Hiking trails provide an active outdoor experience with well-marked routes designed for physical exercise and exploration. Forest bathing paths offer a more immersive and mindful nature connection, emphasizing sensory engagement and relaxation in a natural setting. Both enhance recreational time but cater to different preferences--vigorous activity versus tranquil immersion.
Table of Comparison
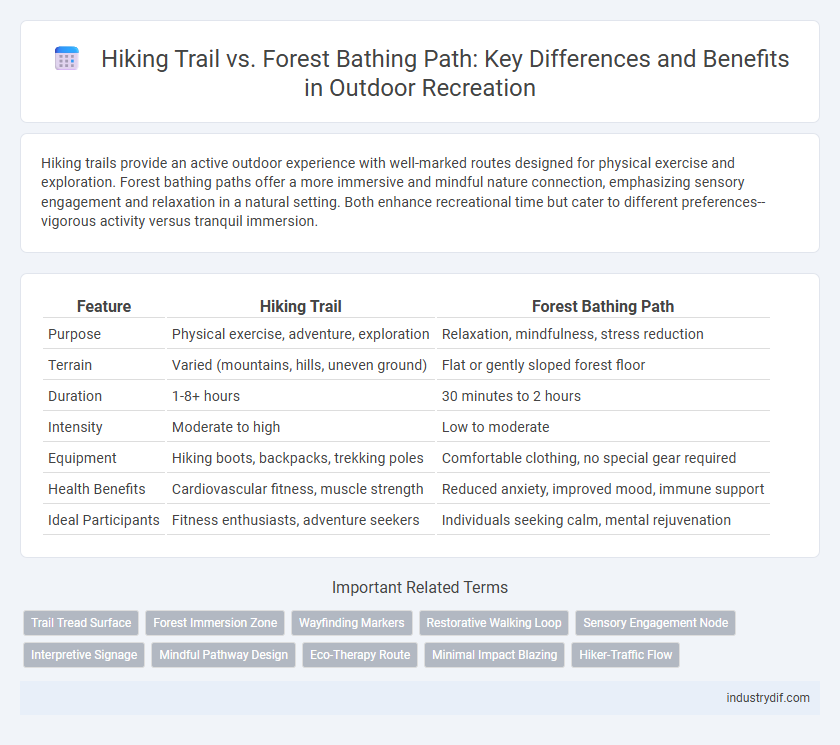
| Feature | Hiking Trail | Forest Bathing Path |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Physical exercise, adventure, exploration | Relaxation, mindfulness, stress reduction |
| Terrain | Varied (mountains, hills, uneven ground) | Flat or gently sloped forest floor |
| Duration | 1-8+ hours | 30 minutes to 2 hours |
| Intensity | Moderate to high | Low to moderate |
| Equipment | Hiking boots, backpacks, trekking poles | Comfortable clothing, no special gear required |
| Health Benefits | Cardiovascular fitness, muscle strength | Reduced anxiety, improved mood, immune support |
| Ideal Participants | Fitness enthusiasts, adventure seekers | Individuals seeking calm, mental rejuvenation |
Understanding Hiking Trails: Key Features
Hiking trails are specifically designed paths that guide outdoor enthusiasts through diverse terrains, often marked with signs and maintained for safety and accessibility. These trails vary in difficulty, length, and elevation, catering to hikers of all experience levels while showcasing natural landmarks and scenic viewpoints. Understanding the key features of hiking trails, such as trailheads, waypoints, and trail blazes, enhances navigation and ensures a rewarding adventure in nature.
Exploring Forest Bathing Paths: Core Concepts
Forest bathing paths emphasize immersive sensory experiences, encouraging hikers to engage deeply with natural surroundings through mindfulness and slow walking. These trails are designed to reduce stress and enhance well-being by promoting connection with the forest environment, distinct from the goal-oriented approach of traditional hiking trails. Core concepts include attentiveness to sounds, scents, and textures, fostering mental clarity and emotional balance.
Historical Origins of Hiking and Forest Bathing
Hiking trails trace their origins back to ancient trade routes and migratory paths used by early civilizations for exploration and survival, evolving into recreational activities during the 19th century with the rise of outdoor leisure culture. Forest bathing, or Shinrin-yoku, originated in Japan during the 1980s as a nature therapy practice developed to combat stress and improve mental health by immersing individuals in natural woodland environments. Both practices emphasize a deep connection with nature but differ historically in purpose--hiking focused on physical challenge and exploration, while forest bathing centers on mindfulness and healing.
Purpose and Benefits: Hiking Trails vs Forest Bathing Paths
Hiking trails primarily serve the purpose of physical exercise and exploration, offering cardiovascular benefits, muscle strengthening, and endurance improvement through varied terrains. Forest bathing paths focus on mindfulness and stress reduction by immersing individuals in natural environments to enhance mental clarity, lower cortisol levels, and boost immune function. Both recreation types contribute to overall well-being but emphasize different aspects of health: physical fitness for hiking and psychological restoration for forest bathing.
Trail Design and Layout: Differences and Similarities
Hiking trails are typically designed for longer, more strenuous walks with clear markers, elevation changes, and varied terrain to challenge hikers and provide scenic viewpoints. Forest bathing paths prioritize gentle, meandering routes that encourage mindfulness and sensory engagement, often incorporating natural features like water bodies and quiet resting spots. Both paths emphasize accessibility to nature and conservation of the environment but differ fundamentally in their approach to user experience and physical intensity.
