A manager directs tasks and enforces rules to achieve organizational goals, focusing on control and efficiency. In contrast, a servant leader prioritizes the growth and well-being of team members, fostering collaboration and empowerment. Servant leadership promotes a positive work culture that drives long-term success through trust and support.
Table of Comparison
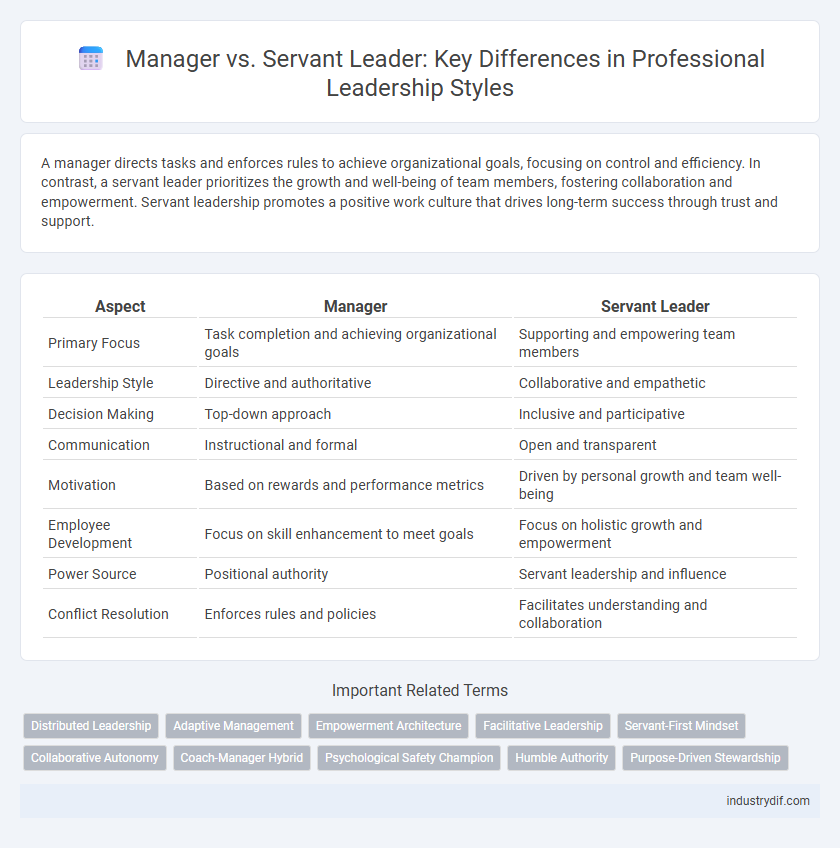
| Aspect | Manager | Servant Leader |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Task completion and achieving organizational goals | Supporting and empowering team members |
| Leadership Style | Directive and authoritative | Collaborative and empathetic |
| Decision Making | Top-down approach | Inclusive and participative |
| Communication | Instructional and formal | Open and transparent |
| Motivation | Based on rewards and performance metrics | Driven by personal growth and team well-being |
| Employee Development | Focus on skill enhancement to meet goals | Focus on holistic growth and empowerment |
| Power Source | Positional authority | Servant leadership and influence |
| Conflict Resolution | Enforces rules and policies | Facilitates understanding and collaboration |
Defining Managerial Leadership
Managerial leadership is defined by the ability to coordinate resources, set clear goals, and ensure organizational efficiency through structured processes. In contrast, servant leadership prioritizes the growth and well-being of team members, fostering collaboration and empowerment. Effective managerial leadership balances task-oriented direction with empathetic support to achieve sustainable success.
Understanding Servant Leadership
Servant leadership emphasizes prioritizing the growth, well-being, and empowerment of team members over traditional authority, contrasting with conventional managerial roles focused on control and results. This leadership style nurtures trust, collaboration, and ethical behavior, fostering a positive organizational culture conducive to innovation and long-term success. Understanding servant leadership involves recognizing its impact on employee engagement, retention, and overall performance, making it a strategic approach for sustainable business growth.
Core Principles of Management
Managers emphasize planning, organizing, and controlling resources to achieve organizational goals efficiently, while servant leaders prioritize empowering and supporting their teams to foster collaboration and personal growth. Core principles of management under a managerial approach involve hierarchical decision-making, task delegation, and performance monitoring. In contrast, servant leadership focuses on empathy, active listening, and ethical behavior to build trust and enhance team motivation.
Key Attributes of Servant Leaders
Servant leaders prioritize empathy, active listening, and empowerment, fostering a collaborative environment that drives team success. They demonstrate strong ethical standards and a commitment to the growth and well-being of employees, which contrasts with traditional managerial roles focused on authority and task delegation. Key attributes include humility, stewardship, and a focus on serving others to achieve organizational goals.
Decision-Making Styles: Manager vs Servant Leader
Managers typically adopt a directive decision-making style, emphasizing control, efficiency, and goal achievement through top-down directives. Servant leaders prioritize collaborative decision-making, fostering trust and empowering team members to contribute insights and solutions. This contrast influences organizational agility, with managers driving swift action and servant leaders encouraging shared ownership and innovation.
