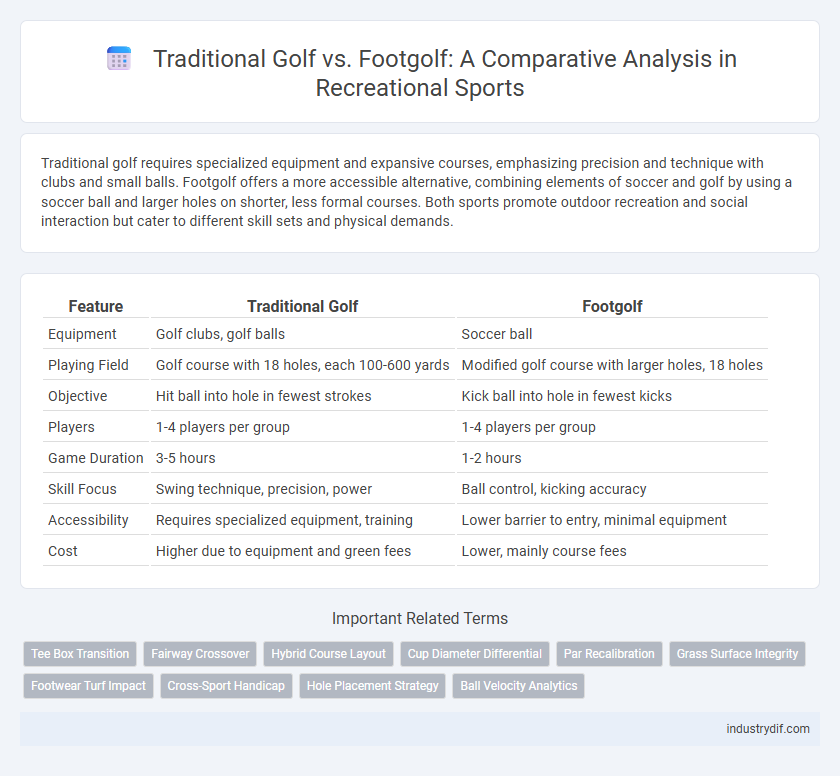
Traditional golf requires specialized equipment and expansive courses, emphasizing precision and technique with clubs and small balls. Footgolf offers a more accessible alternative, combining elements of soccer and golf by using a soccer ball and larger holes on shorter, less formal courses. Both sports promote outdoor recreation and social interaction but cater to different skill sets and physical demands.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Traditional Golf | Footgolf |
|---|---|---|
| Equipment | Golf clubs, golf balls | Soccer ball |
| Playing Field | Golf course with 18 holes, each 100-600 yards | Modified golf course with larger holes, 18 holes |
| Objective | Hit ball into hole in fewest strokes | Kick ball into hole in fewest kicks |
| Players | 1-4 players per group | 1-4 players per group |
| Game Duration | 3-5 hours | 1-2 hours |
| Skill Focus | Swing technique, precision, power | Ball control, kicking accuracy |
| Accessibility | Requires specialized equipment, training | Lower barrier to entry, minimal equipment |
| Cost | Higher due to equipment and green fees | Lower, mainly course fees |
Origins and Evolution of Traditional Golf and Footgolf
Traditional golf originated in 15th-century Scotland, evolving from early stick-and-ball games played on rough terrain to a standardized sport with established rules and dedicated courses by the 18th century. Footgolf emerged in the early 21st century as a hybrid sport combining soccer and golf elements, designed to be played on modified golf courses where players kick a soccer ball into larger holes. Both sports reflect distinct evolutions: traditional golf emphasizes precision and club-based mechanics, while footgolf prioritizes accessibility and a casual fusion of skills from soccer and golf.
Equipment and Attire Differences
Traditional golf requires specialized equipment including golf clubs, balls, tees, and often a golf cart for course navigation, with attire typically consisting of collared shirts, tailored pants or shorts, and golf shoes with spikes. Footgolf uses a standard size 5 soccer ball and demands less technical gear, emphasizing comfortable athletic clothing and soccer or turf shoes without spikes to accommodate running on grass. These distinctions in equipment and attire reflect the different physical demands and playing styles of both sports.
Course Design and Playing Environment
Traditional golf courses feature meticulously maintained fairways, bunkers, and greens designed for 18 holes with varied elevations and hazards, offering a challenging and strategic playing environment. Footgolf courses often adapt existing golf landscapes or open fields with larger holes and simplified layouts, promoting faster play and accommodating players using soccer balls. Both types prioritize open green spaces but differ in scale and equipment requirements, influencing player interaction and pace of play.
Rules and Gameplay Comparison
Traditional golf requires players to use a set of clubs to hit a small ball into a series of holes on a course in as few strokes as possible, following strict rules set by organizations like the USGA. Footgolf combines soccer and golf, where players kick a soccer ball into larger holes on a golf course, with simplified rules emphasizing fewer strokes and quicker play. Scoring in traditional golf depends on strokes per hole, while footgolf scores count each kick, making gameplay faster and more accessible.
Skill Sets Required for Each Sport
Traditional golf demands precision in swing mechanics, strong hand-eye coordination, and refined putting techniques, emphasizing mental focus and strategic course management. Footgolf requires accurate ball control, agility, and endurance to navigate the course and deliver powerful, well-aimed kicks. Both sports develop spatial awareness and concentration but differ in their reliance on fine motor skills versus lower body coordination.
