Public policy shapes societal norms by establishing rules and regulations, while behavioral insights enhance policy effectiveness by understanding human decision-making patterns. Integrating behavioral insights into public policy results in more targeted interventions that align with actual behaviors rather than theoretical assumptions. This fusion improves compliance rates and fosters positive social outcomes through evidence-based strategies.
Table of Comparison
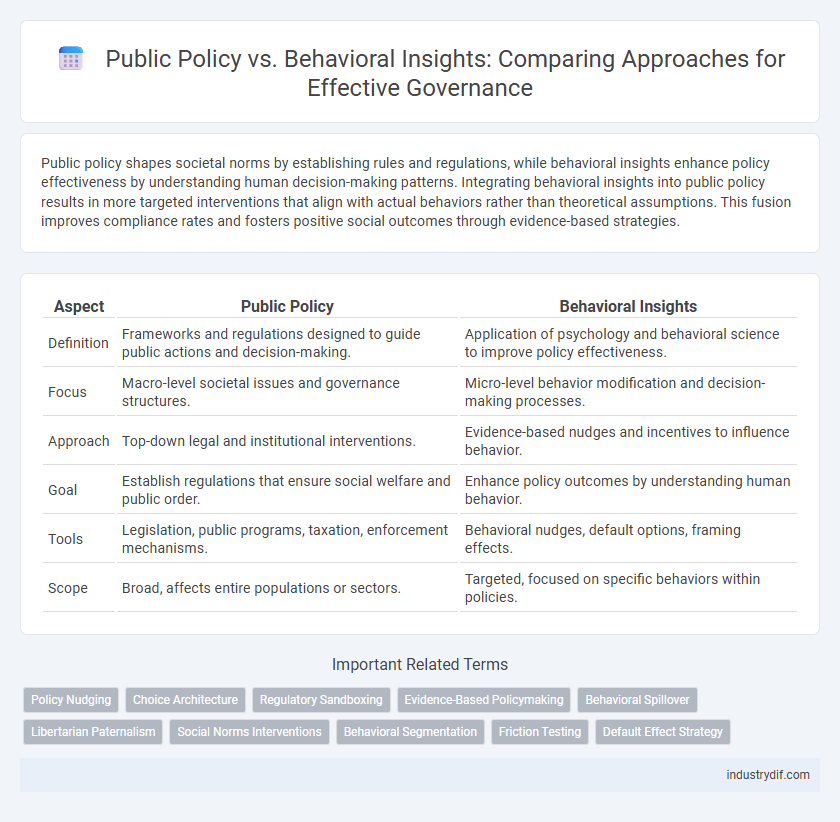
| Aspect | Public Policy | Behavioral Insights |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Frameworks and regulations designed to guide public actions and decision-making. | Application of psychology and behavioral science to improve policy effectiveness. |
| Focus | Macro-level societal issues and governance structures. | Micro-level behavior modification and decision-making processes. |
| Approach | Top-down legal and institutional interventions. | Evidence-based nudges and incentives to influence behavior. |
| Goal | Establish regulations that ensure social welfare and public order. | Enhance policy outcomes by understanding human behavior. |
| Tools | Legislation, public programs, taxation, enforcement mechanisms. | Behavioral nudges, default options, framing effects. |
| Scope | Broad, affects entire populations or sectors. | Targeted, focused on specific behaviors within policies. |
Defining Public Policy and Behavioral Insights
Public policy encompasses the set of laws, regulations, and actions undertaken by governments to address societal issues and guide public behavior. Behavioral insights apply psychological and behavioral economics principles to design policies that effectively influence individual and collective decision-making. Integrating behavioral insights into public policy enhances the efficacy and responsiveness of government interventions by leveraging evidence-based approaches.
Historical Evolution of Public Policy
Public policy has evolved from traditional top-down government directives to incorporating behavioral insights that emphasize human decision-making and cognitive biases. Early public policy focused on legal frameworks and institutional arrangements, while recent approaches integrate psychology and economics to design more effective interventions. The historical shift reflects a growing recognition of behavioral science as a critical tool for improving policy outcomes.
Origins and Principles of Behavioral Insights
Behavioral insights stem from the integration of psychology, economics, and neuroscience to better understand how individuals make decisions, diverging from traditional public policy assumptions of purely rational actors. Originating in the late 20th century with the work of scholars like Daniel Kahneman and Amos Tversky, these insights emphasize cognitive biases, heuristics, and social influences. The principles of behavioral insights focus on designing policies that account for actual human behavior, employing nudges and choice architecture to improve societal outcomes.
Key Differences Between Public Policy and Behavioral Insights
Public policy centers on creating laws and regulations to address societal issues through formal governance structures. Behavioral insights analyze human behavior patterns using psychological and economic principles to design interventions that nudge individuals toward better decisions. The key difference lies in public policy's reliance on traditional legislative tools versus behavioral insights' emphasis on empirical data-driven strategies to influence behavior subtly.
Integration of Behavioral Insights into Public Policy
Integrating behavioral insights into public policy enhances decision-making by leveraging empirical evidence on human behavior, leading to more effective and efficient interventions. Policymakers utilize techniques such as nudging, choice architecture, and behavioral experiments to design policies that align with how people naturally think and act, increasing compliance and positive outcomes. This integration supports data-driven strategies that improve public welfare while reducing costs and unintended consequences.