Communication Approaches in Leadership
Managers typically utilize directive communication, emphasizing clear instructions and task-oriented feedback to ensure team alignment and productivity. Servant leaders prioritize empathetic listening and open dialogue, fostering trust and collaboration by addressing individual team members' needs and perspectives. This contrast in communication approaches significantly influences team morale, engagement, and overall organizational effectiveness.
Impact on Team Performance
Managers who focus on task delegation and performance metrics often drive short-term productivity but may limit team creativity and engagement. Servant leaders prioritize employee growth and well-being, fostering trust and collaboration that enhance long-term team performance and innovation. Studies show teams led by servant leaders experience higher job satisfaction, lower turnover rates, and improved overall outcomes.
Employee Engagement and Motivation
Managers often rely on authority and task delegation to achieve goals, which may limit employee engagement and intrinsic motivation. Servant leaders prioritize the needs of their team, fostering a supportive environment that enhances trust, collaboration, and sustained motivation. Research shows servant leadership correlates with higher employee satisfaction and increased productivity due to its focus on empowerment and personal growth.
Organizational Outcomes and Culture
Managers typically emphasize task completion, control, and maintaining organizational structure, which can drive short-term performance but may limit innovation and employee engagement. Servant leaders prioritize employee development, empowerment, and collaboration, fostering a culture of trust and intrinsic motivation that enhances long-term organizational resilience and adaptability. Organizations led by servant leaders often experience higher employee satisfaction, retention, and a stronger alignment with core values, positively impacting overall outcomes.
Choosing the Right Leadership Style for Your Industry
Selecting the appropriate leadership style hinges on industry demands and organizational culture, where managers ensure structure and efficiency through task delegation and performance metrics, while servant leaders prioritize employee empowerment and collaborative problem-solving to foster innovation. In industries like manufacturing or finance, a managerial approach accelerates productivity and compliance, whereas technology and creative sectors benefit from servant leadership by enhancing adaptability and team motivation. Assessing workforce dynamics and business goals guides leaders to integrate or balance these styles for optimal organizational success.
Related Important Terms
Distributed Leadership
Managers typically exercise hierarchical authority to coordinate tasks and enforce policies, whereas servant leaders prioritize empowering team members and fostering collaboration to enhance distributed leadership. Distributed leadership thrives when servant leaders delegate decision-making, promote shared responsibility, and cultivate an environment where every member contributes their unique expertise.
Adaptive Management
Adaptive management distinguishes servant leaders by emphasizing flexibility and responsiveness to team needs over traditional command-and-control approaches characteristic of managers. Servant leaders prioritize empowering employees and fostering collaboration, enhancing organizational agility in dynamic environments.
Empowerment Architecture
A manager typically directs tasks and enforces control, while a servant leader prioritizes empowerment by fostering collaboration, trust, and personal growth within the team. Empowerment architecture under a servant leader includes decentralized decision-making, transparent communication, and a commitment to developing individual strengths.
Facilitative Leadership
Facilitative leadership in the context of Manager vs Servant Leader emphasizes empowering teams through active listening, fostering collaboration, and enabling decision-making rather than directing tasks. This approach enhances employee engagement and drives innovation by prioritizing the development and autonomy of team members.
Servant-First Mindset
A servant-first mindset in leadership prioritizes empathy, active listening, and the growth of team members, fostering a collaborative and supportive work environment that enhances overall organizational performance. Unlike traditional managers who focus on authority and task execution, servant leaders empower their teams by putting others' needs first, driving sustainable success through trust and shared purpose.
Collaborative Autonomy
Managers often direct teams through hierarchical control, while servant leaders prioritize collaborative autonomy by empowering team members to take initiative and share responsibility. This approach enhances innovation and accountability, fostering a culture where individuals contribute actively to collective goals.
Coach-Manager Hybrid
A Coach-Manager Hybrid integrates the directive focus of a Manager with the empathetic guidance of a Servant Leader, fostering high performance through personalized development and accountability. This approach leverages strategic decision-making and active coaching to enhance team engagement and drive sustained organizational success.
Psychological Safety Champion
A manager typically enforces policies and oversees productivity, while a servant leader prioritizes fostering psychological safety by encouraging open communication, trust, and employee well-being. Servant leaders create environments where team members feel secure to express ideas and take risks, driving innovation and engagement.
Humble Authority
Humble authority in servant leadership balances firm decision-making with empathy and support, fostering trust and collaboration within teams. Unlike traditional managers who prioritize control and hierarchy, servant leaders elevate others' growth and accountability through humility and servant-first mindset.
Purpose-Driven Stewardship
A manager directs teams through task-oriented goals and performance metrics, emphasizing control and efficiency, while a servant leader prioritizes purpose-driven stewardship by fostering growth, empowerment, and ethical responsibility within the organization. Servant leadership aligns organizational objectives with a higher mission, cultivating trust and sustainable impact through empathetic support and shared vision.
Manager vs Servant Leader Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com