Traditional hierarchy relies on rigid, top-down management structures that emphasize clear authority and standardized processes for decision-making. Fluid organizations prioritize flexibility, collaborative networks, and adaptive roles to foster innovation and responsiveness in dynamic environments. Embracing fluidity over rigidity enables businesses to better navigate change and leverage diverse talents across all levels.
Table of Comparison
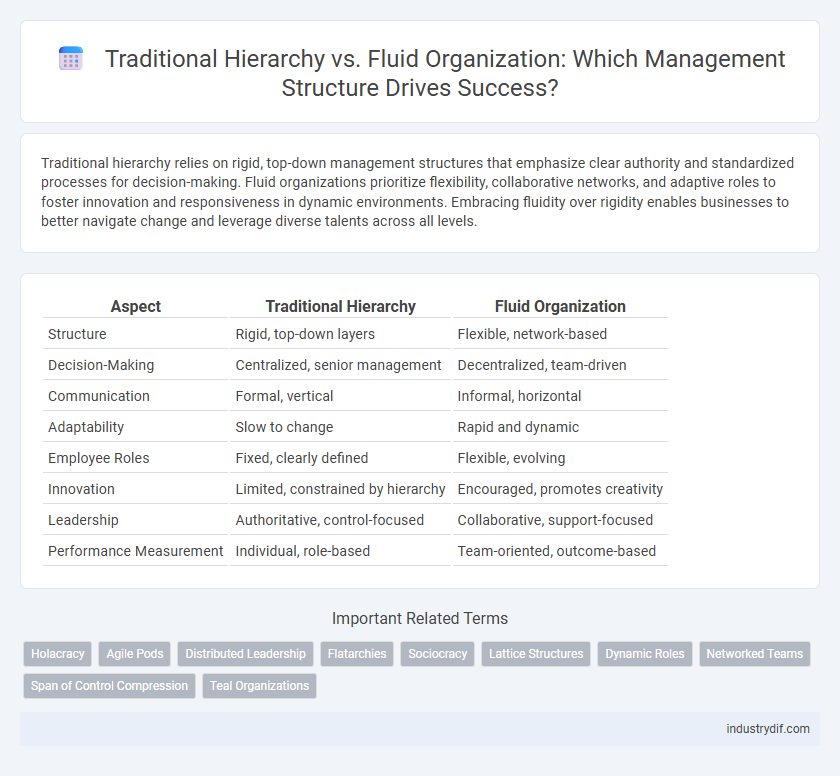
| Aspect | Traditional Hierarchy | Fluid Organization |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Rigid, top-down layers | Flexible, network-based |
| Decision-Making | Centralized, senior management | Decentralized, team-driven |
| Communication | Formal, vertical | Informal, horizontal |
| Adaptability | Slow to change | Rapid and dynamic |
| Employee Roles | Fixed, clearly defined | Flexible, evolving |
| Innovation | Limited, constrained by hierarchy | Encouraged, promotes creativity |
| Leadership | Authoritative, control-focused | Collaborative, support-focused |
| Performance Measurement | Individual, role-based | Team-oriented, outcome-based |
Defining Traditional Hierarchy and Fluid Organization
Traditional hierarchy in management is characterized by a clear, fixed structure with defined roles, centralized decision-making, and a top-down chain of command that promotes stability and control. Fluid organization emphasizes adaptability, decentralization, and dynamic team structures, enabling rapid response to change through collaborative decision-making and flexible roles. These contrasting models reflect differing approaches to authority distribution, communication flow, and organizational agility in contemporary business environments.
Key Characteristics of Hierarchical Management
Hierarchical management features a clear, top-down chain of command with defined roles and responsibilities that streamline decision-making and accountability. It emphasizes structured reporting lines and formal communication channels, facilitating control and consistency across departments. This model often results in slower adaptability but offers stability and predictability in organizational processes.
Core Features of Fluid Organizational Structures
Fluid organizational structures emphasize flexibility, decentralized decision-making, and dynamic team formations that adapt rapidly to changing market conditions. Unlike traditional hierarchies with rigid chains of command, these structures promote cross-functional collaboration and empower employees at all levels to take initiative. Core features include networked communication, minimal managerial layers, and a culture that prioritizes innovation and responsiveness over fixed roles.
Decision-Making: Centralized vs Distributed
In traditional hierarchies, decision-making is centralized, with authority concentrated at the top levels of management, ensuring uniformity and control but often slowing response times. Fluid organizations employ distributed decision-making, empowering teams across various functions to make real-time decisions, enhancing agility and innovation. This shift supports faster problem-solving and responsiveness in dynamic environments by decentralizing authority and promoting collaborative leadership.
Communication Flow in Hierarchical vs Fluid Models
Communication flow in traditional hierarchy models is typically top-down, with information passing through defined managerial levels, which can slow decision-making and reduce feedback opportunities. Fluid organizations emphasize open, multidirectional communication channels, enabling rapid information exchange and enhancing collaboration across roles. This dynamic flow supports agility and responsiveness in complex business environments.
