Museum exhibits provide a traditional, curated experience where visitors observe and learn from carefully preserved artifacts related to pet recreation history. Interactive installations engage visitors through hands-on activities, fostering active participation and deeper emotional connections with pet-related themes. Both formats enhance understanding but cater to different learning styles and visitor preferences.
Table of Comparison
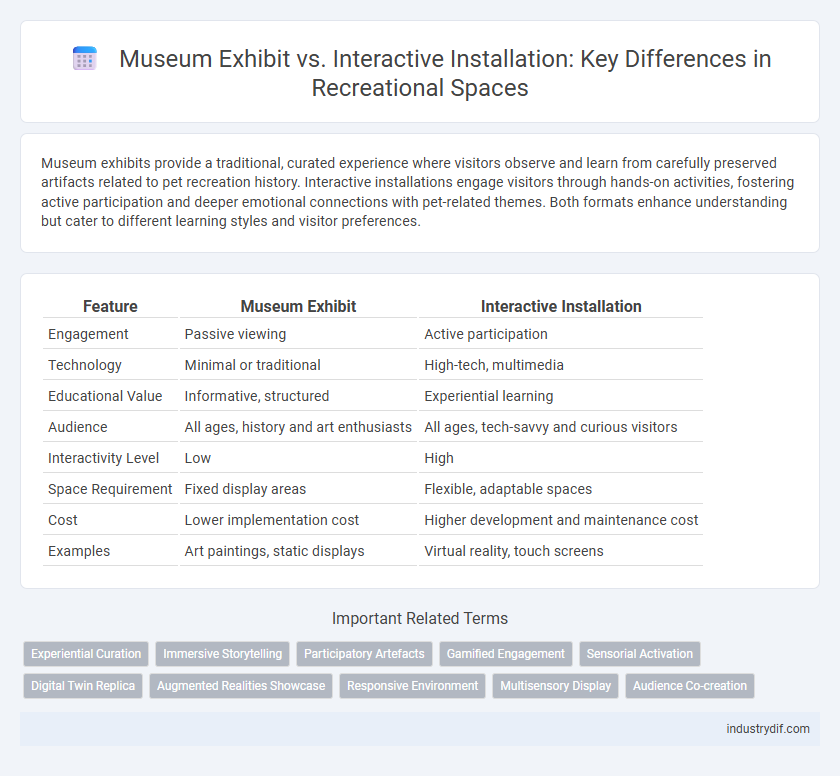
| Feature | Museum Exhibit | Interactive Installation |
|---|---|---|
| Engagement | Passive viewing | Active participation |
| Technology | Minimal or traditional | High-tech, multimedia |
| Educational Value | Informative, structured | Experiential learning |
| Audience | All ages, history and art enthusiasts | All ages, tech-savvy and curious visitors |
| Interactivity Level | Low | High |
| Space Requirement | Fixed display areas | Flexible, adaptable spaces |
| Cost | Lower implementation cost | Higher development and maintenance cost |
| Examples | Art paintings, static displays | Virtual reality, touch screens |
Defining Museum Exhibits: Tradition and Structure
Museum exhibits traditionally prioritize curated displays that emphasize historical accuracy, cultural significance, and educational narratives. They are structured environments with carefully selected artifacts, informative labels, and a linear flow designed to guide visitors through a cohesive story. This approach ensures preservation of heritage while facilitating scholarly interpretation and public understanding.
What Constitutes an Interactive Installation?
An interactive installation is a dynamic recreation space designed to actively engage visitors through sensory, digital, or physical participation rather than passive observation. Unlike traditional museum exhibits that primarily display artifacts or information, interactive installations use technology, tactile elements, or immersive environments to create experiential learning opportunities. These installations emphasize user interaction, enabling visitors to influence or contribute to the exhibit, enhancing engagement and personalized exploration.
Historical Evolution of Exhibition Design
Museum exhibits have traditionally emphasized static displays of artifacts with detailed labels, prioritizing historical accuracy and preservation. Interactive installations emerged in the late 20th century, incorporating technology and multisensory elements to engage visitors actively and create immersive learning experiences. This evolution reflects a shift from passive observation to participatory engagement, enhancing educational impact and visitor retention.
Visitor Experience: Passive Viewing vs Immersive Participation
Museum exhibits offer visitors a passive viewing experience where they observe artifacts and displays, often accompanied by descriptive plaques or audio guides. Interactive installations enhance visitor engagement by allowing immersive participation through touchscreens, motion sensors, or virtual reality, creating a dynamic and memorable encounter. This shift from observation to interaction significantly enriches educational value and emotional connection within recreational settings.
Technology’s Role in Modern Installations
Technology plays a crucial role in modern museum exhibits by enhancing visitor engagement through augmented reality, virtual reality, and interactive touchscreens. Interactive installations leverage sensors, artificial intelligence, and multimedia elements to create immersive and personalized experiences that respond to visitor input in real time. These technological advancements transform traditional static displays into dynamic educational environments, fostering deeper connection and understanding.
Educational Value: Static Displays vs Hands-On Learning
Museum exhibits provide in-depth educational value through carefully curated static displays that offer historical context, detailed descriptions, and authentic artifacts, fostering reflective learning. Interactive installations enhance education by promoting hands-on engagement, encouraging visitors to explore concepts dynamically and retain information through experiential participation. Combining both methods can create a balanced learning environment that appeals to diverse learning styles and deepens understanding.
