Traditional rental involves leasing an entire asset, such as a car or property, for a specific period, offering full control and exclusive use to the renter. Fractional rental divides ownership or usage rights among multiple parties, allowing access to the asset for a fraction of the time and cost, making it a cost-effective alternative. This model enhances flexibility and reduces commitment compared to traditional rental agreements.
Table of Comparison
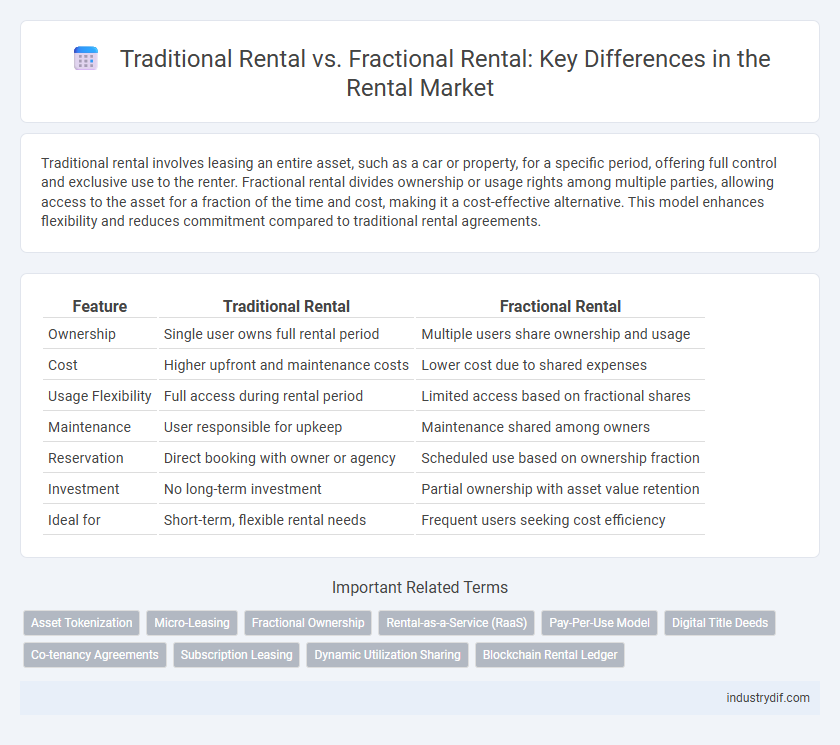
| Feature | Traditional Rental | Fractional Rental |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | Single user owns full rental period | Multiple users share ownership and usage |
| Cost | Higher upfront and maintenance costs | Lower cost due to shared expenses |
| Usage Flexibility | Full access during rental period | Limited access based on fractional shares |
| Maintenance | User responsible for upkeep | Maintenance shared among owners |
| Reservation | Direct booking with owner or agency | Scheduled use based on ownership fraction |
| Investment | No long-term investment | Partial ownership with asset value retention |
| Ideal for | Short-term, flexible rental needs | Frequent users seeking cost efficiency |
Introduction to Rental Models
Traditional rental models involve leasing an entire asset, such as a vehicle or property, for a specified period, typically requiring a single user to bear the full cost and responsibility. Fractional rental allows multiple users to share ownership or usage rights, reducing individual expenses and increasing asset accessibility. This model leverages shared economy principles, optimizing utilization rates and providing flexible rental options for consumers.
Defining Traditional Rental
Traditional rental involves leasing an entire property or asset for a specific period, granting exclusive, full access to the renter. This model requires a longer commitment and often higher upfront costs, making it suitable for those needing uninterrupted use. It contrasts with fractional rental, where ownership or usage rights are divided among multiple users, offering more flexibility and lower individual investment.
Understanding Fractional Rental
Fractional rental allows multiple users to share ownership and usage rights of an asset, significantly reducing individual costs compared to traditional rental models where one user rents exclusively for a set period. This approach maximizes asset utilization and provides flexible access to high-value items, such as vacation properties or luxury vehicles, without the full financial burden. Understanding fractional rental involves recognizing its potential for cost efficiency, shared maintenance responsibilities, and enhanced access flexibility beyond conventional rental agreements.
Key Differences: Traditional vs Fractional
Traditional rental typically involves leasing an entire property or asset for a specific period, often requiring long-term commitments and higher upfront costs. Fractional rental allows multiple users to share ownership or access rights, significantly reducing expenses and increasing flexibility through shorter usage intervals. This model also provides enhanced customization and shared maintenance responsibilities, contrasting with the full control and sole responsibility in traditional rental agreements.
Cost Comparison: Traditional and Fractional
Traditional rental typically requires a full payment or long-term lease commitment, leading to higher upfront costs and limited flexibility. Fractional rental offers shared ownership or usage, significantly reducing the initial financial burden and enabling cost-efficient access to premium assets. By distributing expenses among multiple users, fractional rental maximizes affordability and spreads maintenance costs, making it a smart alternative to traditional full rental fees.
Flexibility and Commitment Levels
Traditional rental agreements typically involve long-term commitments with fixed terms, limiting flexibility for renters who may need varying durations. Fractional rental models offer enhanced flexibility by allowing renters to access properties for shorter, customizable periods with shared ownership or usage rights. This approach reduces financial commitment and adapts better to fluctuating needs, making it ideal for users seeking convenience without long-term obligations.
