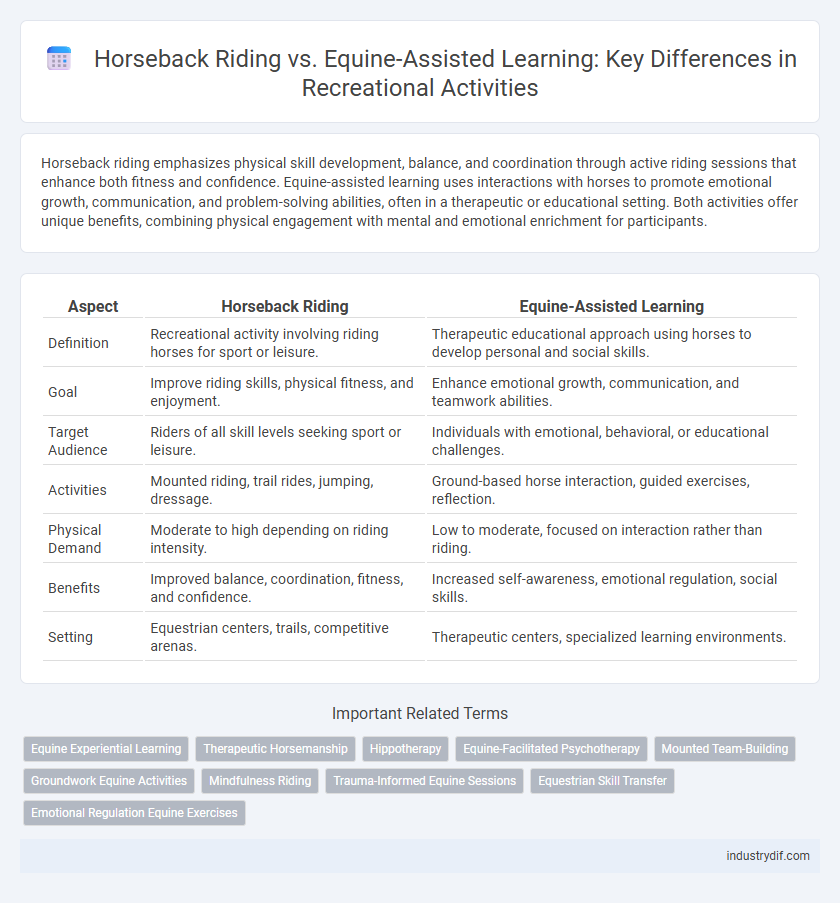
Horseback riding emphasizes physical skill development, balance, and coordination through active riding sessions that enhance both fitness and confidence. Equine-assisted learning uses interactions with horses to promote emotional growth, communication, and problem-solving abilities, often in a therapeutic or educational setting. Both activities offer unique benefits, combining physical engagement with mental and emotional enrichment for participants.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Horseback Riding | Equine-Assisted Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Recreational activity involving riding horses for sport or leisure. | Therapeutic educational approach using horses to develop personal and social skills. |
| Goal | Improve riding skills, physical fitness, and enjoyment. | Enhance emotional growth, communication, and teamwork abilities. |
| Target Audience | Riders of all skill levels seeking sport or leisure. | Individuals with emotional, behavioral, or educational challenges. |
| Activities | Mounted riding, trail rides, jumping, dressage. | Ground-based horse interaction, guided exercises, reflection. |
| Physical Demand | Moderate to high depending on riding intensity. | Low to moderate, focused on interaction rather than riding. |
| Benefits | Improved balance, coordination, fitness, and confidence. | Increased self-awareness, emotional regulation, social skills. |
| Setting | Equestrian centers, trails, competitive arenas. | Therapeutic centers, specialized learning environments. |
Understanding Horseback Riding: Traditional Recreation Explained
Horseback riding, a traditional form of recreation, involves skillful control and communication with the horse through reins, posture, and balance. It offers physical benefits including improved coordination, core strength, and cardiovascular fitness while fostering a connection with the animal. Unlike equine-assisted learning, which emphasizes therapeutic and educational outcomes, horseback riding primarily focuses on leisure, sport, and mastery of riding techniques.