Physical Activity Levels: Hiking versus Forest Bathing
Hiking trails typically demand moderate to vigorous physical activity, involving varied terrain that enhances cardiovascular endurance and muscle strength. Forest bathing paths emphasize gentle movement and mindfulness, promoting relaxation and mental well-being with minimal physical exertion. Choosing between hiking and forest bathing depends on whether the goal is intense exercise or restorative nature immersion.
Environmental Impact and Conservation Methods
Hiking trails often require extensive maintenance, including clearing, signage, and erosion control, which can disrupt local wildlife habitats and soil stability. In contrast, forest bathing paths emphasize minimal intervention, preserving natural vegetation and promoting biodiversity. Conservation methods for hiking trails include sustainable trail design and regular monitoring, while forest bathing paths rely on passive conservation through restricted access and guided mindfulness practices.
User Experience: What to Expect on Each Path
Hiking trails offer a physically engaging experience characterized by varied terrain, elevation changes, and panoramic views that challenge endurance and stamina. Forest bathing paths prioritize sensory immersion and mindfulness, with gentle, flat routes designed to deepen connection with nature through sights, sounds, and scents. Users on hiking trails can expect a vigorous workout and adventure, while those on forest bathing paths typically enjoy relaxation, stress reduction, and mental clarity.
Suitable Audiences for Hiking Trails and Forest Bathing Paths
Hiking trails cater to adventure seekers and fitness enthusiasts who enjoy rigorous physical activity and exploring diverse terrains. Forest bathing paths attract individuals seeking stress relief, mindfulness, and gentle immersion in nature, often favored by those desiring relaxation and mental wellness. Both trails offer unique benefits but suit different preferences based on intensity and purpose of outdoor experience.
Choosing the Right Path for Your Recreation Goals
Selecting a hiking trail suits individuals looking for physical exertion and scenic adventure, offering varied terrain and distance options to match fitness levels. Forest bathing paths emphasize immersive nature experiences with slow, mindful walking designed to reduce stress and enhance mental clarity. Aligning your choice with goals like cardiovascular exercise or relaxation ensures maximum fulfillment and well-being benefits.
Related Important Terms
Trail Tread Surface
Hiking trails typically feature rugged, uneven surfaces such as rocky or dirt paths designed to challenge stamina and endurance, while forest bathing paths have smooth, soft tread surfaces like moss or compacted soil to encourage gentle walking and sensory immersion. The distinct trail tread surfaces cater to different recreational goals, with hiking prioritizing physical activity and forest bathing emphasizing relaxation and connection with nature.
Forest Immersion Zone
Forest immersion zones offer a tranquil environment where forest bathing paths promote mindfulness and sensory connection to nature, contrasting with hiking trails that emphasize physical activity and endurance. These zones enhance mental wellbeing by encouraging slow, deliberate movement and deep breathing among dense woodland, fostering stress reduction and restorative benefits.
Wayfinding Markers
Hiking trails utilize color-coded blazes, numbered posts, and directional arrows to guide hikers through varied terrain, ensuring safe navigation and route clarity. Forest bathing paths often feature subtle natural markers such as carved wood signs or stone cairns that blend with the environment, promoting a sensory, mindful experience without disrupting the natural ambiance.
Restorative Walking Loop
Restorative walking loops offer distinct benefits in both hiking trails and forest bathing paths by promoting mental clarity and physical rejuvenation through immersive natural experiences. While hiking trails emphasize physical endurance and scenic exploration, forest bathing paths prioritize sensory engagement and mindfulness to reduce stress and enhance overall well-being.
Sensory Engagement Node
Hiking trails engage multiple senses through dynamic terrain and expansive views, stimulating sight, proprioception, and endurance. Forest bathing paths emphasize gentle sensory immersion with subtle sounds, textures, and scents, fostering deep mindfulness and relaxation.
Interpretive Signage
Hiking trails often feature detailed interpretive signage that provides information about local flora, fauna, geological formations, and historical context, enhancing the educational experience for outdoor enthusiasts. In contrast, forest bathing paths typically minimize signage to encourage mindfulness and sensory immersion, focusing on natural sounds and sights without the distraction of textual explanations.
Mindful Pathway Design
Mindful pathway design in hiking trails emphasizes flow, elevation changes, and scenic viewpoints to engage physical and mental stamina, while forest bathing paths prioritize gentle gradients and sensory immersion elements to foster relaxation and mindfulness. Incorporating natural materials, minimal signage, and strategic resting spots enhances the restorative benefits and ecological harmony of both trail types.
Eco-Therapy Route
Eco-therapy routes such as hiking trails emphasize physical activity and engagement with natural landscapes, promoting cardiovascular health and endurance, while forest bathing paths focus on immersive sensory experiences that reduce stress and enhance mental well-being through slow, mindful walking. Both eco-therapy routes contribute to holistic health by fostering a strong connection to nature, though hiking trails tend to cover longer distances and varied terrains compared to the calming, meditative environment provided by forest bathing paths.
Minimal Impact Blazing
Minimal impact blazing on hiking trails involves discreet markers that preserve the natural environment and prevent soil erosion, while forest bathing paths emphasize subtle guidance using existing natural features to maintain ecological balance. Both approaches prioritize sustainable recreation by minimizing disturbances to wildlife habitats and promoting conservation awareness.
Hiker-Traffic Flow
Hiking trails typically experience higher hiker-traffic flow due to their longer distances and challenging terrain, attracting outdoor enthusiasts seeking physical activity and exploration. In contrast, forest bathing paths prioritize tranquility and immersive nature experiences, resulting in lower foot traffic that supports mindfulness and stress reduction.
Hiking Trail vs Forest Bathing Path Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com