Theme parks offer extensive attractions, immersive themed environments, and large-scale entertainment experiences that cater to diverse age groups and interests. Micro-amusement parks provide a more compact, accessible option with simpler rides and games, often designed for local neighborhoods or smaller communities. Choosing between the two depends on preferences for variety, scale, and convenience in recreational pet-friendly activities.
Table of Comparison
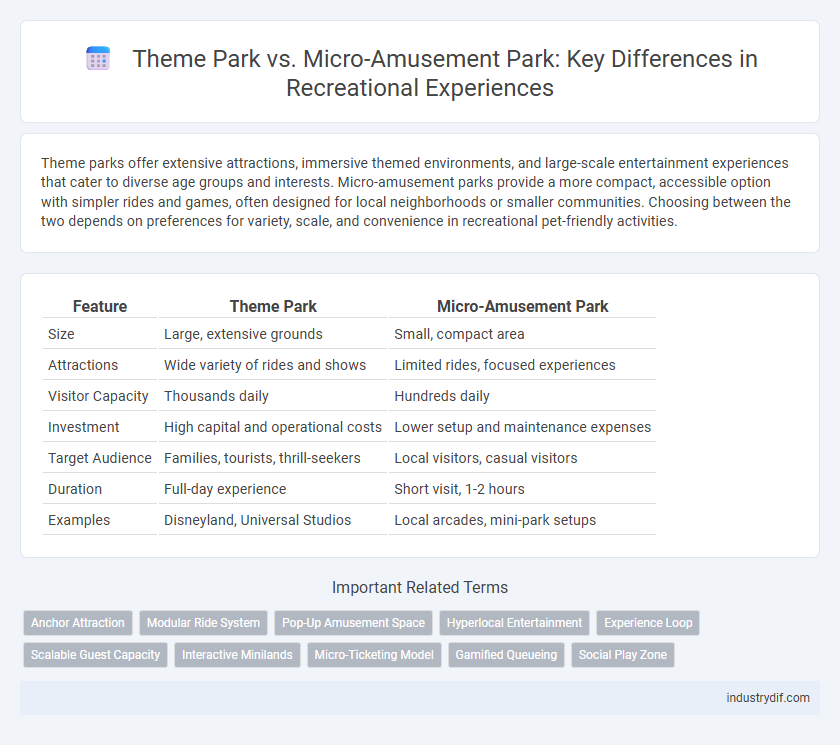
| Feature | Theme Park | Micro-Amusement Park |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Large, extensive grounds | Small, compact area |
| Attractions | Wide variety of rides and shows | Limited rides, focused experiences |
| Visitor Capacity | Thousands daily | Hundreds daily |
| Investment | High capital and operational costs | Lower setup and maintenance expenses |
| Target Audience | Families, tourists, thrill-seekers | Local visitors, casual visitors |
| Duration | Full-day experience | Short visit, 1-2 hours |
| Examples | Disneyland, Universal Studios | Local arcades, mini-park setups |
Understanding Theme Parks and Micro-Amusement Parks
Theme parks are large-scale entertainment complexes featuring extensive themed zones, diverse attractions, and immersive experiences designed to cater to wide audiences. Micro-amusement parks offer compact recreational areas with a select number of rides and games, focusing on convenience and quick entertainment in urban or limited spaces. Both types of parks prioritize visitor engagement but differ significantly in size, scope, and attraction variety.
Key Differences in Size and Scale
Theme parks typically span hundreds of acres, featuring large-scale attractions like roller coasters, water rides, and elaborate themed zones designed for full-day visits. Micro-amusement parks, in contrast, occupy smaller spaces often less than five acres, offering compact rides and interactive experiences targeted for shorter visits and local audiences. The size difference directly influences the scope of attractions, operational complexity, and visitor capacity, defining the unique scale and visitor experience of each park type.
Typical Attractions and Experiences
Theme parks feature large-scale attractions such as roller coasters, water rides, and themed live shows, offering immersive storytelling and expansive entertainment suitable for all ages. Micro-amusement parks concentrate on compact attractions like mini carousels, kiddie rides, and interactive games, providing a family-friendly environment designed for shorter visits. Both options deliver unique experiences, but theme parks prioritize high-thrill, wide-ranging entertainment while micro-amusement parks focus on accessibility and convenience.
Target Audience and Demographics
Theme parks primarily attract families and tourists seeking large-scale, immersive entertainment experiences with varied attractions suitable for all ages, often drawing visitors from regional or national demographics. Micro-amusement parks cater to local communities, focusing on younger children and casual visitors with smaller, more accessible rides and games that emphasize convenience and affordability. The targeted demographic for micro-amusement parks is generally more localized and age-specific, while theme parks appeal to a broader, multi-generational audience.
Investment and Operational Costs
Theme parks require significant investment, often exceeding hundreds of millions of dollars for large-scale attractions, extensive infrastructure, and branded experiences, while micro-amusement parks have lower upfront costs, typically under a few million dollars, due to their compact size and simpler ride options. Operational costs for theme parks include high staffing levels, extensive maintenance, marketing, and utilities, compared to micro-amusement parks which incur reduced labor expenses and streamlined maintenance needs. Investors often consider micro-amusement parks attractive for lower financial risk and faster breakeven points, whereas theme parks demand long-term capital and complex operational management.
