Public engagement involves informing and consulting citizens to gather input on community decisions, fostering transparency and trust. Participatory budgeting goes further by directly involving residents in allocating public funds, empowering them to influence fiscal priorities. This active participation enhances democratic governance by making budget decisions more inclusive and responsive to community needs.
Table of Comparison
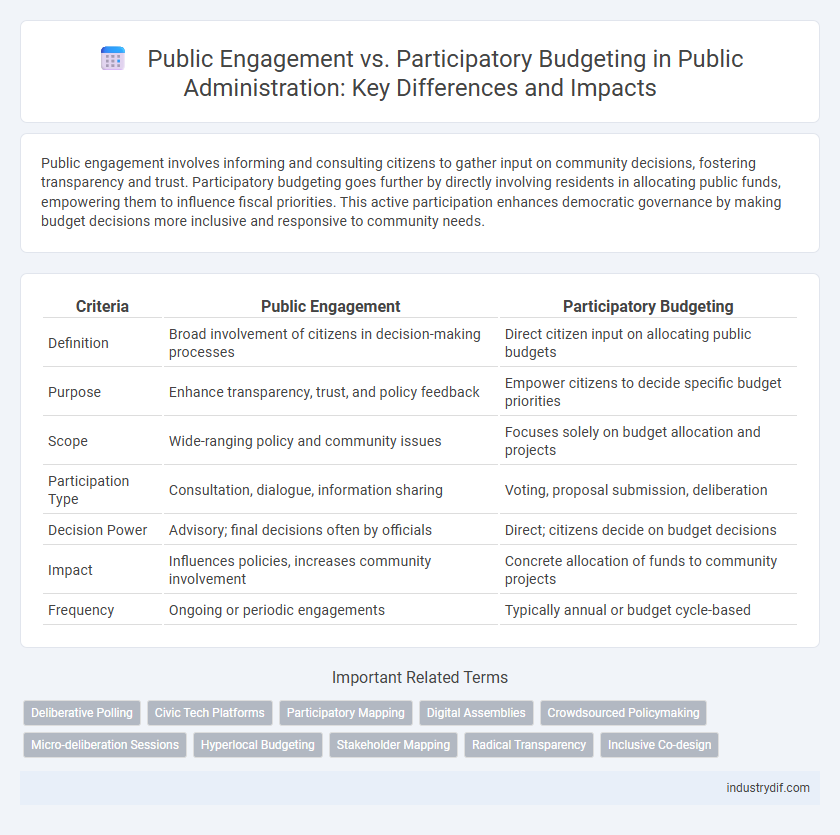
| Criteria | Public Engagement | Participatory Budgeting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Broad involvement of citizens in decision-making processes | Direct citizen input on allocating public budgets |
| Purpose | Enhance transparency, trust, and policy feedback | Empower citizens to decide specific budget priorities |
| Scope | Wide-ranging policy and community issues | Focuses solely on budget allocation and projects |
| Participation Type | Consultation, dialogue, information sharing | Voting, proposal submission, deliberation |
| Decision Power | Advisory; final decisions often by officials | Direct; citizens decide on budget decisions |
| Impact | Influences policies, increases community involvement | Concrete allocation of funds to community projects |
| Frequency | Ongoing or periodic engagements | Typically annual or budget cycle-based |
Defining Public Engagement: Scope and Purpose
Public engagement encompasses a wide range of activities designed to involve community members in decision-making processes, promoting transparency and inclusivity. It aims to gather diverse perspectives on policy issues, fostering a sense of shared responsibility and trust between governments and citizens. Unlike participatory budgeting, which specifically allocates fiscal resources through citizen input, public engagement covers broader practices such as consultations, forums, and surveys to shape governance and community development.
Understanding Participatory Budgeting: Key Features
Participatory budgeting is a democratic process enabling community members to directly decide how to allocate part of a public budget, enhancing transparency and civic engagement. Key features include inclusive citizen involvement, deliberative discussions, and collaborative decision-making that reflect diverse community priorities. This approach fosters accountability and empowers residents to influence government spending, contrasting with traditional public engagement that often limits input to feedback rather than budget control.
Historical Evolution of Public Involvement Methods
Public engagement has evolved from traditional town hall meetings to more inclusive, technology-driven platforms, reflecting societal shifts toward greater transparency and accountability. Participatory budgeting emerged in the late 20th century as a direct democratic process, enabling citizens to decide on the allocation of public funds, thereby deepening civic involvement. These methods illustrate a historical trajectory where public involvement increasingly emphasizes empowerment and collaborative governance.
Stakeholder Roles in Public Engagement and Participatory Budgeting
Stakeholder roles in public engagement often include informing, consulting, and collaborating with the community to gather diverse input and build trust in decision-making processes. In participatory budgeting, stakeholders such as local residents, government officials, and community organizations actively co-create budget priorities, ensuring transparency and shared accountability. Effective participation by these stakeholders enhances project relevance, resource allocation, and democratic legitimacy.
Levels of Influence: Informing vs Decision-Making
Public engagement primarily centers on informing citizens, ensuring transparency and awareness about policies and projects without granting direct control over outcomes. In contrast, participatory budgeting elevates public involvement by granting community members decision-making power to allocate portions of municipal budgets, fostering deeper influence and accountability. This shift from passive reception of information to active fiscal decision-making marks a significant evolution in democratic participation.
