Warehouses offer large-scale storage capacity ideal for bulk inventory, enabling retailers to store a wide variety of products under one roof. Micro-fulfillment centers prioritize speed and efficiency by utilizing automated systems in smaller, urban locations to fulfill online orders quickly. Retailers benefit from combining both solutions to balance extensive inventory management with rapid last-mile delivery.
Table of Comparison
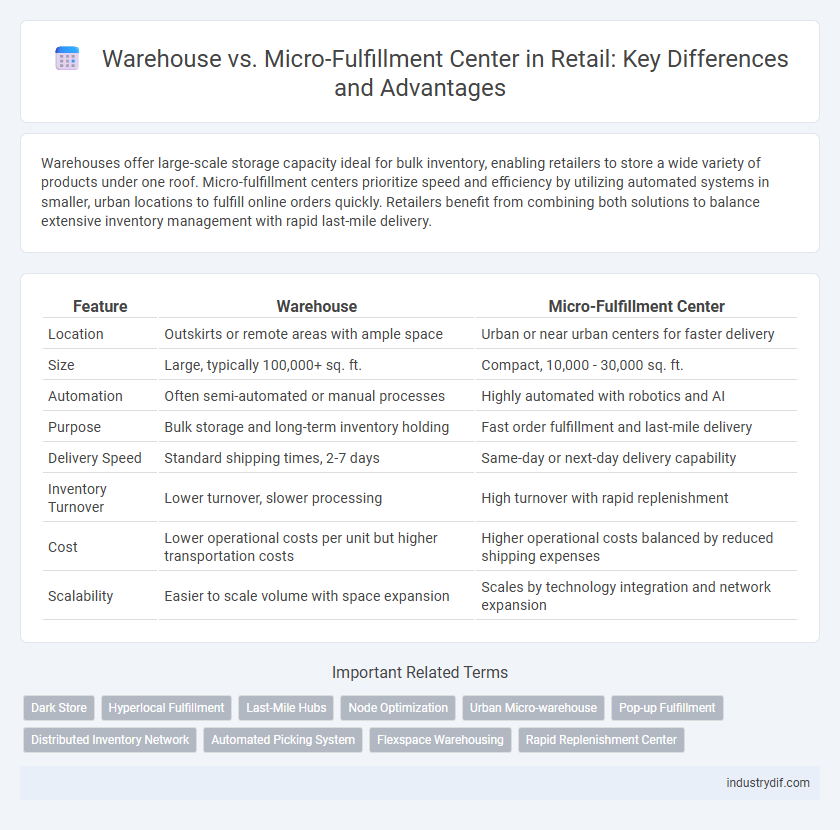
| Feature | Warehouse | Micro-Fulfillment Center |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Outskirts or remote areas with ample space | Urban or near urban centers for faster delivery |
| Size | Large, typically 100,000+ sq. ft. | Compact, 10,000 - 30,000 sq. ft. |
| Automation | Often semi-automated or manual processes | Highly automated with robotics and AI |
| Purpose | Bulk storage and long-term inventory holding | Fast order fulfillment and last-mile delivery |
| Delivery Speed | Standard shipping times, 2-7 days | Same-day or next-day delivery capability |
| Inventory Turnover | Lower turnover, slower processing | High turnover with rapid replenishment |
| Cost | Lower operational costs per unit but higher transportation costs | Higher operational costs balanced by reduced shipping expenses |
| Scalability | Easier to scale volume with space expansion | Scales by technology integration and network expansion |
Defining Warehouses and Micro-fulfillment Centers
Warehouses are large-scale storage facilities designed to hold extensive inventories for long-term distribution, typically serving multiple retail locations or customers. Micro-fulfillment centers are compact, automated spaces located closer to end consumers, enabling rapid order processing and last-mile delivery in urban environments. These centers optimize inventory flow by combining storage and fulfillment functions on a smaller footprint compared to traditional warehouses.
