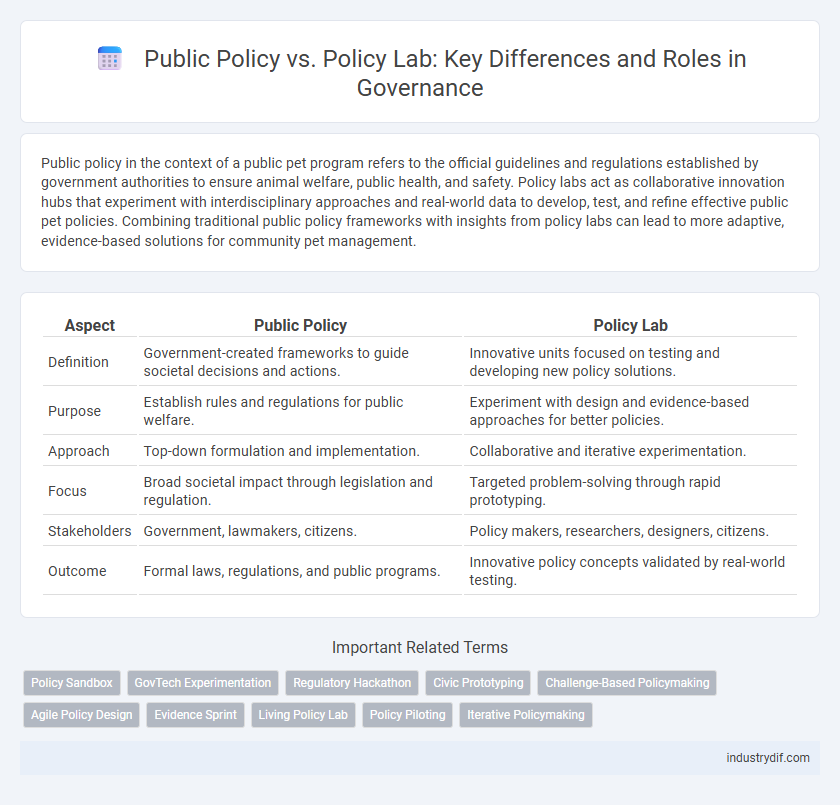
Public policy in the context of a public pet program refers to the official guidelines and regulations established by government authorities to ensure animal welfare, public health, and safety. Policy labs act as collaborative innovation hubs that experiment with interdisciplinary approaches and real-world data to develop, test, and refine effective public pet policies. Combining traditional public policy frameworks with insights from policy labs can lead to more adaptive, evidence-based solutions for community pet management.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Public Policy | Policy Lab |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Government-created frameworks to guide societal decisions and actions. | Innovative units focused on testing and developing new policy solutions. |
| Purpose | Establish rules and regulations for public welfare. | Experiment with design and evidence-based approaches for better policies. |
| Approach | Top-down formulation and implementation. | Collaborative and iterative experimentation. |
| Focus | Broad societal impact through legislation and regulation. | Targeted problem-solving through rapid prototyping. |
| Stakeholders | Government, lawmakers, citizens. | Policy makers, researchers, designers, citizens. |
| Outcome | Formal laws, regulations, and public programs. | Innovative policy concepts validated by real-world testing. |
Defining Public Policy and Policy Lab: Key Differences
Public policy refers to government actions and decisions aimed at addressing societal issues through laws, regulations, and programs, often shaped by political processes and public administration. A policy lab, by contrast, is an experimental, interdisciplinary environment where innovative solutions are designed, tested, and evaluated using data-driven methods to improve policy outcomes. The key difference lies in public policy's role as the formal framework of governance versus policy labs serving as agile incubators for evidence-based policy innovation.
Historical Evolution of Public Policy and Policy Labs
Public policy has evolved through centuries of governance, shaped by changing societal needs and political ideologies, with formal frameworks emerging in the 20th century to address complex public issues. Policy labs, originating in the early 2000s, represent a modern innovation, using experimental methods and data analytics to co-create and test public policy solutions in real-time. This historical evolution highlights a shift from top-down policy formulation towards collaborative, evidence-based policymaking driven by interdisciplinary teams.
Objectives and Approaches: Public Policy vs Policy Lab
Public policy aims to develop comprehensive frameworks addressing societal challenges through legislation, regulation, and resource allocation, focusing on broad, long-term objectives. In contrast, policy labs employ experimental and iterative approaches, utilizing design thinking and stakeholder engagement to test innovative solutions in real-world settings. While public policy emphasizes formal decision-making processes, policy labs prioritize agility, collaboration, and evidence-based prototyping to refine policy interventions.
Stakeholder Involvement in Public Policy and Policy Labs
Public policy typically involves a broad range of stakeholder involvement, including government agencies, community groups, and citizens, to ensure diverse perspectives influence decision-making processes. Policy labs emphasize collaborative, experimental approaches where stakeholders actively co-create solutions through iterative feedback and prototyping. This dynamic engagement enhances responsiveness and innovation in addressing complex societal challenges.
Methodology: Traditional Policy-making vs Experimental Labs
Traditional public policy methodology relies on top-down decision-making, comprehensive data analysis, and expert consultations to develop regulations and programs. Policy labs employ experimental approaches, including randomized controlled trials and iterative prototyping, to test and refine policy interventions in real-world settings. This shift towards evidence-based experimentation enhances adaptability and effectiveness in addressing complex social issues.