Case Studies: Behavioral Insights Shaping Policy Outcomes
Case studies reveal how behavioral insights have transformed public policy by utilizing nudges to improve health, finance, and social welfare outcomes. Programs employing default options, social norms, and simplified communication demonstrate increased effectiveness and cost-efficiency compared to traditional policy approaches. The UK Government Behavioral Insights Team's work highlights measurable improvements in tax compliance and organ donation rates, showcasing behavioral strategies as key drivers in shaping successful policy outcomes.
Advantages of Using Behavioral Insights in Public Policy
Behavioral insights enhance public policy effectiveness by leveraging real-world human behavior data to design interventions that increase compliance and engagement. Utilizing techniques such as nudging and choice architecture, policies become more cost-efficient and targeted, reducing the need for heavy regulation. The integration of behavioral science leads to improved public service delivery, higher policy impact, and better societal outcomes.
Challenges and Limitations in Applying Behavioral Insights
Applying behavioral insights in public policy faces challenges such as ethical considerations regarding manipulation and consent, limited generalizability of findings across diverse populations, and difficulties in integrating qualitative behavioral data with traditional policy frameworks. Behavioral interventions often struggle with sustainability and scalability, as effects can diminish over time or fail when expanded beyond controlled environments. Data privacy concerns and the complexity of human behavior further limit the effective implementation of behavioral insights in large-scale public policy design.
Future Trends in Public Policy and Behavioral Insights
Future trends in public policy emphasize incorporating behavioral insights to design more effective interventions that leverage human psychology and decision-making patterns. Advancements in data analytics and experimental methods enable policymakers to test and refine approaches, enhancing policy responsiveness and outcomes. The integration of behavioral science with digital technologies predicts a shift towards personalized, adaptive public services that promote positive social behaviors and improve public welfare.
Best Practices for Policymakers Using Behavioral Insights
Policymakers utilizing behavioral insights should prioritize evidence-based interventions that leverage cognitive biases and social norms to enhance policy effectiveness. Incorporating randomized controlled trials and iterative testing ensures policies are data-driven and adaptable to real-world behaviors. Transparency and ethical considerations remain essential to maintain public trust while maximizing positive behavioral outcomes.
Related Important Terms
Policy Nudging
Policy nudging leverages behavioral insights to subtly influence public decisions without restricting choice, enhancing the effectiveness of public policy by addressing cognitive biases. Integrating nudges into policy design improves social outcomes by encouraging healthier, more sustainable, and financially responsible behaviors across populations.
Choice Architecture
Choice architecture shapes public policy by structuring environments that subtly guide citizens' decisions toward desired outcomes without limiting freedom of choice. Behavioral insights leverage this approach to design policies that improve social welfare through nudges, such as default options in organ donation or automatic enrollment in retirement savings programs.
Regulatory Sandboxing
Regulatory sandboxing in public policy enables controlled experimentation with innovative regulations to address complex societal challenges efficiently. Behavioral insights integrated within these sandboxes help policymakers test and refine interventions by analyzing real-world behavioral responses, thereby improving regulatory effectiveness.
Evidence-Based Policymaking
Evidence-based policymaking leverages rigorous data analysis and behavioral insights to design and implement public policies that effectively address societal challenges. Integrating behavioral science techniques enhances the precision of interventions by accounting for human decision-making patterns, increasing policy efficacy and public trust.
Behavioral Spillover
Behavioral spillover occurs when interventions targeting specific behaviors lead to unintended changes in related behaviors, either positive or negative, impacting overall policy effectiveness. Understanding these spillover effects through behavioral insights enables policymakers to design more comprehensive strategies that maximize desired outcomes and minimize counterproductive actions.
Libertarian Paternalism
Libertarian paternalism, a key concept in behavioral insights, subtly steers public policy by designing choice architectures that nudge individuals towards better decisions without restricting freedom of choice. This approach balances government intervention with respect for personal autonomy, effectively improving public outcomes in areas like health, finance, and education.
Social Norms Interventions
Social norms interventions leverage behavioral insights to subtly influence public behavior by reshaping perceptions of common practices and acceptable conduct within a community. Integrating these interventions into public policy enhances effectiveness by targeting underlying social motivations, leading to sustainable behavioral change in areas such as health, environmental conservation, and social welfare.
Behavioral Segmentation
Behavioral segmentation in public policy enables targeted interventions by categorizing populations based on actions, preferences, and decision-making patterns, enhancing the precision and effectiveness of policy measures. Utilizing data-driven insights, policymakers can design customized programs that address specific behavioral motivations, leading to improved public outcomes and resource allocation.
Friction Testing
Friction testing in public policy evaluates how subtle design changes influence citizen behavior, leveraging behavioral insights to reduce barriers and improve compliance. This method identifies specific points of resistance within public services, enabling policymakers to implement targeted interventions that streamline decision-making and enhance policy effectiveness.
Default Effect Strategy
The Default Effect Strategy leverages behavioral insights by setting pre-selected options to influence public policy outcomes, significantly increasing participation rates in programs like organ donation and pension enrollment. This approach reduces decision-making friction and aligns policy design with human cognitive biases, enhancing effectiveness without restricting freedom of choice.
Public Policy vs Behavioral Insights Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com