Location and Space Requirements
Theme parks require extensive land, often spanning hundreds of acres to accommodate large-scale rides, themed zones, and visitor amenities, making them suitable for suburban or rural settings with ample space. Micro-amusement parks thrive in compact urban locations, utilizing limited space efficiently with smaller rides and attractions designed for high-density areas. The significant difference in spatial needs influences accessibility, with theme parks typically necessitating longer travel distances, while micro-amusement parks prioritize convenience and quick visits.
The Guest Experience: Large vs. Intimate
Theme parks offer expansive environments with diverse attractions, providing guests with immersive and varied experiences that cater to large crowds and extended visits. Micro-amusement parks prioritize intimacy and personalized interaction, delivering a more focused and accessible atmosphere that fosters closer social connections and quicker engagement. Both settings emphasize guest satisfaction but differ significantly in scale, pacing, and the overall nature of visitor experience.
Trends Shaping Theme Parks and Micro-Amusement Parks
Emerging trends in theme parks emphasize immersive technology, interactive storytelling, and sustainability to enhance visitor experiences and reduce environmental impact. Micro-amusement parks capitalize on urbanization by offering compact, accessible entertainment with VR attractions and modular designs that fit limited spaces. Both types increasingly incorporate data analytics for personalized experiences and crowd management, driving innovation in recreation.
Business Models and Revenue Streams
Theme parks generate revenue primarily through ticket sales, merchandise, food and beverage concessions, and themed experiences that attract large crowds over extended periods. Micro-amusement parks focus on smaller-scale attractions, often located in urban or mixed-use areas, leveraging pay-per-ride systems, event hosting, and partnerships with local businesses for diversified revenue. Both business models capitalize on customer engagement, but theme parks invest heavily in large-scale infrastructure, while micro-amusement parks prioritize flexibility and lower operating costs.
Which is Right for Your Community or Investment?
Theme parks offer expansive attractions with diverse rides and entertainment suitable for large crowds, creating significant economic impact through tourism and job creation. Micro-amusement parks, smaller in scale, provide more localized, family-friendly experiences with lower initial investment and maintenance costs, ideal for tight-knit communities or urban areas. Choosing the right option depends on community size, budget, and long-term goals for economic growth and recreational engagement.
Related Important Terms
Anchor Attraction
Theme parks feature large-scale anchor attractions such as roller coasters and immersive themed lands that drive high visitor turnout and extended stays. Micro-amusement parks rely on smaller, targeted anchor attractions like interactive play zones or single signature rides to create a focused, convenient entertainment experience.
Modular Ride System
Theme parks utilize large-scale modular ride systems designed for high capacity and extensive thematic integration, enhancing immersive guest experiences through sophisticated engineering and customizable ride elements. Micro-amusement parks employ compact modular ride systems optimized for limited space and quicker assembly, offering versatile and scalable attractions tailored to smaller venues and niche markets.
Pop-Up Amusement Space
Theme parks feature expansive attractions and extensive infrastructure designed for large crowds and long visits, while micro-amusement parks emphasize compact, versatile layouts ideal for pop-up amusement spaces that can be quickly installed and removed. Pop-up amusement spaces capitalize on temporary setups with modular rides and interactive experiences, maximizing engagement in limited urban areas and event venues.
Hyperlocal Entertainment
Theme parks offer extensive attractions and immersive experiences designed to draw visitors from broad regions, while micro-amusement parks prioritize hyperlocal entertainment by providing compact, community-focused venues that emphasize convenience and easy accessibility. These smaller parks leverage localized themes and tailored attractions to engage nearby residents, fostering frequent visits and strong neighborhood connections.
Experience Loop
Theme parks offer extensive experience loops with large-scale attractions, immersive storytelling, and multi-sensory environments that engage visitors for several hours. Micro-amusement parks provide compact, high-intensity experience loops featuring rapid rides and interactive games designed for shorter, repeatable visits.
Scalable Guest Capacity
Theme parks accommodate large visitor volumes with expansive attractions designed for thousands of guests, while micro-amusement parks optimize scalability through compact layouts that support smaller, manageable crowds. Efficient guest capacity management in micro-amusement parks enables flexible event hosting and personalized experiences in limited spaces, contrasting with the high throughput environments of traditional theme parks.
Interactive Minilands
Theme parks offer expansive interactive minilands featuring immersive landscapes, detailed miniatures, and advanced motion simulations that engage visitors for hours. Micro-amusement parks focus on compact interactive minilands designed for quick exploration, emphasizing tactile experiences and accessibility within smaller spaces.
Micro-Ticketing Model
Micro-amusement parks leverage a micro-ticketing model that allows visitors to pay per ride or attraction, creating an affordable and flexible recreation option compared to traditional theme parks with high admission fees. This pay-as-you-go approach enhances visitor experience by enabling personalized entertainment choices and maximizing value, especially in urban or limited-space environments.
Gamified Queueing
Theme parks integrate gamified queueing systems using immersive apps, interactive displays, and augmented reality to enhance guest engagement during wait times, reducing perceived wait duration significantly. Micro-amusement parks employ compact, technology-driven gamified queues with QR-coded challenges and mini-games, maximizing limited space to maintain visitor interest and streamline crowd flow efficiently.
Social Play Zone
Theme parks offer expansive social play zones designed for large groups and immersive, collaborative experiences, featuring diverse attractions that encourage interaction and teamwork. Micro-amusement parks prioritize intimate, community-focused social play areas with compact, accessible designs that foster casual socializing and repeated visits.
Theme Park vs Micro-Amusement Park Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com