Key Differences Between Warehouses and Micro-fulfillment Centers
Warehouses are large-scale facilities designed for bulk storage and long-term inventory management, often located on the outskirts of urban areas, while micro-fulfillment centers (MFCs) are compact, automated spaces situated closer to consumers to enable rapid order processing. Warehouses emphasize volume and cost-efficiency in storing products, whereas MFCs prioritize speed, agility, and last-mile delivery optimization using robotics and advanced software. The key difference lies in their operational purpose: warehouses support inventory holding on a macro level, whereas micro-fulfillment centers facilitate fast, localized e-commerce fulfillment.
Space Utilization and Layout Comparison
Warehouses typically require larger footprints with open floor plans optimized for bulk storage, resulting in lower space utilization efficiency compared to micro-fulfillment centers. Micro-fulfillment centers leverage vertical storage systems and automated technology to maximize storage density within compact urban spaces, enhancing layout efficiency. This optimized space utilization enables faster order processing and reduces inventory footprint, making micro-fulfillment centers ideal for last-mile delivery in retail operations.
Order Processing Speed and Efficiency
Micro-fulfillment centers significantly enhance order processing speed by leveraging automation and proximity to urban consumers, reducing delivery times compared to traditional warehouses. Their compact size allows for faster picking and packing cycles, increasing efficiency in handling smaller, high-frequency orders. Warehouses excel in bulk storage but often experience slower order fulfillment due to larger scales and less automation integration.
Technology Integration in Fulfillment Operations
Warehouse fulfillment operations utilize traditional inventory management systems, while micro-fulfillment centers leverage advanced automation technologies such as robotics, AI-driven picker systems, and real-time data analytics. The integration of IoT sensors and machine learning algorithms in micro-fulfillment centers enhances order accuracy, reduces processing time, and optimizes space utilization. Retailers implementing technology-driven micro-fulfillment hubs achieve faster delivery speeds and greater operational efficiency compared to conventional warehouse setups.
Cost Analysis: Warehouses vs Micro-fulfillment Centers
Warehouses typically incur higher operational costs due to larger space requirements and increased labor expenses for manual order picking and inventory management. Micro-fulfillment centers leverage automation and proximity to urban areas, reducing last-mile delivery costs and accelerating order fulfillment while maintaining lower storage overheads. Analyzing cost per order reveals micro-fulfillment centers offer greater efficiency for fast-moving consumer goods, whereas warehouses remain cost-effective for bulk storage and slower turnover items.
Impact on Last-Mile Delivery
Warehouses centralize inventory storage, leading to longer last-mile delivery times due to distance from end customers, while micro-fulfillment centers, located within urban areas, drastically reduce delivery distances and accelerate order fulfillment. Micro-fulfillment centers leverage automation and proximity to increase delivery speed and customer satisfaction, crucial in meeting same-day or next-day delivery expectations. The strategic implementation of micro-fulfillment centers effectively lowers transportation costs and carbon emissions, optimizing the last-mile delivery process for retailers.
Scalability and Flexibility in Retail Fulfillment
Warehouse operations offer scalability through large storage capacities and centralized inventory management, enabling retailers to handle high order volumes efficiently. Micro-fulfillment centers provide enhanced flexibility by situating closer to end consumers, allowing faster order processing and adaptable inventory distribution for localized demand fluctuations. Combining both models optimizes retail fulfillment by balancing extensive scalability with agile, customer-centric responsiveness.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
Micro-fulfillment centers reduce carbon emissions by minimizing delivery distances through their proximity to urban areas, lowering transportation-related environmental impacts compared to traditional warehouses. Warehouses typically require larger building footprints and consume more energy for climate control, whereas micro-fulfillment centers optimize energy efficiency by leveraging smaller, automated spaces. Implementing micro-fulfillment can significantly decrease waste and resource consumption, aligning retail operations with sustainability goals and reducing overall ecological footprints.