Target Customers for Each Model
Traditional rental models primarily target customers seeking short-term, flexible access to vehicles or properties without long-term commitments, appealing to travelers, occasional users, and those needing temporary solutions. Fractional rental attracts customers interested in partial ownership or shared usage of premium assets such as luxury cars, vacation homes, or yachts, typically targeting affluent individuals or businesses seeking cost-effective access to high-value items. Both models serve distinct market segments by addressing varying needs for access, control, and investment in rental assets.
Risk and Liability Assessment
Traditional rental agreements usually place full risk and liability on the renter, requiring comprehensive insurance coverage and often higher security deposits. Fractional rental models distribute risk among multiple owners, reducing individual liability and potentially lowering insurance costs through shared responsibility agreements. Assessing risk in fractional rentals involves evaluating collective asset management practices, maintenance protocols, and transparent usage schedules to mitigate disputes and damages.
Technology’s Role in Rental Platforms
Traditional rental platforms often rely on manual processes and limited digital integration, resulting in slower booking and less transparency. Fractional rental platforms leverage advanced technologies such as blockchain, AI-driven personalization, and real-time data analytics to enhance user experience, streamline transactions, and improve asset utilization. These innovations enable more efficient management, dynamic pricing, and secure, transparent contracts, distinguishing fractional rentals from traditional models.
Future Trends in the Rental Industry
Traditional rental models, where customers rent entire assets for a fixed period, face challenges from rising costs and underutilization. Fractional rental, allowing multiple users to share ownership and usage rights, is gaining traction due to its cost-efficiency and flexibility. Future trends indicate a shift towards digitized platforms facilitating fractional rentals, increased use of IoT for asset tracking, and sustainability-driven demand reducing waste through shared consumption.
Related Important Terms
Asset Tokenization
Traditional rental models involve full ownership and direct management of assets, limiting liquidity and access for individual investors, whereas fractional rental leverages asset tokenization to divide ownership into digital tokens, enabling shared investment and increased market fluidity. Asset tokenization enhances transparency, reduces entry barriers, and facilitates secondary market trading, revolutionizing how rental assets are acquired and monetized.
Micro-Leasing
Traditional rental typically involves long-term leasing agreements with fixed terms and higher upfront costs, whereas fractional rental, particularly micro-leasing, offers flexible, short-duration access to assets with lower financial commitment and increased utilization efficiency. Micro-leasing enables renters to pay only for the time and usage needed, optimizing asset allocation and reducing overall leasing expenses in the rental market.
Fractional Ownership
Fractional ownership in rental markets offers a cost-effective alternative to traditional rental models by allowing multiple individuals to share equity and usage rights in high-value assets such as vacation homes, luxury cars, or yachts. This model maximizes asset utilization, reduces individual financial burden, and provides participants with increased flexibility and long-term investment potential compared to conventional full-ownership rentals.
Rental-as-a-Service (RaaS)
Rental-as-a-Service (RaaS) revolutionizes traditional rental models by offering flexible, on-demand access to assets through fractional rental, allowing customers to pay only for the exact usage period without long-term commitments. This approach enhances cost efficiency, scalability, and convenience compared to traditional rentals that require full asset commitment and often involve higher upfront costs.
Pay-Per-Use Model
The traditional rental model involves fixed periodic payments regardless of usage, often resulting in higher costs during low-demand periods. Fractional rental leverages a pay-per-use model, allowing renters to pay strictly based on actual consumption, optimizing cost-efficiency and flexibility in asset utilization.
Digital Title Deeds
Fractional rental leverages digital title deeds to enable multiple co-owners to hold and transfer shares seamlessly, enhancing transparency and reducing transaction time compared to traditional rental agreements governed by physical or centralized title documents. Digital title deeds facilitate secure, blockchain-based record-keeping, making fractional rentals more efficient by enabling real-time verification and automated smart contract execution.
Co-tenancy Agreements
Traditional rental agreements typically involve a single tenant responsible for the entire lease, while fractional rental models utilize co-tenancy agreements allowing multiple tenants to share rental space and costs proportionally. Co-tenancy agreements in fractional rentals enhance flexibility and reduce individual financial burden by clearly defining rights, responsibilities, and shared expenses among all parties involved.
Subscription Leasing
Subscription leasing in fractional rental models offers flexible vehicle access without full ownership, reducing upfront costs and long-term commitments compared to traditional rental agreements that typically involve fixed durations and higher expenses. This approach enhances user convenience by providing customizable terms and inclusive maintenance packages, aligning with evolving consumer preferences for cost-effective mobility solutions.
Dynamic Utilization Sharing
Traditional rental models typically involve a single user leasing an asset for a fixed period, resulting in underutilization during idle times; fractional rental optimizes dynamic utilization sharing by allowing multiple users to access the asset in varying time slots, maximizing efficiency and reducing downtime. This approach leverages real-time scheduling and digital platforms to allocate usage dynamically, increasing revenue potential and customer flexibility.
Blockchain Rental Ledger
Blockchain rental ledgers enhance transparency and security in both traditional and fractional rental models by providing immutable records of transactions and agreements. Fractional rental benefits especially from blockchain technology through automated smart contracts that enable seamless, trustless sharing of assets among multiple tenants.
Traditional Rental vs Fractional Rental Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com