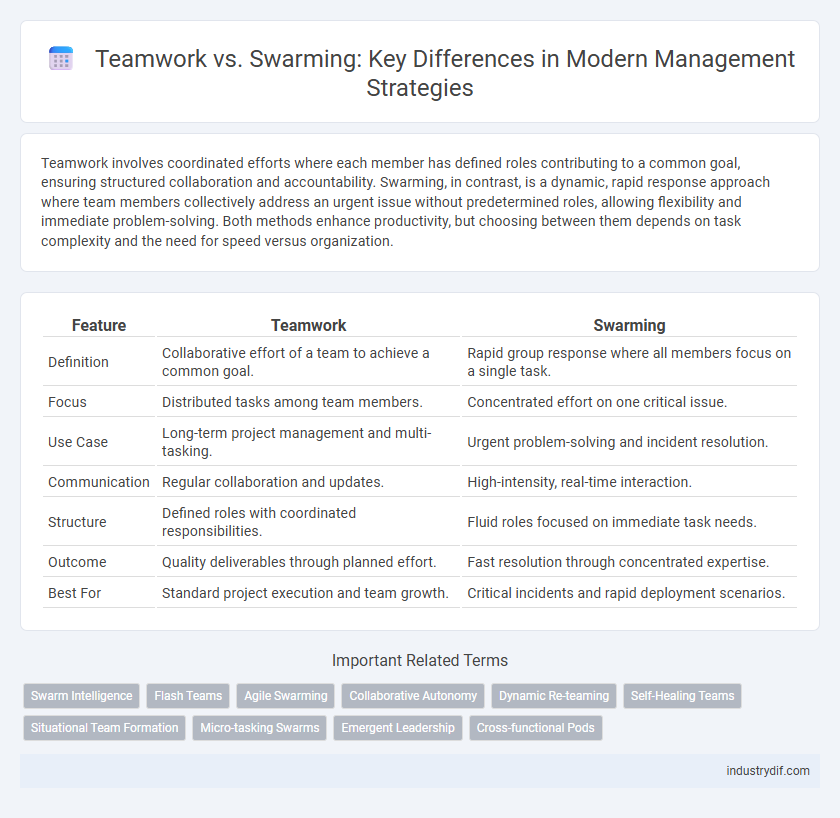
| Feature | Teamwork | Swarming |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Collaborative effort of a team to achieve a common goal. | Rapid group response where all members focus on a single task. |
| Focus | Distributed tasks among team members. | Concentrated effort on one critical issue. |
| Use Case | Long-term project management and multi-tasking. | Urgent problem-solving and incident resolution. |
| Communication | Regular collaboration and updates. | High-intensity, real-time interaction. |
| Structure | Defined roles with coordinated responsibilities. | Fluid roles focused on immediate task needs. |
| Outcome | Quality deliverables through planned effort. | Fast resolution through concentrated expertise. |
| Best For | Standard project execution and team growth. | Critical incidents and rapid deployment scenarios. |
Defining Teamwork in Modern Management
Teamwork in modern management emphasizes collaborative efforts where members share responsibilities, communicate effectively, and align their skills toward common organizational goals. It fosters trust, accountability, and a structured workflow, enabling consistent progress and long-term success. Effective teamwork integrates diverse expertise, enhancing problem-solving and innovation in dynamic business environments.
Understanding the Concept of Swarming
Swarming in management refers to a dynamic approach where a group of team members simultaneously focus on a single task or problem until it is resolved, promoting rapid problem-solving and collaboration. Unlike traditional teamwork, which distributes tasks among individuals, swarming harnesses collective expertise in real-time to address urgent issues efficiently. This method enhances agility and responsiveness, particularly in environments requiring quick decision-making and adaptive solutions.
Key Differences: Teamwork vs. Swarming
Teamwork involves a stable group of individuals collaborating over time toward common goals, emphasizing defined roles and structured communication. Swarming is a dynamic approach where multiple team members rapidly converge on a task or problem, prioritizing speed and flexibility over role specialization. Key differences lie in their operational models: teamwork supports long-term coordination and accountability, while swarming enhances rapid response and collective problem-solving in urgent situations.
Advantages of Teamwork Practices
Teamwork enhances organizational productivity by leveraging diverse skills and perspectives, fostering collaboration, and improving problem-solving capabilities. Effective teamwork promotes consistent communication, accountability, and trust among members, which leads to stronger commitment and higher quality outcomes. Established teamwork practices also support long-term relationship building and knowledge retention, driving sustainable growth and innovation.
Benefits of Swarming in Agile Environments
Swarming enhances Agile environments by enabling rapid problem-solving through collective team focus on high-priority tasks, which accelerates delivery and increases flexibility. Unlike traditional teamwork, swarming fosters real-time collaboration and immediate knowledge sharing, reducing bottlenecks and improving overall product quality. This approach supports continuous improvement and adaptability, critical for meeting dynamic customer demands in Agile frameworks.
