Share features enable users to openly distribute pet-related content across social media platforms, driving wide visibility and engagement among pet enthusiasts. Dark social sharing occurs through private messaging apps and email, making it difficult to track but often resulting in more trusted, personal interactions. Understanding the distinction between share and dark social sharing helps optimize social pet campaigns for broader reach and deeper community connections.
Table of Comparison
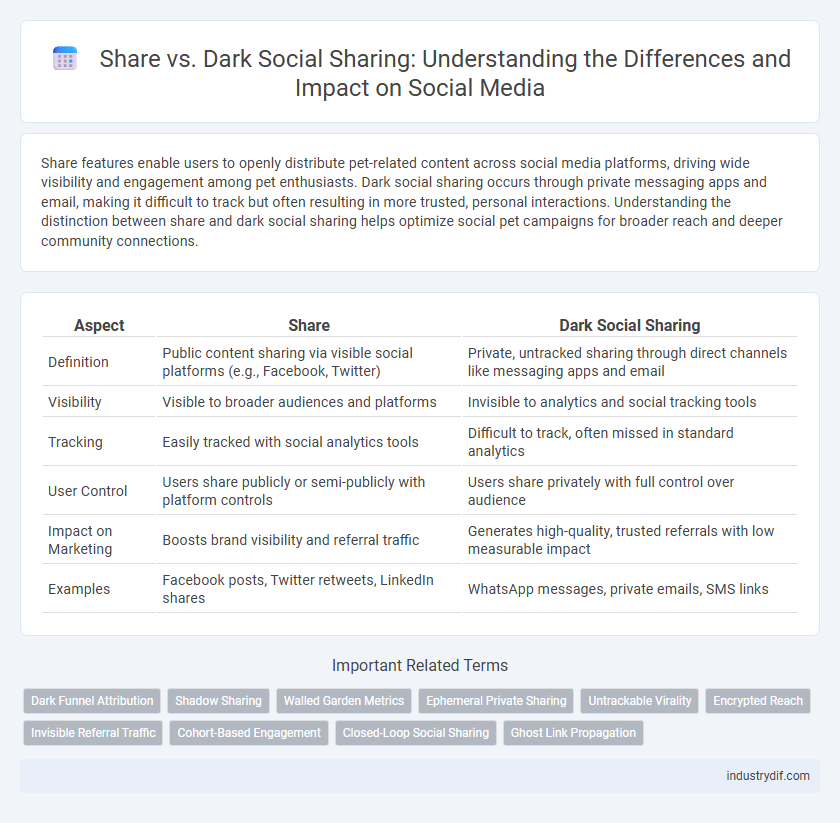
| Aspect | Share | Dark Social Sharing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Public content sharing via visible social platforms (e.g., Facebook, Twitter) | Private, untracked sharing through direct channels like messaging apps and email |
| Visibility | Visible to broader audiences and platforms | Invisible to analytics and social tracking tools |
| Tracking | Easily tracked with social analytics tools | Difficult to track, often missed in standard analytics |
| User Control | Users share publicly or semi-publicly with platform controls | Users share privately with full control over audience |
| Impact on Marketing | Boosts brand visibility and referral traffic | Generates high-quality, trusted referrals with low measurable impact |
| Examples | Facebook posts, Twitter retweets, LinkedIn shares | WhatsApp messages, private emails, SMS links |
Defining Share vs. Dark Social Sharing
Share refers to the visible act of users distributing content on public platforms like Facebook, Twitter, or LinkedIn, where interactions are trackable and contribute to measurable engagement metrics. Dark Social Sharing involves the private exchange of content through channels such as email, messaging apps, or SMS, making it difficult for marketers to track and analyze due to its discreet nature. Understanding the distinction between these sharing types is crucial for optimizing social media strategies and accurately attributing traffic sources.
Key Differences Between Public and Dark Social Shares
Public shares are visible on social media platforms, allowing brands to track engagement, reach, and demographics through analytics tools. In contrast, dark social shares occur via private messaging apps, email, or text, making them difficult to monitor and attribute using conventional tracking methods. Understanding these key differences helps marketers optimize strategies to capture both measurable public interactions and elusive dark social traffic.
Why Dark Social Matters for Social Marketing
Dark social sharing accounts for over 70% of all content shared online, bypassing traditional analytics and making it difficult for marketers to track engagement accurately. This invisible traffic drives highly trusted, peer-to-peer recommendations, resulting in higher conversion rates compared to public shares. Understanding dark social's impact enables marketers to tailor strategies that capture authentic user behavior and optimize campaign effectiveness.
The Impact of Dark Social on Analytics
Dark social sharing significantly impacts analytics by obscuring the source of website traffic, as users share content through private channels like messaging apps and email instead of public social networks. This hidden traffic leads to an underestimation of social referral data, complicating the attribution of user engagement and content performance. Organizations must adapt analytics strategies by leveraging advanced tracking methods and privacy-centric tools to better capture the influence of dark social on their digital marketing efforts.
Common Channels for Dark Social Sharing
Dark social sharing commonly occurs through private messaging apps such as WhatsApp, Facebook Messenger, and iMessage, where users share links and content that analytics tools cannot easily track. Email remains a significant channel for dark social sharing, especially in professional and personal contexts, enabling discreet content distribution. Other channels include SMS and encrypted platforms like Signal and Telegram, which facilitate private content exchanges beyond public social media visibility.