Accessibility and Inclusivity in Presentations
Museum exhibits traditionally emphasize visual and informational accessibility through clear signage, tactile models, and audio guides, ensuring visitors with diverse sensory needs can engage meaningfully. Interactive installations enhance inclusivity by incorporating multisensory experiences, adaptive technology, and customizable interfaces that accommodate varying physical abilities and cognitive levels. Both formats strive to create welcoming environments, but interactive installations often provide more dynamic, individualized interaction, promoting broader participation across diverse visitor backgrounds.
Audience Engagement and Retention Comparison
Museum exhibits provide structured narratives that engage audiences through curated artifacts and informative displays, fostering deep educational retention. Interactive installations enhance audience engagement by encouraging hands-on participation and multisensory experiences, leading to higher immediate emotional involvement and memorable interactions. Combining tactile interaction with contextual information in exhibits can optimize long-term learning and sustained visitor interest.
Curatorial Challenges: Preservation vs Innovation
Museum exhibits demand stringent preservation methods to protect artifacts from environmental damage, ensuring historical authenticity remains intact. Interactive installations prioritize innovation, integrating technology and user engagement that often challenge traditional conservation techniques. Balancing these curatorial challenges requires adaptive strategies to maintain artifact integrity while delivering immersive, modern experiences.
Future Trends in Recreational Exhibition Spaces
Future trends in recreational exhibition spaces emphasize integrating advanced technologies such as augmented reality and AI to create immersive interactive installations that surpass traditional museum exhibits in engagement and personalization. These installations leverage real-time data and sensory feedback to offer dynamic, participatory experiences that adapt to visitor preferences and learning styles. As museums evolve, the fusion of digital interactivity with physical artifacts is enhancing accessibility, educational value, and visitor retention in recreational environments.
Related Important Terms
Experiential Curation
Museum exhibits emphasize curated artifacts and historical narratives to provide educational and immersive experiences, while interactive installations engage visitors through hands-on participation and sensory stimulation, enhancing experiential curation with dynamic, personalized interactions. Both approaches prioritize visitor engagement but differ in delivering knowledge through observation versus active involvement.
Immersive Storytelling
Museum exhibits provide curated, static displays that communicate historical and cultural narratives through artifacts and interpretive signage, offering visitors a reflective educational experience. Interactive installations enhance immersive storytelling by engaging multiple senses and encouraging active participation, creating dynamic environments that foster deeper emotional connections and personalized interpretations.
Participatory Artefacts
Museum exhibits typically feature static displays of artefacts intended for observation, while interactive installations emphasize participatory artefacts that engage visitors through touch, movement, or digital interaction. These hands-on elements enhance learning and retention by enabling immersive, multisensory experiences that foster deeper connections with the subject matter.
Gamified Engagement
Museum exhibits often present static displays that convey historical or artistic information, while interactive installations incorporate gamified engagement to actively involve visitors through challenges, rewards, and immersive storytelling. Gamified features in interactive installations enhance visitor participation and retention by transforming the learning experience into an engaging, playful activity.
Sensorial Activation
Museum exhibits primarily engage visitors through visual and informational content, offering curated artifacts and interpretive displays that stimulate cognitive understanding. Interactive installations enhance sensorial activation by incorporating touch, sound, and movement sensors, creating immersive experiences that encourage active participation and multisensory engagement.
Digital Twin Replica
Digital Twin Replica technology enhances museum exhibits by creating precise, interactive digital models of artifacts, enabling remote exploration and detailed analysis without physical handling. Interactive installations leverage these replicas to provide immersive, real-time engagement, enriching visitor experience through augmented reality and responsive interfaces.
Augmented Realities Showcase
Museum exhibits featuring augmented reality showcase immersive storytelling by overlaying digital content onto physical artifacts, enhancing educational value and engagement. Interactive installations leverage real-time user interaction with AR elements to create personalized and dynamic recreational experiences.
Responsive Environment
Museum exhibits provide curated, static displays that emphasize historical context and artistic interpretation, while interactive installations create a responsive environment where visitors engage dynamically through sensory input and real-time feedback, enhancing immersion and personalized experiences. Responsive environments in interactive installations utilize technology like motion sensors, touchscreens, and augmented reality to adapt to visitor behavior, fostering deeper emotional connections and active participation compared to traditional museum exhibits.
Multisensory Display
Museum exhibits often rely on static multisensory displays that combine visual artifacts with audio guides and tactile elements to enhance educational engagement. Interactive installations amplify this experience by integrating responsive technologies such as motion sensors and augmented reality, creating immersive environments that actively involve visitors' senses for deeper recreational interaction.
Audience Co-creation
Museum exhibits typically present curated artifacts and narratives for passive audience viewing, while interactive installations emphasize active participation and co-creation, engaging visitors in shaping the experience through hands-on involvement and collaborative content generation. Interactive installations foster deeper emotional connections and personalized learning by allowing audiences to influence and contribute to the unfolding exhibit in real time.
Museum Exhibit vs Interactive Installation Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com