Challenges of Implementing Teamwork
Implementing teamwork often faces challenges such as communication barriers, conflicting personalities, and unclear roles that hinder collaboration and productivity. Differences in individual work styles and resistance to group decisions can lead to reduced efficiency and frustration among team members. Overcoming these obstacles requires structured conflict resolution strategies and consistent team-building efforts to foster trust and alignment.
Obstacles to Effective Swarming
Obstacles to effective swarming in management include lack of clear communication channels, which hinder rapid information sharing among team members. Insufficient trust and collaboration skills can cause delays and conflicts, preventing swift problem resolution. Additionally, inadequate training on swarming methodologies results in inconsistent participation and reduced overall efficiency.
When to Choose Teamwork Over Swarming
Choose teamwork over swarming when tasks require long-term collaboration, consistent role clarity, and stable communication channels. Teamwork excels in projects involving complex problem-solving, where individual expertise contributes to defined roles and goals within a structured environment. Opting for teamwork supports sustained productivity and accountability in organizations prioritizing efficiency and cohesion.
Industry Case Studies: Teamwork vs. Swarming
Industry case studies reveal that teamwork structures enable clear role definitions and accountability, which optimize project timelines in sectors like construction and manufacturing. Swarming techniques, prevalent in IT and customer support industries, drive rapid problem resolution by mobilizing cross-functional experts simultaneously on high-priority issues. Data from these case studies indicate swarming improves incident response times by up to 40%, whereas teamwork enhances long-term project efficiency through sustained collaboration.
Future Trends in Collaborative Management
Future trends in collaborative management emphasize increased integration of swarming techniques, leveraging real-time data and AI-driven decision-making to enhance agility and problem-solving efficiency. Teams are shifting from traditional hierarchical structures to dynamic, cross-functional swarms that adapt rapidly to changing project demands. Embracing swarming fosters continuous collaboration, accelerates innovation cycles, and improves responsiveness in complex environments.
Related Important Terms
Swarm Intelligence
Swarm intelligence leverages decentralized, collective behavior inspired by natural systems to optimize problem-solving and decision-making in teams, enhancing adaptability and innovation. Unlike traditional teamwork, swarming emphasizes real-time collaboration and dynamic role allocation, enabling quicker responses to complex challenges.
Flash Teams
Flash teams leverage rapid, purpose-driven collaboration by assembling diverse experts on-demand to tackle complex projects efficiently, contrasting with traditional teamwork's longer-term group dynamics. This agile approach enhances innovation and problem-solving speed through real-time coordination and flexible role assignments.
Agile Swarming
Agile swarming accelerates project delivery by enabling cross-functional teams to collaborate intensively on high-priority tasks, improving problem-solving speed compared to traditional teamwork where roles and responsibilities are more segmented. This dynamic approach maximizes resource utilization and adaptability, fostering continuous feedback and rapid iteration in Agile environments.
Collaborative Autonomy
Teamwork involves coordinated efforts where team members share responsibilities while maintaining distinct roles, fostering collaborative autonomy through structured interdependence. Swarming accelerates problem-solving by dynamically reallocating resources and expertise, enhancing collaborative autonomy via real-time, flexible collaboration across teams.
Dynamic Re-teaming
Dynamic re-teaming enhances organizational agility by enabling teams to quickly dissolve and reform around evolving project needs, contrasting with traditional teamwork's fixed structures. Swarming accelerates problem-solving as cross-functional experts converge temporarily, fostering rapid knowledge sharing and adaptive collaboration.
Self-Healing Teams
Self-healing teams leverage swarming by rapidly mobilizing collective expertise to address issues in real time, enhancing adaptability and minimizing downtime. Unlike traditional teamwork, swarming empowers teams to dynamically reconfigure roles and responsibilities, fostering resilience and continuous improvement.
Situational Team Formation
Situational team formation adapts collaboration methods by choosing teamwork for structured, role-specific tasks and swarming for urgent, dynamic problem-solving requiring rapid, collective action. This approach enhances efficiency by aligning team structure with task complexity, promoting optimal resource utilization and faster decision-making.
Micro-tasking Swarms
Micro-tasking swarms enhance project efficiency by rapidly distributing specific, well-defined tasks across small, skilled groups, facilitating real-time collaboration and dynamic problem-solving. Unlike traditional teamwork structures, micro-tasking swarms leverage agility and scalability, optimizing resource allocation and accelerating delivery timelines in complex management environments.
Emergent Leadership
Emergent leadership in teamwork arises naturally as individuals adapt roles based on skills and situational needs, fostering collaboration and shared responsibility. In swarming, leadership is fluid and decentralized, enabling rapid, collective responses by leveraging real-time expertise across the group for dynamic problem-solving.
Cross-functional Pods
Cross-functional pods excel in swarming by rapidly mobilizing diverse expertise to solve complex problems simultaneously, enhancing agility beyond traditional teamwork's sequential task approach. This dynamic collaboration model accelerates innovation and decision-making in management by fostering real-time communication and shared ownership across functions.
Teamwork vs Swarming Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com