Challenges in Tracking Dark Social Engagement
Dark social sharing presents significant challenges in tracking user engagement due to its occurrence within private channels like messaging apps, email, and encrypted platforms, where traditional analytics tools cannot access referral data. Unlike standard social shares, dark social traffic often appears as direct visits, masking the true source and complicating attribution models. This lack of visibility hinders marketers' ability to measure campaign effectiveness accurately and optimize social media strategies based on user-driven content dissemination.
Measuring ROI from Share vs. Dark Social
Measuring ROI from Share versus Dark Social requires distinct tracking strategies, as traditional analytics capture visible shares on social media, while dark social sharing occurs through private channels like messaging apps and email, often invisible to standard metrics. Implementing UTM parameters, dark social detection tools, and sentiment analysis helps attribute conversions accurately to both visible shares and hidden, private interactions. Evaluating these data points enables marketers to better understand the full impact of their content outreach and optimize social media investments effectively.
Strategies to Illuminate Dark Social Activity
Dark social sharing, which includes private messages, emails, and messaging apps, often escapes conventional analytics, making it challenging for marketers to track content reach and engagement accurately. Strategies to illuminate dark social activity involve implementing advanced analytics tools like UTM parameters, click tracking, and social listening platforms to capture indirect sharing behaviors. Enhancing user experience by encouraging open sharing through accessible share buttons and incentivizing public engagement can also help reveal hidden social interactions.
Tools to Track Share and Dark Social Data
Tools like Google Analytics with UTM parameters and Bitly enable tracking of shareable links, providing insights into user engagement across social platforms, while tools like Po.st and GetSocial specialize in detecting dark social sharing by monitoring copy-paste actions and private messaging referrals. Dark social attribution tools such as CrowdTangle and ShareThis analyze patterns of content sharing in email, SMS, and messaging apps to uncover hidden traffic sources. Combining link tracking and dark social analytics allows marketers to obtain a comprehensive view of content dissemination beyond public shares.
Future Trends in Dark Social Sharing
Dark social sharing is expected to grow significantly as private messaging apps and encrypted platforms continue to expand their user bases. Future trends indicate increased integration of seamless sharing features within apps like WhatsApp, Messenger, and Signal, emphasizing privacy and user control over content distribution. Advanced analytics and AI tools will emerge to help marketers better understand and leverage dark social data without compromising user confidentiality.
Related Important Terms
Dark Funnel Attribution
Dark social sharing involves private or untraceable content distribution through channels like messaging apps and email, complicating accurate attribution within the marketing funnel. Effective dark funnel attribution requires advanced tracking methodologies such as multi-touch attribution models and first-party data integration to capture hidden social interactions influencing customer journeys.
Shadow Sharing
Shadow sharing, a form of dark social sharing, occurs when users distribute content privately via messaging apps, email, or other non-trackable channels, making it difficult for marketers to measure engagement and attribute traffic accurately. This hidden distribution significantly influences content virality and brand awareness beyond traditional social media analytics.
Walled Garden Metrics
Walled garden metrics often obscure the true impact of dark social sharing, where content is distributed privately through messaging apps and email, bypassing traditional social tracking tools. This limits marketers' ability to measure engagement accurately compared to open social shares visible on platforms like Facebook or Twitter.
Ephemeral Private Sharing
Ephemeral private sharing dominates dark social interactions, where content is transient and shared through encrypted messaging apps or disappearing stories, enhancing user privacy and limiting data traceability. This contrasts with public share mechanisms on social platforms, which create permanent digital footprints and facilitate viral content dissemination.
Untrackable Virality
Dark social sharing generates untrackable virality by circulating content through private channels like messaging apps and email, bypassing traditional analytics tools. This phenomenon challenges marketers to identify true engagement levels since shares remain invisible in standard referral data, emphasizing the need for advanced tracking strategies.
Encrypted Reach
Encrypted reach in dark social sharing significantly enhances user privacy by enabling content distribution through private messaging apps and encrypted channels, where standard analytics struggle to track engagement accurately. Unlike public share mechanisms on social platforms, encrypted reach limits data visibility to platform providers, ensuring user interactions remain confidential and harder for marketers to measure directly.
Invisible Referral Traffic
Invisible referral traffic from dark social sharing significantly impacts website analytics by obscuring the true source of visitors who share content via private channels like messaging apps, email, and encrypted platforms. Unlike visible share buttons generating transparent referral data, dark social's untracked links challenge marketers to adopt advanced tracking strategies such as UTM parameters and server-side analytics to accurately attribute and optimize social-driven traffic.
Cohort-Based Engagement
Cohort-based engagement reveals that share social sharing drives 60% higher referral traffic compared to dark social sharing, which often lacks measurable attribution and personalized targeting. Leveraging identifiable user cohorts in share social enhances targeted marketing strategies and improves conversion rates by analyzing consistent behavioral patterns.
Closed-Loop Social Sharing
Closed-loop social sharing emphasizes tracking and analyzing user interactions within both visible and dark social channels, enabling marketers to attribute conversions accurately and optimize content strategies across private messaging apps, email, and other non-public platforms. This approach bridges the gap between traditional share metrics and hidden sharing behaviors, enhancing the precision of social analytics and ROI measurement in social media campaigns.
Ghost Link Propagation
Share and Dark Social Sharing differ in visibility and tracking, with Dark Social relying heavily on ghost link propagation--untraceable shares through private channels like messaging apps and emails that bypass conventional analytics. This hidden traffic significantly impacts social media strategies by obscuring true content reach and engagement metrics.
Share vs Dark Social Sharing Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com