Innovation and Flexibility in Policy Development
Public policy emphasizes structured frameworks and regulatory compliance to address societal challenges, often resulting in slower adaptation to emerging issues. Policy labs prioritize innovation and flexibility by employing experimental methods, iterative testing, and user-centered design to craft responsive and adaptive solutions. This agile approach enables real-time feedback integration, fostering dynamic policy development that better meets evolving public needs.
Role of Evidence and Data in Shaping Policies
Public policy relies heavily on empirical evidence and robust data to formulate effective regulations that address societal challenges. Policy labs utilize experimental methods and data analytics to test assumptions and generate actionable insights, enabling policymakers to design adaptive and evidence-based interventions. The integration of real-time data and iterative evaluation in policy labs enhances the precision and responsiveness of public policy decisions.
Policy Labs as Catalysts for Social Change
Policy Labs serve as dynamic catalysts for social change by utilizing experimental approaches and data-driven methods to design, test, and implement innovative public policies. Unlike traditional public policy frameworks, these labs foster collaboration among governments, communities, and experts to address complex social issues through iterative problem-solving and evidence-based interventions. This results in more adaptive, inclusive, and effective policies that drive measurable improvements in societal outcomes.
Implementation Challenges: Public Policy vs Policy Lab Models
Public policy implementation faces challenges such as bureaucratic inertia, limited stakeholder engagement, and resource constraints, which can delay or dilute intended outcomes. Policy labs, leveraging iterative prototyping, data-driven experimentation, and cross-sector collaboration, address these issues by fostering adaptive solutions tailored to real-world complexities. The dynamic and user-centered nature of policy labs contrasts with traditional top-down approaches, enhancing responsiveness and practical impact in complex governance environments.
Future Trends: Integration of Policy Labs in Public Policy
Policy labs are increasingly shaping future public policy by employing data-driven experimentation and agile methodologies to address complex societal challenges. The integration of policy labs enhances evidence-based decision-making through rapid prototyping, stakeholder engagement, and real-time feedback mechanisms. This trend supports adaptive governance, fostering innovation and more responsive public services aligned with dynamic community needs.
Related Important Terms
Policy Sandbox
Policy Sandbox offers a controlled environment where innovative public policies can be tested and refined before full-scale implementation, reducing risks and improving outcomes. Unlike traditional public policy methods, Policy Sandboxes foster experimentation and stakeholder collaboration, accelerating the adoption of effective solutions in governance.
GovTech Experimentation
Public policy shapes governance frameworks and societal priorities through legislative and regulatory measures, while policy labs serve as innovation hubs leveraging GovTech experimentation to design, test, and refine data-driven solutions for complex public challenges. GovTech experimentation within policy labs accelerates the iterative development of digital tools and evidence-based interventions, enhancing transparency, efficiency, and citizen engagement in public administration.
Regulatory Hackathon
Public policy frameworks establish regulatory objectives and legal boundaries, while policy labs employ experimental methodologies such as Regulatory Hackathons to co-create innovative solutions with stakeholders. Regulatory Hackathons facilitate real-time collaboration, enabling rapid prototyping and testing of regulatory reforms to enhance governance efficiency and adaptability.
Civic Prototyping
Public policy involves creating regulations and guidelines to address societal issues, while policy labs use Civic Prototyping to design, test, and refine innovative solutions through community engagement and iterative development processes. Civic Prototyping empowers citizens to collaborate with policymakers, enhancing transparency and effectiveness in crafting responsive public policies.
Challenge-Based Policymaking
Challenge-Based Policymaking drives innovation by directly engaging stakeholders to identify and solve specific public issues, fostering collaborative problem-solving and adaptive strategies. Unlike traditional public policy that often follows hierarchical decision-making, policy labs experiment with agile, user-centered approaches to rapidly prototype and test solutions within real-world contexts.
Agile Policy Design
Agile Policy Design leverages iterative development and stakeholder collaboration to create public policies that adapt swiftly to emerging challenges, contrasting with traditional Public Policy approaches that often rely on linear, top-down decision-making processes. Policy Labs serve as experimental hubs where Agile methodologies foster real-time testing and refinement, enhancing policy effectiveness and responsiveness in complex environments.
Evidence Sprint
Public policy development relies on comprehensive data analysis and stakeholder engagement, while policy labs prioritize rapid experimentation and iterative testing to design innovative solutions. Evidence Sprints in policy labs accelerate data collection and real-time analysis, enabling policymakers to make informed decisions with actionable insights within condensed timelines.
Living Policy Lab
Living Policy Lab serves as an innovative approach within public policy frameworks by integrating real-time data and community feedback to design more adaptable and effective solutions. Unlike traditional public policy methods that often rely on static analyses, Living Policy Labs enable iterative experimentation and co-creation with stakeholders to address complex societal challenges dynamically.
Policy Piloting
Policy piloting involves testing innovative public policies on a smaller scale to evaluate effectiveness before wider implementation, enabling data-driven adjustments and minimizing risks. Public policy development relies on these pilot programs to gather real-world insights that inform scalable, evidence-based decisions for societal benefit.
Iterative Policymaking
Iterative policymaking in public policy involves continuous testing, feedback, and refinement to address complex societal challenges effectively. Policy labs serve as experimental hubs where governments pilot innovative solutions, collect real-time data, and adapt policies in response to stakeholder input and emerging insights.
public policy vs policy lab Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com