Accessibility and Inclusivity
Traditional golf often requires expensive equipment and exclusive course access, limiting participation for many individuals, whereas footgolf uses a standard soccer ball, significantly reducing costs and enhancing accessibility. Footgolf courses are typically integrated into existing golf courses or open fields, making the sport more approachable for diverse age groups and skill levels. The relaxed pace and simplified rules of footgolf promote inclusivity, allowing people with varying physical abilities to enjoy the game together.
Physical Health and Fitness Benefits
Traditional golf promotes moderate physical activity through walking and swinging, enhancing cardiovascular health, muscle tone, and coordination. Footgolf combines soccer and golf, requiring more intense running and kicking, which boosts aerobic endurance, lower body strength, and agility. Both sports support mental well-being by encouraging outdoor activity and social interaction.
Social and Cultural Impact
Traditional golf has long been associated with exclusivity and established social norms, often perceived as a sport for affluent communities, while Footgolf promotes inclusivity by blending soccer and golf, attracting diverse age groups and backgrounds. The rise of Footgolf fosters community engagement and breaks cultural barriers by making the sport accessible and affordable, encouraging social interaction in a relaxed setting. These contrasting social and cultural impacts highlight a shift towards more inclusive recreational practices that challenge traditional sporting hierarchies.
Cost Differences for Players and Operators
Traditional golf demands significant investment in equipment, green fees, and maintenance, resulting in higher costs for players and operators alike. Footgolf requires minimal equipment, no specialized clubs, and benefits from lower course maintenance expenses, offering a more affordable option. Operators typically face reduced overhead costs with footgolf, enabling more accessible pricing and potentially higher player turnout.
Future Trends in Golf and Footgolf
The future trends in golf and footgolf emphasize sustainability and accessibility, with traditional golf courses increasingly integrating eco-friendly designs to reduce water usage and environmental impact. Footgolf gains popularity as a low-cost, fast-paced alternative that appeals to younger generations and urban players, expanding the sport's demographic reach. Innovations such as digital scoring apps and mixed-use recreational facilities are poised to enhance player engagement and drive growth across both sports.
Related Important Terms
Tee Box Transition
The transition from traditional golf to Footgolf requires adapting from the precise placement and stance at the tee box to a more dynamic approach, emphasizing foot control and ball placement. Footgolf tee boxes are typically larger and more open, allowing for greater freedom of movement compared to the confined mats and defined tees in traditional golf.
Fairway Crossover
Traditional golf and footgolf share the green fairway, yet their differing equipment and play styles create a unique crossover experience where precision swinging meets strategic kicking. Footgolf's larger ball and shorter tee distances intersect with traditional golf paths, offering players diverse challenges while maintaining the natural flow of the fairway landscape.
Hybrid Course Layout
Hybrid course layouts blend the precision of traditional golf greens with the larger, accessible tees and fairways designed for Footgolf, optimizing space and gameplay for both sports. This innovative design enhances recreational appeal by accommodating diverse player skills and promoting multifunctional use of golf facilities.
Cup Diameter Differential
Traditional golf cups measure 4.25 inches in diameter, providing a challenging target for precision putting, while Footgolf cups are significantly larger at 21 inches, accommodating the size of a soccer ball and emphasizing foot accuracy over hand-eye coordination. This considerable cup diameter differential directly influences gameplay strategies, as Footgolf requires less precision aiming but demands greater control in ball placement and power.
Par Recalibration
Traditional golf features a consistent par system based on stroke counts for a player to complete each hole, typically ranging from par 3 to par 5. Footgolf recalibrates par values to accommodate the use of a soccer ball and foot strikes, often increasing par numbers to reflect the greater difficulty and different skill set required for this hybrid sport.
Grass Surface Integrity
Traditional golf relies on meticulously maintained grass surfaces like bentgrass or Bermuda, which demand regular mowing, aeration, and watering to preserve turf health and playability. Footgolf, played with a soccer ball, exerts less concentrated pressure on greens, reducing turf damage and maintenance needs while promoting longer grass durability and soil stability.
Footwear Turf Impact
Footgolf requires specialized turf-friendly footwear with minimal spikes to reduce damage, unlike traditional golf shoes designed for enhanced grip and stability on varied terrain. The reduced ground penetration of Footgolf shoes helps preserve turf integrity by minimizing soil compaction and grass wear.
Cross-Sport Handicap
Cross-sport handicap systems bridge Traditional golf and Footgolf by allowing players to compete equitably despite differing skill sets and rules, using adjusted scoring methods that reflect each sport's unique difficulty levels. This integration promotes inclusivity and skill comparison, enhancing recreational opportunities while maintaining competitive balance across golf's varied formats.
Hole Placement Strategy
Traditional golf hole placement involves strategic positioning to maximize challenge through varied distances and hazards, whereas footgolf hole placement prioritizes larger, open areas to accommodate kicking accuracy and player safety. Footgolf courses often adapt existing golf layouts by expanding hole sizes and simplifying terrain features to enhance flow and accessibility for players.
Ball Velocity Analytics
Traditional golf typically features ball velocities ranging from 120 to 180 mph depending on club type and swing speed, emphasizing precision and long-distance control. Footgolf, however, involves ball velocities averaging around 20 to 30 mph, prioritizing accuracy and foot contact techniques to optimize gameplay on shorter courses.
Traditional golf vs Footgolf Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com