Choosing the Right Fulfillment Solution for Your Retail Business
Selecting the right fulfillment solution involves evaluating warehouse capacity, location, and technology integration versus the speed, proximity, and scalability of micro-fulfillment centers. Warehouses offer bulk storage and cost efficiency for large inventories, while micro-fulfillment centers provide faster order processing and last-mile delivery advantages in urban areas. Retailers must align fulfillment choices with customer expectations, order volumes, and geographic distribution to optimize supply chain performance.
Related Important Terms
Dark Store
Dark stores function as micro-fulfillment centers designed to optimize urban retail logistics by enabling rapid, efficient order processing and delivery within densely populated areas. Unlike traditional warehouses, dark stores are strategically located closer to consumers, reducing last-mile delivery time and enhancing inventory turnover for e-commerce and omnichannel retail operations.
Hyperlocal Fulfillment
Micro-fulfillment centers optimize hyperlocal fulfillment by enabling faster order processing and reduced delivery times within dense urban areas compared to traditional warehouses. These compact facilities leverage automation and proximity to customers, enhancing inventory turnover and minimizing last-mile logistics costs in retail operations.
Last-Mile Hubs
Micro-fulfillment centers act as strategic last-mile hubs by enabling rapid order processing and delivery within urban areas, significantly reducing delivery times compared to traditional warehouses. Their compact footprint and automation technology optimize inventory management and distribution efficiency, meeting growing consumer demand for fast, accurate fulfillment.
Node Optimization
Warehouse and micro-fulfillment center nodes optimize retail supply chains by balancing inventory storage with rapid order processing, enabling more precise location-based fulfillment. Micro-fulfillment centers reduce last-mile delivery costs and enhance customer satisfaction through strategic placement in urban areas, while warehouses maintain bulk storage efficiency in centralized locations.
Urban Micro-warehouse
Urban micro-warehouses strategically positioned within city limits enable faster order fulfillment and reduced last-mile delivery costs compared to traditional large-scale warehouses located on the urban periphery. These compact facilities leverage automation and advanced inventory management systems to optimize stock levels and meet rising consumer demand for rapid, same-day delivery in dense retail markets.
Pop-up Fulfillment
Pop-up fulfillment centers leverage micro-fulfillment strategies to enhance retail agility by enabling faster order processing and reducing last-mile delivery costs compared to traditional warehouses. These compact, strategically located facilities integrate automation and real-time inventory management to meet rising consumer demand for rapid, localized delivery.
Distributed Inventory Network
A Distributed Inventory Network enhances retail efficiency by leveraging both traditional warehouses and micro-fulfillment centers to optimize stock placement closer to demand hotspots, reducing delivery times and shipping costs. Micro-fulfillment centers act as agile, technology-driven nodes within this network, supporting rapid, localized order fulfillment while warehouses maintain bulk inventory and manage long-term stock replenishment.
Automated Picking System
Automated picking systems in micro-fulfillment centers significantly enhance order accuracy and reduce fulfillment time by using robotics and AI-driven technology tailored for small-scale, urban environments. Traditional warehouses benefit from automated systems by optimizing bulk storage and large order processing, but micro-fulfillment centers excel in rapid, last-mile delivery through compact, high-density automation solutions.
Flexspace Warehousing
Flexspace warehousing enhances retail logistics by offering scalable, on-demand storage solutions that bridge the gap between traditional warehouses and micro-fulfillment centers, optimizing inventory management and reducing lead times. This hybrid model supports rapid order fulfillment and cost efficiency, leveraging flexible locations closer to urban markets for improved last-mile delivery performance.
Rapid Replenishment Center
Rapid replenishment centers utilize micro-fulfillment centers located closer to demand points, enabling faster inventory turnover and reduced delivery times compared to traditional large warehouses. These centers leverage automation and data analytics to streamline order fulfillment, optimizing supply chain efficiency and meeting consumer expectations for rapid delivery.
Warehouse vs Micro-fulfillment center Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com