What is Equine-Assisted Learning?
Equine-Assisted Learning (EAL) is an experiential learning approach that uses interactions with horses to promote emotional growth, communication skills, and self-awareness. Unlike traditional horseback riding, EAL involves ground-based activities where participants engage with horses to develop leadership, trust, and problem-solving abilities. This therapeutic method supports personal development and mental health through guided exercises facilitated by certified instructors in controlled environments.
Key Differences Between Horseback Riding and Equine-Assisted Learning
Horseback riding primarily involves the physical skill of controlling and riding a horse for recreational or competitive purposes, emphasizing balance, coordination, and technique. Equine-assisted learning (EAL) focuses on therapeutic interactions with horses to develop personal growth, emotional awareness, and social skills through structured activities without necessarily riding. While horseback riding centers on sport and recreation, EAL serves as a developmental and therapeutic tool utilizing equine behavior as a catalyst for learning and self-improvement.
Goals and Outcomes: Recreation vs Therapeutic Approaches
Horseback riding primarily focuses on recreation, providing physical exercise, enjoyment, and skill-building for riders of all ages. Equine-assisted learning emphasizes therapeutic goals, targeting emotional regulation, behavior improvement, and personal development through structured interactions with horses. Outcomes in recreational riding often include enhanced coordination and confidence, while equine-assisted learning aims for psychological healing and social skill enhancement.
Skills Developed in Horseback Riding
Horseback riding develops essential skills such as balance, coordination, and core strength through active engagement with the horse's movements. Riders also enhance their communication abilities by learning to give clear cues and respond sensitively to the animal's behavior. This practice cultivates patience, focus, and problem-solving skills as riders navigate different terrains and riding techniques.
How Equine-Assisted Learning Supports Personal Growth
Equine-assisted learning promotes personal growth by enhancing emotional awareness, improving communication skills, and fostering trust through interaction with horses. Unlike traditional horseback riding, this experiential approach encourages self-reflection and builds confidence by addressing individual challenges in a supportive environment. Participants often experience increased empathy, stress reduction, and improved problem-solving abilities, making equine-assisted learning a powerful tool for personal development.
Safety Considerations for Both Activities
Horseback riding and equine-assisted learning both require strict safety measures to minimize risks such as falls, kicks, or bites. Proper helmet use, well-maintained tack, and trained supervision are essential to ensure participant safety during riding lessons or therapeutic sessions. Tailoring safety protocols to the specific activity--whether focusing on riding skills or therapeutic interactions--helps protect both riders and horses effectively.
Choosing the Right Program: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right program between horseback riding and equine-assisted learning depends on individual goals, such as skill development, therapeutic benefits, or personal growth. Horseback riding programs emphasize riding technique, balance, and physical fitness, while equine-assisted learning focuses on emotional awareness, communication skills, and confidence-building. Evaluating factors like instructor qualifications, program structure, and specific participant needs ensures a tailored experience that maximizes the benefits of either recreational activity.
Horse Selection and Care in Each Setting
Horseback riding demands selecting horses based on temperament, training level, and suitability for riding skill to ensure safety and enjoyment, while equine-assisted learning prioritizes horses with calm, patient, and responsive behaviors to facilitate therapeutic interactions. In riding environments, care focuses on maintaining peak physical condition, including regular grooming, exercise, and tack fitting, whereas equine-assisted programs emphasize the horse's mental well-being and emotional readiness, with tailored feeding, stress reduction, and gentle handling techniques. Both settings require expert knowledge in equine health and behavior to optimize horse selection and ensure comprehensive care that supports specific activity goals.