Tools and Techniques Used in Public Engagement
Public engagement employs diverse tools such as surveys, public forums, and digital platforms to gather broad community input and foster transparent communication. Participatory budgeting utilizes specific techniques like facilitated workshops, voting systems, and interactive budgeting software to enable citizens directly in allocating public funds. Both approaches leverage technology and structured methodologies to enhance inclusivity and democratic decision-making in governance.
The Process Framework of Participatory Budgeting
Participatory budgeting (PB) follows a structured process framework that includes proposal collection, community deliberation, and transparent voting to allocate public funds democratically. This framework emphasizes direct citizen involvement in decision-making, contrasting with broader public engagement that often seeks feedback without binding outcomes. The iterative structure of PB fosters accountability and empowerment by enabling residents to shape budget priorities based on shared community needs.
Measuring Impact: Outcomes of Each Approach
Public engagement often fosters broad community awareness and input, resulting in increased trust and enhanced decision-making transparency. Participatory budgeting produces tangible outcomes by directly allocating funds to community-prioritized projects, leading to measurable improvements in local infrastructure and social programs. Both approaches contribute to civic empowerment, but participatory budgeting offers clearer metrics for assessing impact through budget distribution and project completion rates.
Inclusivity and Representation: Comparative Analysis
Public engagement fosters broad inclusivity by inviting diverse community input through surveys, forums, and workshops, ensuring multiple viewpoints inform policy decisions. Participatory budgeting emphasizes direct representation by allowing residents to actively decide on budget allocation, empowering marginalized groups to influence financial priorities. Comparative analysis reveals that while public engagement ensures wide-reaching inclusivity, participatory budgeting delivers focused representation through tangible decision-making roles.
Best Practices for Selecting Public Involvement Methods
Effective public involvement methods prioritize transparency, inclusivity, and clear communication to foster trust and meaningful input. Selecting approaches such as participatory budgeting requires assessing community demographics, resource availability, and the complexity of issues to ensure equitable participation. Incorporating diverse techniques like surveys, focus groups, and public workshops enhances stakeholder engagement and supports informed decision-making in public projects.
Related Important Terms
Deliberative Polling
Deliberative Polling enhances public engagement by combining random sampling with informed discussion, allowing citizens to deliberate on budget priorities before expressing preferences. This approach contrasts with traditional participatory budgeting by emphasizing informed consensus rather than direct allocation decisions.
Civic Tech Platforms
Civic tech platforms enhance public engagement by providing accessible digital channels for dialogue, while participatory budgeting leverages these tools to directly involve citizens in allocating municipal funds, increasing transparency and accountability. Integrating real-time feedback and data analytics, these platforms optimize decision-making processes and foster inclusive community participation in local governance.
Participatory Mapping
Participatory mapping enhances public engagement by enabling community members to visually identify and prioritize local issues, fostering deeper involvement in participatory budgeting processes. This spatial approach ensures that resource allocation reflects accurate, ground-level insights, increasing transparency and equitable decision-making.
Digital Assemblies
Digital assemblies enhance public engagement by enabling wider access and real-time interaction, fostering inclusivity and transparency in decision-making processes. Unlike traditional participatory budgeting, these online platforms facilitate continuous community input and data-driven prioritization of public funds, optimizing democratic participation and resource allocation.
Crowdsourced Policymaking
Crowdsourced policymaking leverages public engagement by inviting diverse community input to co-create policies, enhancing transparency and inclusivity beyond traditional participatory budgeting's focus on allocating funds. This method amplifies democratic participation, enabling citizens to propose, deliberate, and prioritize comprehensive policy solutions in real-time platforms.
Micro-deliberation Sessions
Micro-deliberation sessions enhance public engagement by facilitating focused, small-group discussions that allow diverse community members to voice their priorities and concerns. These sessions complement participatory budgeting processes by generating detailed, localized insights that inform resource allocation decisions and ensure more democratic and transparent outcomes.
Hyperlocal Budgeting
Hyperlocal budgeting empowers residents in specific neighborhoods to directly allocate municipal funds, fostering deeper community involvement than traditional public engagement methods. By integrating participatory budgeting principles at a micro-scale, hyperlocal budgeting enhances transparency, accountability, and tailored resource distribution for localized public projects.
Stakeholder Mapping
Stakeholder mapping is essential in public engagement to identify and analyze all individuals and groups affected by or interested in a project, ensuring inclusive input and transparent decision-making. In participatory budgeting, stakeholder mapping prioritizes community members with diverse economic backgrounds and local organizations to allocate resources effectively and reflect collective priorities.
Radical Transparency
Radical transparency in public engagement ensures that all decision-making processes and financial allocations are openly shared with the community, fostering trust and accountability beyond traditional participatory budgeting frameworks. This approach emphasizes clear, accessible data disclosure that empowers citizens to critically evaluate and influence public spending without barriers.
Inclusive Co-design
Inclusive co-design fosters equitable collaboration by integrating diverse community voices into public engagement processes, ensuring decisions reflect varied stakeholder needs. Participatory budgeting amplifies this inclusivity by allowing citizens to directly influence budget allocations, promoting transparency and shared ownership in financial governance.
public engagement vs participatory budgeting Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com