Impact on Employee Engagement and Morale
Traditional hierarchy structures often limit employee engagement by reinforcing rigid roles and top-down communication, which can lead to decreased morale and innovation. Fluid organizations promote adaptability and empower employees through decentralized decision-making, enhancing collaboration and job satisfaction. Higher engagement in fluid models correlates with improved productivity and retention rates.
Adaptability and Innovation Potential
Traditional hierarchy structures emphasize clear roles and top-down decision-making, which can limit adaptability and slow innovation due to rigid communication channels. In contrast, fluid organizations promote cross-functional teams and decentralized authority, enhancing responsiveness to market changes and fostering a culture of continuous innovation. Organizations adopting fluid models report higher innovation potential, driven by faster feedback loops and empowered employees who contribute to dynamic problem-solving.
Leadership Roles in Different Structures
Leadership roles in traditional hierarchies are defined by clear authority levels and rigid reporting lines, emphasizing control and top-down decision-making. In fluid organizations, leadership is distributed and adaptive, promoting collaboration, autonomy, and rapid response to change. This shift requires leaders to act more as facilitators and coaches, fostering innovation and empowering teams.
Performance Measurement and Accountability
Traditional hierarchy relies on fixed performance metrics and clearly defined accountability through top-down management, ensuring stable evaluation but potentially limiting flexibility. Fluid organizations use dynamic performance measurement systems that adapt to changing project goals and emphasize collaboration, distributing accountability across teams to enhance responsiveness. This shift in accountability models fosters innovation but requires transparent communication and trust within decentralized structures.
Choosing the Right Structure for Your Organization
Selecting the right organizational structure depends on company size, industry, and strategic goals. Traditional hierarchy offers clear authority lines and predictable decision-making, suitable for established firms requiring stability and control. Fluid organizations promote agility and collaboration, ideal for innovative environments needing rapid response and flexibility in dynamic markets.
Related Important Terms
Holacracy
Holacracy replaces traditional hierarchy by distributing authority through self-organizing teams called circles, enhancing agility and employee empowerment in management structures. This fluid organization model promotes transparency, accountability, and faster decision-making processes by assigning roles dynamically rather than relying on fixed job titles.
Agile Pods
Agile Pods operate within fluid organizations by enabling cross-functional teams to dynamically self-organize and adapt to changing project demands, significantly reducing the rigid, top-down decision-making found in traditional hierarchies. This decentralized structure enhances collaboration, accelerates innovation, and improves responsiveness to customer needs compared to conventional management models.
Distributed Leadership
Distributed leadership in fluid organizations promotes shared responsibility and decision-making across multiple levels, enhancing agility and innovation compared to traditional hierarchy's top-down authority model. This approach leverages diverse expertise and fosters collaboration, resulting in faster problem-solving and increased employee empowerment.
Flatarchies
Flatarchies combine the stability of traditional hierarchy with the flexibility of fluid organizations, enabling faster decision-making and enhanced innovation. This hybrid model reduces bureaucratic layers, promotes cross-functional collaboration, and adapts quickly to changing market demands.
Sociocracy
Sociocracy replaces traditional hierarchy by promoting decentralized decision-making and equivalence among members, enhancing collaboration and transparency in organizations. Its structure relies on interconnected circles that enable continuous feedback and adaptive governance, fostering agility and employee empowerment.
Lattice Structures
Lattice structures in management emphasize decentralized authority and open communication, enabling employees across levels to collaborate directly without rigid chains of command. This approach contrasts with traditional hierarchy by fostering agility, innovation, and cross-functional teamwork within fluid organizations.
Dynamic Roles
Dynamic roles in fluid organizations enable employees to adapt quickly to changing demands, fostering innovation and collaboration unlike traditional hierarchy where fixed roles limit flexibility and slow decision-making. Fluid structures prioritize cross-functional teams and continuous role evolution, enhancing responsiveness and agility in complex business environments.
Networked Teams
Networked teams in fluid organizations enable dynamic collaboration, leveraging decentralized decision-making and agile workflows to enhance innovation and responsiveness. This contrasts with traditional hierarchies where rigid structures and top-down communication often hinder flexibility and swift problem-solving.
Span of Control Compression
Traditional hierarchy often limits agility due to narrow spans of control, resulting in multiple management layers that slow decision-making and communication. Fluid organizations compress spans of control, enabling broader management oversight, faster information flow, and increased adaptability in dynamic business environments.
Teal Organizations
Teal organizations emphasize self-management, wholeness, and evolutionary purpose, breaking away from traditional hierarchy's rigid, top-down control structures. By fostering decentralized decision-making and empowering employees, Teal organizations enhance adaptability and innovation in complex business environments.
Traditional Hierarchy vs Fluid Organization Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com