The Future of Horse-Based Recreational and Learning Programs
Horse-based recreational activities are evolving with growing emphasis on Equine-Assisted Learning (EAL), which integrates therapeutic techniques to enhance emotional intelligence and leadership skills. Advances in equine-assisted therapy technologies and research support expanded accessibility, making programs more inclusive for diverse populations. Future developments prioritize personalized experiences leveraging biomechanical monitoring and virtual reality to deepen engagement and improve outcomes in both leisure riding and structured learning environments.
Related Important Terms
Equine Experiential Learning
Equine Experiential Learning emphasizes hands-on interaction with horses to develop emotional awareness, leadership, and teamwork skills through guided activities, contrasting with traditional horseback riding, which primarily focuses on riding techniques and physical skills. This approach leverages the horse's intuitive responses to facilitate personal growth and therapeutic outcomes, making it a valuable tool in recreational and educational settings.
Therapeutic Horsemanship
Therapeutic horsemanship combines horseback riding with equine-assisted learning to promote physical, emotional, and cognitive development in individuals with disabilities or special needs. Unlike recreational horseback riding, therapeutic horsemanship uses structured activities and trained horses to improve balance, coordination, self-confidence, and social skills through guided interaction and riding lessons.
Hippotherapy
Horseback riding enhances physical fitness and balance through active engagement with the horse, while equine-assisted learning, particularly hippotherapy, uses horse movement therapeutically to improve neurological and sensory processing in individuals with disabilities. Hippotherapy integrates specialized therapeutic techniques guided by licensed therapists to achieve functional outcomes beyond traditional recreational riding.
Equine-Facilitated Psychotherapy
Equine-Facilitated Psychotherapy harnesses the therapeutic bond between horses and individuals to support emotional healing, promoting mental health through guided interactions in a controlled environment. Unlike casual horseback riding focused on recreation, this specialized form integrates psychological techniques with equine activities to address trauma, anxiety, and behavioral challenges effectively.
Mounted Team-Building
Mounted team-building in horseback riding emphasizes coordinated group skills and communication through shared equestrian activities, enhancing trust and collaboration among participants. Equine-assisted learning integrates therapeutic techniques with mounted exercises, fostering emotional intelligence and leadership development within a supportive, experiential framework.
Groundwork Equine Activities
Horseback riding develops balance and coordination through active riding, while equine-assisted learning emphasizes personal growth via groundwork equine activities that build trust and communication without mounting. Groundwork exercises include leading, grooming, and obstacle navigation, promoting emotional insight and social skills alongside physical engagement.
Mindfulness Riding
Mindfulness riding in horseback riding emphasizes present-moment awareness and deep connection with the horse, enhancing stress reduction and emotional regulation through rhythmic movement and synchronized breathing. Equine-assisted learning utilizes mindfulness riding techniques to promote self-awareness, improved focus, and therapeutic benefits, fostering mental well-being and personal growth in structured sessions.
Trauma-Informed Equine Sessions
Horseback riding offers recreational enjoyment and physical exercise, while trauma-informed equine-assisted learning sessions utilize horses as therapeutic partners to promote emotional healing and resilience. These specialized sessions incorporate trauma-sensitive approaches, emphasizing safety, trust, and nonverbal communication to support individuals processing trauma.
Equestrian Skill Transfer
Horseback riding develops core equestrian skills such as balance, coordination, and communication with the horse, which directly enhance riding proficiency. Equine-assisted learning emphasizes transferring these skills to real-life scenarios, improving emotional regulation, leadership, and non-verbal communication beyond traditional riding expertise.
Emotional Regulation Equine Exercises
Horseback riding enhances emotional regulation by promoting mindfulness and sensory awareness through direct interaction with the horse's movements and behavior. Equine-assisted learning specifically targets emotional regulation exercises by facilitating safe emotional expression and self-regulation skills during structured activities with horses.
Horseback Riding vs Equine-Assisted Learning Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com